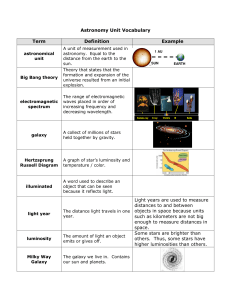
Astronomy Unit Vocabulary Term Definition Example Light years are
... The distance light travels in one objects in space because units year. such as kilometers are not big enough to measure distances in space. Some stars are brighter than The amount of light an object others. Thus, some stars have emits or gives off. higher luminosities than others. The galaxy we live ...
... The distance light travels in one objects in space because units year. such as kilometers are not big enough to measure distances in space. Some stars are brighter than The amount of light an object others. Thus, some stars have emits or gives off. higher luminosities than others. The galaxy we live ...
Vampy Astronomy Syllabus
... related to both observational astronomy and physical astronomy. While some of you may have some astronomyrelated experience, the assumption is that each student is a tabula rasa when it comes to understanding the field. So, we will start at the ground level and work our way up. However, you should n ...
... related to both observational astronomy and physical astronomy. While some of you may have some astronomyrelated experience, the assumption is that each student is a tabula rasa when it comes to understanding the field. So, we will start at the ground level and work our way up. However, you should n ...
Astronomy - Calendar
... about 75 years before Eratosthenes measured the Earth’s size These relative sizes were based on the angular size of objects and a simple geometry formula relating the object’s diameter, its angular size, and its distance Aristarchus realizing the Sun was very large proposed the Sun as center of the ...
... about 75 years before Eratosthenes measured the Earth’s size These relative sizes were based on the angular size of objects and a simple geometry formula relating the object’s diameter, its angular size, and its distance Aristarchus realizing the Sun was very large proposed the Sun as center of the ...
History of Astronomy
... Aristotle’s and Ptolemy’s model of the universe was reintroduced to scholars. 1. The stationary Earth is at the center of the universe. 2. The planets and other celestial bodies travel in perfect circles around it. 3. The heavens are made of a perfect, unchanging substance different from substances ...
... Aristotle’s and Ptolemy’s model of the universe was reintroduced to scholars. 1. The stationary Earth is at the center of the universe. 2. The planets and other celestial bodies travel in perfect circles around it. 3. The heavens are made of a perfect, unchanging substance different from substances ...
Astronomy
... • differentiate among the end states of stars, including white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes.[11D] • compare how the mass and gravity of a main sequence star will determine its end state as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole.[11E] • relate the use of spectroscopy in obtaining physic ...
... • differentiate among the end states of stars, including white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes.[11D] • compare how the mass and gravity of a main sequence star will determine its end state as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole.[11E] • relate the use of spectroscopy in obtaining physic ...
Overview Notes - School District of La Crosse
... e. Astronomers can make observations which in turn become theories, hypothesis, and speculation. 1. enables the astronomer to make predictions when given similar astronomical conditions 2. evidence is often indirect, and supports more than one hypothesis. 3. Questions are not resolved immediately, o ...
... e. Astronomers can make observations which in turn become theories, hypothesis, and speculation. 1. enables the astronomer to make predictions when given similar astronomical conditions 2. evidence is often indirect, and supports more than one hypothesis. 3. Questions are not resolved immediately, o ...
Part I: Moons, Asteroids, and Comets
... Using the Web Surfing Science websites your teacher has assigned to you, complete the following online treasure hunt. ...
... Using the Web Surfing Science websites your teacher has assigned to you, complete the following online treasure hunt. ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Astronomy: The Moon, Sun
... Name __________________________ Class Period ________ ...
... Name __________________________ Class Period ________ ...
The History of Astronomy
... Developed the law of universal gravitation Developed the first reflecting telescope ...
... Developed the law of universal gravitation Developed the first reflecting telescope ...
How do stars form?
... • Since all elements heavier than H are produced by fusion in stars, • We are made of Stardust !!! ...
... • Since all elements heavier than H are produced by fusion in stars, • We are made of Stardust !!! ...
PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Syllabus: Phys 200 (3 cr
... Astronomy and the Universe: a general introduction. ...
... Astronomy and the Universe: a general introduction. ...
1 Intro to Astronomy
... wasn't quite as good as lighting up the night; they probably also noticed that when certain stars appeared in the sky, the weather started getting warmer and the days longer when humans settled down, discovered agriculture and started farming, those patterns told them e.g. when to plant seeds → cons ...
... wasn't quite as good as lighting up the night; they probably also noticed that when certain stars appeared in the sky, the weather started getting warmer and the days longer when humans settled down, discovered agriculture and started farming, those patterns told them e.g. when to plant seeds → cons ...
Cool Dudes of Astronomy!
... Sun • His work was published in1543 – while he was on his deathbed! ...
... Sun • His work was published in1543 – while he was on his deathbed! ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... B. Motion of the fixed stars, constellations, and the Celestial Sphere C. Phases of the Moon D. Motion of the Sun and the planets defines the ecliptic and the Zodiac Historical perspective on the co-evolution of Astronomy and Physics A. Contributions by the ancient Greeks B. Heliocentric and G ...
... B. Motion of the fixed stars, constellations, and the Celestial Sphere C. Phases of the Moon D. Motion of the Sun and the planets defines the ecliptic and the Zodiac Historical perspective on the co-evolution of Astronomy and Physics A. Contributions by the ancient Greeks B. Heliocentric and G ...
Early Astronomy
... The planets (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn) appeared only as points of light on the sky, like the stars, but unlike the Sun and Moon. These objects received special attention because they: moved against the background of stars, are always located within several degrees of the ecliptic ...
... The planets (Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn) appeared only as points of light on the sky, like the stars, but unlike the Sun and Moon. These objects received special attention because they: moved against the background of stars, are always located within several degrees of the ecliptic ...
Quiz # 5
... A protoplanetary disk, such as those observed around some stars in the Orion nebula. Any planet of greater mass than Jupiter. A planet orbiting a star beyond the Sun; for example, the planet orbiting the star 51 Pegasi. D) A primitive organism thought to exist on Jupiter's moon, Europa. ...
... A protoplanetary disk, such as those observed around some stars in the Orion nebula. Any planet of greater mass than Jupiter. A planet orbiting a star beyond the Sun; for example, the planet orbiting the star 51 Pegasi. D) A primitive organism thought to exist on Jupiter's moon, Europa. ...
Astronomy
... gazed to the heavens and pondered just what it was that they were seeing. The earliest astronomers concocted stories that attempted to explain how terrestrial events were tied to celestial events. In this way, both astronomy and astrology were born. Astronomy differs from Astrology in that one ...
... gazed to the heavens and pondered just what it was that they were seeing. The earliest astronomers concocted stories that attempted to explain how terrestrial events were tied to celestial events. In this way, both astronomy and astrology were born. Astronomy differs from Astrology in that one ...























