Astronomy in Ancient Cultures
... Astronomy arose independently in many areas around the Earth: • Egypt, before 3,000 B.C. • Mesopotamia, before 1,200 B.C. • China, before 600 B.C. • Greece, before 400 B.C. • India, before 1 A.D. In each area, different cultural patterns, religious beliefs, and political influences developed due to ...
... Astronomy arose independently in many areas around the Earth: • Egypt, before 3,000 B.C. • Mesopotamia, before 1,200 B.C. • China, before 600 B.C. • Greece, before 400 B.C. • India, before 1 A.D. In each area, different cultural patterns, religious beliefs, and political influences developed due to ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Welcome to Modern Astronomy Fall 2003
... Tomorrow Morning: Total Eclipse of the Moon Timetable for lunar eclipse ...
... Tomorrow Morning: Total Eclipse of the Moon Timetable for lunar eclipse ...
Astronomy, Mr - Mentor Public Schools
... Astronomy during the middle ages—the rise of science. Science, Technology and Society-- Copernicus, Brahe, Kepler, Galileo Newton--Gravity, Laws of motion The electromagnetic spectrum in astronomy Visible spectra in astronomy Telescopes and observatories Review and Unit 1 test Unit 2: Solar System C ...
... Astronomy during the middle ages—the rise of science. Science, Technology and Society-- Copernicus, Brahe, Kepler, Galileo Newton--Gravity, Laws of motion The electromagnetic spectrum in astronomy Visible spectra in astronomy Telescopes and observatories Review and Unit 1 test Unit 2: Solar System C ...
Astronomy - Wappingers Central School District
... beyond the introductory Regents or non-Regents science courses. This course will have more flexibility than a Regents curriculum, allowing the students to help drive the direction and depth of the topics covered. Astronomy is an extremely diverse science that gets less than 3 weeks coverage through ...
... beyond the introductory Regents or non-Regents science courses. This course will have more flexibility than a Regents curriculum, allowing the students to help drive the direction and depth of the topics covered. Astronomy is an extremely diverse science that gets less than 3 weeks coverage through ...
Astronomy Unit Study Guide
... B. the “star” in the middle of our solar system C. he formed three law’s of planetary motion D. a cloud of dust and gas in space E. the idea that the sun is the center of the solar system F. he developed a model of a sun-centered solar system G. a pattern of stars in the sky H. color that is emitted ...
... B. the “star” in the middle of our solar system C. he formed three law’s of planetary motion D. a cloud of dust and gas in space E. the idea that the sun is the center of the solar system F. he developed a model of a sun-centered solar system G. a pattern of stars in the sky H. color that is emitted ...
Galileo and Newton
... The Ptolemaic (a) and Copernican (b) systems both assumed that all orbits are circular. The fundamental difference is that Copernicus placed the Sun at the center. ...
... The Ptolemaic (a) and Copernican (b) systems both assumed that all orbits are circular. The fundamental difference is that Copernicus placed the Sun at the center. ...
Where We Were to Where We Are: The History of Astronomy
... center of the solar system • The earth rotates around its axis and revolves around the sun ...
... center of the solar system • The earth rotates around its axis and revolves around the sun ...
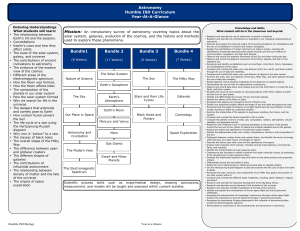
Astronomy Humble ISD Curriculum Year-At-A
... • Compare the planets in terms of orbit, size, composition, rotation, atmosphere, natural satellites, and geological activity. • Relate the role of Newton's law of universal gravitation to the motion of the planets around the Sun and to the motion of natural and artificial satellites around the plan ...
... • Compare the planets in terms of orbit, size, composition, rotation, atmosphere, natural satellites, and geological activity. • Relate the role of Newton's law of universal gravitation to the motion of the planets around the Sun and to the motion of natural and artificial satellites around the plan ...
“The Southern Cross”
... spheres, each with a different period of revolution. It was a far from accurate model, but it started a tradition which others followed. Aristotle was one of those who later expanded and refined this model into his well-known geocentric model. The premise underlying this was a core philosophical pos ...
