Слайд 1 - SPACE RESEARCH at FMI
... To develop adequate models of the most important processes occurred in the magnetosphere and ionosphere, we need complex analysis of data; the simultaneous measurements are to be done in all crucial parts of the Sun-Earth system such as the Sun, heliosphere, magnetosphere, ionosphere, and atmosphere ...
... To develop adequate models of the most important processes occurred in the magnetosphere and ionosphere, we need complex analysis of data; the simultaneous measurements are to be done in all crucial parts of the Sun-Earth system such as the Sun, heliosphere, magnetosphere, ionosphere, and atmosphere ...
Space Test Essay Questions
... during each of the 4 seasons. You may draw, label, and describe OR write in paragraph form. 2. Why don’t we see a lunar and solar eclipse EVERY month? Describe in detail how lunar and solar eclipses happen AND what is seen from Earth during each eclipse. You may draw, label and describe OR write in ...
... during each of the 4 seasons. You may draw, label, and describe OR write in paragraph form. 2. Why don’t we see a lunar and solar eclipse EVERY month? Describe in detail how lunar and solar eclipses happen AND what is seen from Earth during each eclipse. You may draw, label and describe OR write in ...
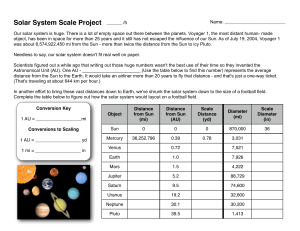
Solar System Scale Handout
... was about 8,574,922,450 mi from the Sun - more than twice the distance from the Sun to icy Pluto. Needless to say, our solar system doesn't fit real well on paper. Scientists figured out a while ago that writing out those huge numbers wasn't the best use of their time so they invented the Astronomic ...
... was about 8,574,922,450 mi from the Sun - more than twice the distance from the Sun to icy Pluto. Needless to say, our solar system doesn't fit real well on paper. Scientists figured out a while ago that writing out those huge numbers wasn't the best use of their time so they invented the Astronomic ...
Science of Sun activity
... Energy and radiation from solar flares and coronal mass ejections can: • Harm astronauts in space • Damage sensitive electronics on orbiting spacecraft… • Cause colorful auroras, often seen in the higher latitudes… • Create blackouts on Earth when they cause surges in power grids. ...
... Energy and radiation from solar flares and coronal mass ejections can: • Harm astronauts in space • Damage sensitive electronics on orbiting spacecraft… • Cause colorful auroras, often seen in the higher latitudes… • Create blackouts on Earth when they cause surges in power grids. ...
(SV) “Ionosat”: Orbital cluster
... Systematic study of the dynamic response of the ionosphere to the influences “from above” (solar and geomagnetic activity) and “from below” (meteorological, seismic and technologic processes), seismo-ionospheric coupling. Synchronous operation with the existing sub-satellite electromagnetic and mete ...
... Systematic study of the dynamic response of the ionosphere to the influences “from above” (solar and geomagnetic activity) and “from below” (meteorological, seismic and technologic processes), seismo-ionospheric coupling. Synchronous operation with the existing sub-satellite electromagnetic and mete ...
384 kb
... The Sun is currently into Solar Cycle 24 – a numbering that starts from the mid18th century when solar activity was first measured. And its progress is proving far from typical. The solar minimum began officially in 2008 but continued for two more years, while the maximum was double, with twin peaks ...
... The Sun is currently into Solar Cycle 24 – a numbering that starts from the mid18th century when solar activity was first measured. And its progress is proving far from typical. The solar minimum began officially in 2008 but continued for two more years, while the maximum was double, with twin peaks ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... At top of corona, typical gas speeds are close to escape speed => Sun losing gas in a solar wind. Wind escapes from "coronal holes", seen in X-ray images. ...
... At top of corona, typical gas speeds are close to escape speed => Sun losing gas in a solar wind. Wind escapes from "coronal holes", seen in X-ray images. ...
Lecture 2: The Sun and the Heliophysics
... radiation as photons Matter in a radiation zone is so dense that photons can travel only a short distance before they are absorbed or scattered by another particle T drops from 15 million K to 1.5 million K it takes an average of 171,000 years for gamma rays from the core of the Sun to leave the rad ...
... radiation as photons Matter in a radiation zone is so dense that photons can travel only a short distance before they are absorbed or scattered by another particle T drops from 15 million K to 1.5 million K it takes an average of 171,000 years for gamma rays from the core of the Sun to leave the rad ...
Geomagnetic storm

A geomagnetic storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase in electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere.During the main phase of a geomagnetic storm, electric current in the magnetosphere creates a magnetic force that pushes out the boundary between the magnetosphere and the solar wind. The disturbance in the interplanetary medium that drives the storm may be due to a solar coronal mass ejection (CME) or a high speed stream (co-rotating interaction region or CIR) of the solar wind originating from a region of weak magnetic field on the Sun’s surface. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. CME driven storms are more common during the maximum of the solar cycle, while CIR driven storms are more common during the minimum of the solar cycle.Several space weather phenomena tend to be associated with or are caused by a geomagnetic storm. These include: solar energetic Particle (SEP) events, geomagnetically induced currents (GIC), ionospheric disturbances that cause radio and radar scintillation, disruption of navigation by magnetic compass and auroral displays at much lower latitudes than normal. In 1989, a geomagnetic storm energized ground induced currents that disrupted electric power distribution throughout most of the province of Quebec and caused aurorae as far south as Texas.




![magnetism review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002621376_1-b85f20a3b377b451b69ac14d495d952c-300x300.png)