Physics@Brock - Brock University
... Some histories of astronomy unfairly treat the ancients as if they were backward compared to modern thinkers. In fact ancient astronomers were quite ingenious, and made amazing advances in our understanding of the heavens with careful observations and clever reasoning. Their advances in understandin ...
... Some histories of astronomy unfairly treat the ancients as if they were backward compared to modern thinkers. In fact ancient astronomers were quite ingenious, and made amazing advances in our understanding of the heavens with careful observations and clever reasoning. Their advances in understandin ...
Ancient astronomy Part 6
... enable them to measure the north polar distance (declination), the basis for Chinese observation. The armillary sphere was definitely known to be in widespread use in China from the 2nd century BCE, its complexity increasing over time. The Chinese have also been attributed as the inventors of the fi ...
... enable them to measure the north polar distance (declination), the basis for Chinese observation. The armillary sphere was definitely known to be in widespread use in China from the 2nd century BCE, its complexity increasing over time. The Chinese have also been attributed as the inventors of the fi ...
File
... (Swiss, MIT) conjectured its existence based on galactic rotation curves. Vera Rubin continued the work in the 1970s. And in 2005 a galaxy made almost entirely of dark matter was unveiled. Team Demonstrates Accelerating Expansion of the Universe In 1989, based on observation of distant supernovae an ...
... (Swiss, MIT) conjectured its existence based on galactic rotation curves. Vera Rubin continued the work in the 1970s. And in 2005 a galaxy made almost entirely of dark matter was unveiled. Team Demonstrates Accelerating Expansion of the Universe In 1989, based on observation of distant supernovae an ...
Department: Physics Course number: 1020Q Course title
... are assigned each week; solutions are posted electronically and exam questions are often taken from these assignments. In addition students can discuss the problems (and other aspects of the course) with the professor in her/his office or go to the Physics Resource Learning Center for help from a gr ...
... are assigned each week; solutions are posted electronically and exam questions are often taken from these assignments. In addition students can discuss the problems (and other aspects of the course) with the professor in her/his office or go to the Physics Resource Learning Center for help from a gr ...
THE STAR - physics.udel.edu
... 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it h ...
... 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'M' shape when in upper culmination but in higher northern locations when near lower culminations in spring and summer it h ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... – The year is the rotation period of the Earth around the Sun – The year is subdivided into months, the period of the Moon around the Earth – The weeks seven days are named after the seven bodies in the solar system known in ...
... – The year is the rotation period of the Earth around the Sun – The year is subdivided into months, the period of the Moon around the Earth – The weeks seven days are named after the seven bodies in the solar system known in ...
PH142 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... The purpose of this course is to give a student a full introductory coverage of astronomy, to provide a means of scientific explanation for new astronomical discoveries and theories, and to put into practice techniques learned in Descriptive Astronomy 1. At the conclusion of the course, the students ...
... The purpose of this course is to give a student a full introductory coverage of astronomy, to provide a means of scientific explanation for new astronomical discoveries and theories, and to put into practice techniques learned in Descriptive Astronomy 1. At the conclusion of the course, the students ...
Introduction to Electromagnetism
... Looking ahead SEMINAR 2:15-3:30 4:00 Math-B: Calculus pre-tests Astro-B: start Astrophysics Ch.1 (Carroll & Ostlie) ...
... Looking ahead SEMINAR 2:15-3:30 4:00 Math-B: Calculus pre-tests Astro-B: start Astrophysics Ch.1 (Carroll & Ostlie) ...
Branches of Astronomy
... astronomy (the use of instruments to study objects in the radio through gamma-ray wavelengths). 1. Optical Astronomy: Today, when we think about optical astronomy, we most instantly visualize the amazing images from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), or close up images of the planets taken by various ...
... astronomy (the use of instruments to study objects in the radio through gamma-ray wavelengths). 1. Optical Astronomy: Today, when we think about optical astronomy, we most instantly visualize the amazing images from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), or close up images of the planets taken by various ...
proposed another geocentric _ _ _ _ _.
... theory, Sun, centre, orbit, position, motion, distant, planets, elliptical, speed , lunar, longer Copernicus (1473-1543) proposed that the sun is stationary near the _ _ _ _ _ _ of the universe. His _ _ _ _ _ _ proposed that the Earth _ _ _ _ _ _ _ on its _ _ _ _ once daily and _ _ _ _ _ _ _ around ...
... theory, Sun, centre, orbit, position, motion, distant, planets, elliptical, speed , lunar, longer Copernicus (1473-1543) proposed that the sun is stationary near the _ _ _ _ _ _ of the universe. His _ _ _ _ _ _ proposed that the Earth _ _ _ _ _ _ _ on its _ _ _ _ once daily and _ _ _ _ _ _ _ around ...
Busemann_final - University of Hertfordshire
... “We found an extraordinary wealth of primitive chemical "fingerprints", including abundant presolar grains, true stardust that has formed around other earlier stars, some during supernova explosions, associated with extremely pristine organic matter that must pre-date the formation of our planets,” ...
