![ASTRONOMY 101 SAMPLE FIRST EXAM [1] Kepler`s Law relating](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017742958_1-c5c5f19bce1080c6ad7c1fc92906a06f-300x300.png)
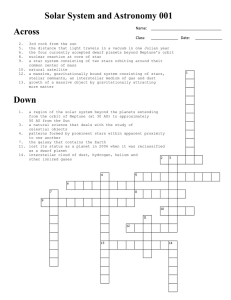
Solar System and Astronomy puzzle 001
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
“The Southern Cross”
... well as calendars for use in religious as well as more general contexts. The ancient Indians used a sidereal system for their astronomical calculations. This uses the stars as a fixed background and times how long it takes an object to make a full orbit relative to them. A year consisted of 360 days ...
... well as calendars for use in religious as well as more general contexts. The ancient Indians used a sidereal system for their astronomical calculations. This uses the stars as a fixed background and times how long it takes an object to make a full orbit relative to them. A year consisted of 360 days ...
Early history of astronomy
... • The motion of a body, such as a planet or moon, along a path around some point in space • Earth's orbit is elliptical • Earth is closest to the Sun (perihelion) in January • Earth is farthest from the Sun (aphelion) in July • The plane of the ecliptic is an imaginary plane that connects Earth's or ...
... • The motion of a body, such as a planet or moon, along a path around some point in space • Earth's orbit is elliptical • Earth is closest to the Sun (perihelion) in January • Earth is farthest from the Sun (aphelion) in July • The plane of the ecliptic is an imaginary plane that connects Earth's or ...
1 DS 3.10 Grade 9 Review
... Grade 9 Astronomy Test Review Concepts and terms to review: □ astronomy □ celestial objects □ luminosity □ sun □ moon □ planet □ star □ asteroid □ comet □ gas giant □ solar system □ nuclear fusion □ astronomical unit (AU) □ light-year □ binary system □ supernova □ nebula □ dwarf star □ hydrogen & he ...
... Grade 9 Astronomy Test Review Concepts and terms to review: □ astronomy □ celestial objects □ luminosity □ sun □ moon □ planet □ star □ asteroid □ comet □ gas giant □ solar system □ nuclear fusion □ astronomical unit (AU) □ light-year □ binary system □ supernova □ nebula □ dwarf star □ hydrogen & he ...
CENTRAL MICHIGAN UNIVERSITY
... be familiar with the appearance, through a telescope, of commonly observed astronomical objects including the sun, the moon, planets, double stars, and diffuse objects (galaxies, nebulae). ...
... be familiar with the appearance, through a telescope, of commonly observed astronomical objects including the sun, the moon, planets, double stars, and diffuse objects (galaxies, nebulae). ...
NOVA COLLEGE-WIDE COURSE CONTENT SUMMARY PHY 150
... Observing the night sky and astronomical time keeping The history & development of astronomy and related laws of physics The nature & physics of light. Optics, telescopes and spectroscopy The Earth as a planet and its nearest neighbor, the Moon Atmospheric and geological characteristics of planets, ...
... Observing the night sky and astronomical time keeping The history & development of astronomy and related laws of physics The nature & physics of light. Optics, telescopes and spectroscopy The Earth as a planet and its nearest neighbor, the Moon Atmospheric and geological characteristics of planets, ...
Document
... a. Isaac Newton and his discoveries b. Newton and Galileo c. Newton’s Laws of Motion i. First Law (Law of Inertia) ii. Second Law (F = ma) iii. Third Law (Action-Reaction Pairs) d. Weight e. Fundamental Forces in Nature f. Universal Gravitation i. Equation ii. Inverse Square Law g. Acceleration due ...
... a. Isaac Newton and his discoveries b. Newton and Galileo c. Newton’s Laws of Motion i. First Law (Law of Inertia) ii. Second Law (F = ma) iii. Third Law (Action-Reaction Pairs) d. Weight e. Fundamental Forces in Nature f. Universal Gravitation i. Equation ii. Inverse Square Law g. Acceleration due ...
Constellations
... interpretation of stars and planets based on the premise that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world. ...
... interpretation of stars and planets based on the premise that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world. ...