Evolution Review Guide
... 13) Summarize 3 ways by which bacterial diseases can be transmitted (passed from 1 individual to another): ...
... 13) Summarize 3 ways by which bacterial diseases can be transmitted (passed from 1 individual to another): ...
Evolution Review Guide
... 13) Summarize 3 ways by which bacterial diseases can be transmitted (passed from 1 individual to another): ...
... 13) Summarize 3 ways by which bacterial diseases can be transmitted (passed from 1 individual to another): ...
Pathogens Practice Quiz - Science with Mrs. Barton
... 2. Which is the best day to help prevent the flu from becoming a pandemic? a. Getting a vaccination b. Taking antibiotics c. Eating fruits and vegetables d. Washing hands often 3. Malaria is a common disease in many countries. What type of pathogen is malaria? a. A virus b. A bacterium c. A fungus d ...
... 2. Which is the best day to help prevent the flu from becoming a pandemic? a. Getting a vaccination b. Taking antibiotics c. Eating fruits and vegetables d. Washing hands often 3. Malaria is a common disease in many countries. What type of pathogen is malaria? a. A virus b. A bacterium c. A fungus d ...
CATEGORY A
... headache, high fever, chills, malaise, myalgia, pulmonary consolidation, and nonproductive cough. Often dissemination to CNS. May cause encephalitis. Occasionally leads to death. Diagnosis is usually made by serology. Treatment with either Tetracyclines or erythromycin ...
... headache, high fever, chills, malaise, myalgia, pulmonary consolidation, and nonproductive cough. Often dissemination to CNS. May cause encephalitis. Occasionally leads to death. Diagnosis is usually made by serology. Treatment with either Tetracyclines or erythromycin ...
Infectious Disease Summary
... infectious agent normally lives and multiplies Inanimate objects contaminated with infectious agent (not the reservoir). Example would be toys in a ...
... infectious agent normally lives and multiplies Inanimate objects contaminated with infectious agent (not the reservoir). Example would be toys in a ...
Chapter 8
... contact; infected individuals may only spread the pathogen to noninfected susceptible individuals (mumps and chicken pox are examples). The term herd immunity refers to the proportion of immunized individuals in a population. The smaller the number of susceptible (nonimmune) individuals in a populat ...
... contact; infected individuals may only spread the pathogen to noninfected susceptible individuals (mumps and chicken pox are examples). The term herd immunity refers to the proportion of immunized individuals in a population. The smaller the number of susceptible (nonimmune) individuals in a populat ...
Role of pathogen-driven selection in shaping the predisposition to IBD
... Why has evolution failed to eliminate the risk alleles? 1) Susceptibility alleles increased in frequency by genetic drift 2) Susceptibility alleles increased in frequency as a result of natural selection (they confer a selective advantage to the carriers; e.g. protection from infection) [hygiene hyp ...
... Why has evolution failed to eliminate the risk alleles? 1) Susceptibility alleles increased in frequency by genetic drift 2) Susceptibility alleles increased in frequency as a result of natural selection (they confer a selective advantage to the carriers; e.g. protection from infection) [hygiene hyp ...
Communicable disease 2017
... streptococcal infection, and many respiratory pathogens • Carrier is a person with inapparent infection who is capable of transmitting the pathogen to others. • Incubatory carriers are those who can transmit the agent during the incubation period before clinical illne ...
... streptococcal infection, and many respiratory pathogens • Carrier is a person with inapparent infection who is capable of transmitting the pathogen to others. • Incubatory carriers are those who can transmit the agent during the incubation period before clinical illne ...
How does the immune system protect the body against disease?
... Your immune system patrols and protects your body from harmful invaders. If your immune system finds an invader, it takes care of the problem. ...
... Your immune system patrols and protects your body from harmful invaders. If your immune system finds an invader, it takes care of the problem. ...
Chapter 15: Bones, Muscle, Skin Chapter 19: Fighting Disease
... Infectious diseases are caused by __________________ 4 major groups of human pathogens: ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ Each infectious disease is caused by a _________________ pathogen Examples: ___________________ causes strep throat ________________ ...
... Infectious diseases are caused by __________________ 4 major groups of human pathogens: ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ Each infectious disease is caused by a _________________ pathogen Examples: ___________________ causes strep throat ________________ ...
Introduction to Environmentally Transmitted Pathogens, Part 1
... • The study of the distribution of health-related states or events in specified populations and the application of this study to the control of health problems. • Epidemiology includes: – 1) methods for measuring the health of groups and for determining the attributes and exposures that influence he ...
... • The study of the distribution of health-related states or events in specified populations and the application of this study to the control of health problems. • Epidemiology includes: – 1) methods for measuring the health of groups and for determining the attributes and exposures that influence he ...
MECHANISMS of PATHOGENESIS Part I
... • Transfer of M/O from feet or other body parts of insects to food or skin of person – Or person can be bitten by insects that are harboring these M/O and thus introduce them to the body ...
