* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Tour of Our Solar System
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
Jumping-Jupiter scenario wikipedia , lookup
Scattered disc wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Kuiper belt wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
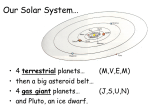
Tour of the Solar System (51) Inner Solar System • Sun – Main sequence, yellow dwarf. – All objects in solar system revolve around it. – Makes up 99% of solar system’s matter. – 804,000 mi across, can hold 109 Earths. Inner Solar System (cont.) • Mercury: – Smallest planet. – Many craters, similar to the moon. – Temperature: 801- 279oF. • Venus: – Similar to Earth’s size and mass. – Atmosphere of CO2 (traps heat). – High temperatures that can melt lead. – Rotates counter-clockwise. Inner Solar System (cont.) Earth •Atmosphere is 78% N, 21% O, 1% other gases. – Allows just enough heat to be trapped and stay warm enough to sustain life. Mars •Structures that look like river beds. •May have once had liquid water on surface. Space Junk Asteroid Belt • Chunks of rock orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter. • May have been a planetesimal that was torn apart by Jupiter’s gravity. – 100,000+ asteroids. – Most less than 1km long. Outer (Gas) Planets Jupiter •Largest planet. •Made Hydrogen and Helium gas. •Could have been a star…if it were 80 times bigger. Outer (Gas) Planets (cont.) Saturn •Winds in upper atmosphere can reach 500m/s (vs. 110m/s). •Rings made of water ice and rock. Outer (Gas) Planets (cont.) Uranus – Appears blue because methane in the atmosphere. – Axis of rotation points at the Sun. Outer (Gas) Planets (cont.) Neptune – Atmosphere of methane, water, helium and hydrogen. – Great Dark Spot: wind storm size of Earth, 750 miles/hr. Dwarf Planet Pluto – About two thirds the size of our Moon. – 3 Moons: the biggest (Charon) is over half the size of Pluto. – Orbits the Kuiper Belt. Other Structures of the Solar System • Kuiper Belt: rocky/icy objects beyond Pluto. – Short orbit comets (orbit less than 100 years). • Oort Cloud: rocky/icy bodies beyond the Kuiper Belt. – Long orbit comets (orbit more than 100 years). Structures of the Solar System (cont.) • Comets: made of ice/rock/dust, tails are debris left behind that are lit up by solar wind. Birth of Our Moon Collisional Ejection: Something impacted the forming Earth and broke off pieces and some became the Moon. – Collisions common in early solar system. – Moon has similar elements to Earth. Mapping the Solar System (50) Object Mercury Venus Mars Asteroid Belt Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto Kuiper Belt Comets Position in Solar System Something to Remember Picture