... “We found an extraordinary wealth of primitive chemical "fingerprints", including abundant presolar grains, true stardust that has formed around other earlier stars, some during supernova explosions, associated with extremely pristine organic matter that must pre-date the formation of our planets,” ...
WORD - UWL faculty websites
... Applications of Light to Astronomy Applications: Based on the spectrum of a celestial object (planet, star, nebula) we can learn: o How hot it is (surface temperature) o What it is made of (chemical composition) o How fast it is moving relative to Earth (towards or away) Continuous Emission: o C ...
... Applications of Light to Astronomy Applications: Based on the spectrum of a celestial object (planet, star, nebula) we can learn: o How hot it is (surface temperature) o What it is made of (chemical composition) o How fast it is moving relative to Earth (towards or away) Continuous Emission: o C ...
Applications of Light to Astronomy
... Applications of Light to Astronomy Applications: • Based on the spectrum of a celestial object (planet, star, nebula) we can learn: o How hot it is (surface temperature) o What it is made of (chemical composition) o How fast it is moving relative to Earth (towards or away) • Continuous Emission: o C ...
... Applications of Light to Astronomy Applications: • Based on the spectrum of a celestial object (planet, star, nebula) we can learn: o How hot it is (surface temperature) o What it is made of (chemical composition) o How fast it is moving relative to Earth (towards or away) • Continuous Emission: o C ...
Ancient astronomy Part 8
... wheels built later by the Aztecs in Mexico, suggesting the consequences of southern migration of early northern tribes and their astronomical knowledge. The Skidi band of the Pawnee, a group from Nebraska, is often seen as the most sophisticated star-watchers. Their attempts to feel connected to the ...
... wheels built later by the Aztecs in Mexico, suggesting the consequences of southern migration of early northern tribes and their astronomical knowledge. The Skidi band of the Pawnee, a group from Nebraska, is often seen as the most sophisticated star-watchers. Their attempts to feel connected to the ...
Astronomy - Earth Systems A
... Made maps: north, south, east and west Also Latitude and longitude ...
... Made maps: north, south, east and west Also Latitude and longitude ...
Astronomy and Humanism by Ray Thompson A. EARLY
... that the spectra of very distant stars were much redder than they should be when the spectral class of the star was taken into account. In addition, the further away the objects were, the more pronounced was the move into the red end of the spectrum. Only one thing could explain this. The objects we ...
... that the spectra of very distant stars were much redder than they should be when the spectral class of the star was taken into account. In addition, the further away the objects were, the more pronounced was the move into the red end of the spectrum. Only one thing could explain this. The objects we ...
Astronomy Impacts our Daily Lives
... 19-century curiosity about electricity led to the electric light, and the world wide web has allowed international teams of researcher to communicate more easily. No amount of applied research on the candle would have brought us the electric light; no amount of research and development on the teleph ...
... 19-century curiosity about electricity led to the electric light, and the world wide web has allowed international teams of researcher to communicate more easily. No amount of applied research on the candle would have brought us the electric light; no amount of research and development on the teleph ...
2b Astronomer space units
... the mysteries of the universe. Sun dials help tell time each day ...
... the mysteries of the universe. Sun dials help tell time each day ...
Early Astronomies
... Extended the idea of deferents and epicycles. Assumed Earth not at the center of the deferent Unclear as to whether he viewed this system as a mathematical tool or reality His model however was taken to be the literal truth for the next fourteen centuries. ...
... Extended the idea of deferents and epicycles. Assumed Earth not at the center of the deferent Unclear as to whether he viewed this system as a mathematical tool or reality His model however was taken to be the literal truth for the next fourteen centuries. ...
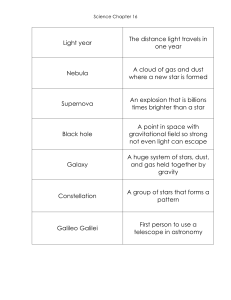
Astronomy Study Guide axis - A real or imaginary line through the
... gravity - The force or pull created by the mass of objects that attracts them to one another celestial bodies - Any objects, including planets, moons, stars, comets, or meteors, which can be found in outer space debris - Bits and pieces of leftover dust and rocks galaxy - A large collection of stars ...
... gravity - The force or pull created by the mass of objects that attracts them to one another celestial bodies - Any objects, including planets, moons, stars, comets, or meteors, which can be found in outer space debris - Bits and pieces of leftover dust and rocks galaxy - A large collection of stars ...
The Ancient Heavens: Exploring the History of Astronomy
... and tracking time. By understanding the roots and origins of Astronomy, and how ancient civilizations studied, used and applied this science, students can begin to appreciate what early astronomers contributed to our understanding of the world and our place in the universe. ...
... and tracking time. By understanding the roots and origins of Astronomy, and how ancient civilizations studied, used and applied this science, students can begin to appreciate what early astronomers contributed to our understanding of the world and our place in the universe. ...