... spheres, each with a different period of revolution. It was a far from accurate model, but it started a tradition which others followed. Aristotle was one of those who later expanded and refined this model into his well-known geocentric model. The premise underlying this was a core philosophical pos ...
Name Period ______ Astronomy Unit Study Guide 1. _____
... following terms in your description: gravity, accretion, nebula.) ...
... following terms in your description: gravity, accretion, nebula.) ...
Unit 1 Cutouts
... Moved Astronomy from a faith based system to an observation based system and made many ...
... Moved Astronomy from a faith based system to an observation based system and made many ...
Chapter03
... film loop shows a lighted ball moving on an epicycle and deferent as seen first, from above, and then from a fixed-view camera at the center (the Earth). 5. Chinese and Mesoamerican Astronomy Many cultures have produced interesting and significant astronomical results. The reason that I haven’t emph ...
... film loop shows a lighted ball moving on an epicycle and deferent as seen first, from above, and then from a fixed-view camera at the center (the Earth). 5. Chinese and Mesoamerican Astronomy Many cultures have produced interesting and significant astronomical results. The reason that I haven’t emph ...
Introduction and some basic concepts
... Five themes of basic astronomy: I. We are a part of the universe and thus can learn about our origins by studying the universe. II. The universe is comprehensible through scientific principles that anyone can understand. III. Science is not a body of facts but rather a process through which we seek ...
... Five themes of basic astronomy: I. We are a part of the universe and thus can learn about our origins by studying the universe. II. The universe is comprehensible through scientific principles that anyone can understand. III. Science is not a body of facts but rather a process through which we seek ...
Ancient Mathematics 450 B.C. 400 B.C. 350 B.C. 300 B.C. 250 B.C.
... to calculate the distance to the Moon and Sun. ...
... to calculate the distance to the Moon and Sun. ...
A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF ASTRONOMY AT THE
... FIVE COLLEGE ASTRONOMY DEPARTMENT Astronomy was the first science: an interest in the universe has characterized the human race throughout recorded history. Today astronomy remains one of the most exciting and active fields of scientific research, and it is making fundamental contributions to our un ...
... FIVE COLLEGE ASTRONOMY DEPARTMENT Astronomy was the first science: an interest in the universe has characterized the human race throughout recorded history. Today astronomy remains one of the most exciting and active fields of scientific research, and it is making fundamental contributions to our un ...
The Dead Guys a.k.a: The development of astronomy
... Astronomy used for positioning of the pyramids. Vents & passageways align with specific stars. Pyramids are slightly off. (Plate Tectonics?) Divide the sky into constellations. ...
... Astronomy used for positioning of the pyramids. Vents & passageways align with specific stars. Pyramids are slightly off. (Plate Tectonics?) Divide the sky into constellations. ...
1 PS 3.9 Grade 9 Review
... Concepts and terms to review: □ astronomy □ celestial objects □ luminosity □ sun □ moon □ planet □ star □ asteroid □ comet □ gas giant □ solar system □ nuclear fusion □ astronomical unit (AU) □ light-year □ supernova □ nebula ...
... Concepts and terms to review: □ astronomy □ celestial objects □ luminosity □ sun □ moon □ planet □ star □ asteroid □ comet □ gas giant □ solar system □ nuclear fusion □ astronomical unit (AU) □ light-year □ supernova □ nebula ...
Astronomy 111 - Lecture 1
... – NOT a weakness, rather a strength (‘not knowing everything with certainty’ does not mean ‘not knowing anything’ !) ...
... – NOT a weakness, rather a strength (‘not knowing everything with certainty’ does not mean ‘not knowing anything’ !) ...
AST 220 Introduction to Astronomy
... This course covers the history of astronomy and the development of astronomical thought leading to the birth of modern astronomy and its most recent development. Emphasis is placed on the coverage of astronomical instruments and measuring technologies, the solar system, the Milky Way galaxy, importa ...
... This course covers the history of astronomy and the development of astronomical thought leading to the birth of modern astronomy and its most recent development. Emphasis is placed on the coverage of astronomical instruments and measuring technologies, the solar system, the Milky Way galaxy, importa ...