... • Transfer of M/O from feet or other body parts of insects to food or skin of person – Or person can be bitten by insects that are harboring these M/O and thus introduce them to the body ...
Diversity of Life
... genetic elements ancestral to viruses evolved prior to typical cells, to become intracellular parasites once bacteria and archaea arrived at the scene. Selection against excessively aggressive parasites that would kill off the host ensembles of genetic elements would lead to early evolution of tempe ...
... genetic elements ancestral to viruses evolved prior to typical cells, to become intracellular parasites once bacteria and archaea arrived at the scene. Selection against excessively aggressive parasites that would kill off the host ensembles of genetic elements would lead to early evolution of tempe ...
Quiz - Web Adventures
... determine if a particular germ causes a certain disease c. determine if a particular germ is a virus d. prepare an antibiotic Prions, viruses, and fungi are three of six kinds of: a. infectious agents b. antibiotics c. vaccines d. antibodies Which of the following is NOT an infectious agent? a. prot ...
... determine if a particular germ causes a certain disease c. determine if a particular germ is a virus d. prepare an antibiotic Prions, viruses, and fungi are three of six kinds of: a. infectious agents b. antibiotics c. vaccines d. antibodies Which of the following is NOT an infectious agent? a. prot ...
Infection and it`s mode of transmission:
... Organisms contained within droplet nuclei or dust particles (i.e. droplet nuclei of tuberculosis ...
... Organisms contained within droplet nuclei or dust particles (i.e. droplet nuclei of tuberculosis ...
Disease evolution - Brian O`Meara Lab
... Red solid = anti-growth rate vaccine (slow parasite growth) Red dashed = anti-toxin immunity (make parasite less harmful w/o affecting transmission and growth rates) ...
... Red solid = anti-growth rate vaccine (slow parasite growth) Red dashed = anti-toxin immunity (make parasite less harmful w/o affecting transmission and growth rates) ...
Use of Bayesian Filtering and Adaptive Learning Methods to
... improve patient adherence to recommended treatments. For example, biosequences, such as sequences from peptide microarrays obtained from a biological sample, can potentially provide pre-symptomatic diagnosis for infectious diseases when processed to associate antibodies to specific pathogens or infe ...
... improve patient adherence to recommended treatments. For example, biosequences, such as sequences from peptide microarrays obtained from a biological sample, can potentially provide pre-symptomatic diagnosis for infectious diseases when processed to associate antibodies to specific pathogens or infe ...
Infectious Diseases
... and the environment. • This is a basic principle of political ecology which has been used in understanding the consequences of human environment interactions. ...
... and the environment. • This is a basic principle of political ecology which has been used in understanding the consequences of human environment interactions. ...
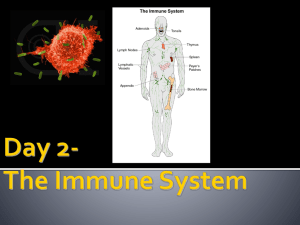
The Immune System day Day 2
... Deliberate passive immunity occurs when travelers to certain regions of the world are given vaccines before leaving home. ...
... Deliberate passive immunity occurs when travelers to certain regions of the world are given vaccines before leaving home. ...
Host-Pathogen Interactions
... ingest, inhale, and transport thousands of organisms (i.e., bacterial, viral, protozoal, or parasitic). Most have no ill effects due to protective mechanisms in our body (i.e., coughing, urinating, sneezing, and defecating). Humans and animals have “friendly” organisms throughout their bodies that s ...
... ingest, inhale, and transport thousands of organisms (i.e., bacterial, viral, protozoal, or parasitic). Most have no ill effects due to protective mechanisms in our body (i.e., coughing, urinating, sneezing, and defecating). Humans and animals have “friendly” organisms throughout their bodies that s ...
Infectious Diseases
... • Minute (very tiny) parasitic microbes that live inside another cell • Over 150 viruses are known to cause diseases in humans • Viral diseases are hard to treat because many can withstand heat, chemicals and large doses of radiation with little effect on their structure ...
... • Minute (very tiny) parasitic microbes that live inside another cell • Over 150 viruses are known to cause diseases in humans • Viral diseases are hard to treat because many can withstand heat, chemicals and large doses of radiation with little effect on their structure ...
Wildlife Trade and the Emergence of Infectious Diseases
... THE MODEL For a new zoonotic disease to emerge, it has to be initially introduced into the human population, followed by subsequent human-to-human transmission. The probability of spread of an infectious pathogen from an animal to human host is determined by a wide range of factors. These include: t ...
... THE MODEL For a new zoonotic disease to emerge, it has to be initially introduced into the human population, followed by subsequent human-to-human transmission. The probability of spread of an infectious pathogen from an animal to human host is determined by a wide range of factors. These include: t ...