PowerPoint - Herschel Space Observatory
... “Black Body” radiation • A black body is a perfect emitter and absorber of radiation – It emits and absorbs radiation with a particular “spectrum” – The shape of the spectrum is always the same, but the peak wavelength changes with temperature. – But not all objects are black bodies. – Atoms, molec ...
... “Black Body” radiation • A black body is a perfect emitter and absorber of radiation – It emits and absorbs radiation with a particular “spectrum” – The shape of the spectrum is always the same, but the peak wavelength changes with temperature. – But not all objects are black bodies. – Atoms, molec ...
Stellar Explosions
... Last nucleus in the alpha-particle chain is nickel56, which is unstable and quickly decays to cobalt-56 and then to iron-56 Iron-56 is the most stable nucleus, so it neither fuses nor decays Within the cores of the most massive stars, neutron capture can create heavier elements, all the way up to bi ...
... Last nucleus in the alpha-particle chain is nickel56, which is unstable and quickly decays to cobalt-56 and then to iron-56 Iron-56 is the most stable nucleus, so it neither fuses nor decays Within the cores of the most massive stars, neutron capture can create heavier elements, all the way up to bi ...
In This Issue The Hottest Planet in the Solar System President`s Article
... on its axis (using a distant star … not our sun … as a way to measure when the rotation is completed.) But in that same amount of time, the Earth will have moved forward in its approximately 365¼ day orbit around the Sun — by just shy of 1º. This means the Sun isn’t at precisely the same location re ...
... on its axis (using a distant star … not our sun … as a way to measure when the rotation is completed.) But in that same amount of time, the Earth will have moved forward in its approximately 365¼ day orbit around the Sun — by just shy of 1º. This means the Sun isn’t at precisely the same location re ...
Lecture 3 - Concord University
... oapparent lack of stellar parallax Proof by contradiction: what if earth orbits sun? lines of sight foreground star should appears to shift w.r.t. background stars ⇒ but parallax effect not observed! Why? ...
... oapparent lack of stellar parallax Proof by contradiction: what if earth orbits sun? lines of sight foreground star should appears to shift w.r.t. background stars ⇒ but parallax effect not observed! Why? ...
Phys133 SAMPLE questions for MidTerm#1
... C) It appears very near the north celestial pole. D) It can be used to determine your longitude on Earth. E) It is the star directly on your northern horizon. ...
... C) It appears very near the north celestial pole. D) It can be used to determine your longitude on Earth. E) It is the star directly on your northern horizon. ...
Theories of the solar system
... The word retrograde applies to the apparent backward motion of a planet. An old encyclopedia of astrology describes this retrograde motion as "…the effect of a slow-moving train as viewed from another train traveling parallel to it but at a more rapid rate, wherein the slower train appears to be mov ...
... The word retrograde applies to the apparent backward motion of a planet. An old encyclopedia of astrology describes this retrograde motion as "…the effect of a slow-moving train as viewed from another train traveling parallel to it but at a more rapid rate, wherein the slower train appears to be mov ...
Chapter 7 Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation is used to explain the tides. ◦ Since the water directly below the moon is closer than Earth as a whole, it accelerates more rapidly toward the moon than Earth, and the water rises. ◦ Similarly, Earth accelerates more rapidly toward the moon than the water on th ...
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation is used to explain the tides. ◦ Since the water directly below the moon is closer than Earth as a whole, it accelerates more rapidly toward the moon than Earth, and the water rises. ◦ Similarly, Earth accelerates more rapidly toward the moon than the water on th ...
black body temperature - Herschel Space Observatory
... “Black Body” radiation • A black body is a perfect emitter and absorber of radiation – It emits and absorbs radiation with a particular “spectrum” – The shape of the spectrum is always the same, but the peak wavelength changes with temperature. – But not all objects are black bodies. – Atoms, molec ...
... “Black Body” radiation • A black body is a perfect emitter and absorber of radiation – It emits and absorbs radiation with a particular “spectrum” – The shape of the spectrum is always the same, but the peak wavelength changes with temperature. – But not all objects are black bodies. – Atoms, molec ...
Stellar Evolution and the Herzsprung-Russell Diagram
... • The ashes of each reaction are the fuel for the next inner shell. • Each reaction is less efficient than the previous: they buy very little time • Iron accumulates because energy cannot be gained by making heavier elements (it has the most stable nucleus) • The iron core is supported by degeneracy ...
... • The ashes of each reaction are the fuel for the next inner shell. • Each reaction is less efficient than the previous: they buy very little time • Iron accumulates because energy cannot be gained by making heavier elements (it has the most stable nucleus) • The iron core is supported by degeneracy ...
Earths Place in the Universe
... • Our sun is just 1 of 100 billion stars that make up the milky way. • It is difficult to determine its size and shape because we are located in the milky way. • The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way Galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ...
... • Our sun is just 1 of 100 billion stars that make up the milky way. • It is difficult to determine its size and shape because we are located in the milky way. • The solar system is located in an outer edge of the disc-shaped Milky Way Galaxy, which spans 100,000 light years. ...
Name - MIT
... A) More distant planets orbit the Sun at slower speeds. B) The orbit of each planet about the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus. C) The force of attraction between any two objects decreases with the square of the distance between their centers. D) As a planet moves around its orbit, it swe ...
... A) More distant planets orbit the Sun at slower speeds. B) The orbit of each planet about the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus. C) The force of attraction between any two objects decreases with the square of the distance between their centers. D) As a planet moves around its orbit, it swe ...
ET: Astronomy 230 Outline Important Caveat
... Not the ones found so far! Haven’t found smaller planets yet! ...
... Not the ones found so far! Haven’t found smaller planets yet! ...
Astronomy
... The Moon, represented by a female deity had an influence on the Mayans. They identified a waxing moon as the ideal woman, and a waning moon as an old woman ruling childbirth. They kept track of synodic- lunation’s (intervals of full moons). They were able to calculate that there were 149 moons in 4 ...
... The Moon, represented by a female deity had an influence on the Mayans. They identified a waxing moon as the ideal woman, and a waning moon as an old woman ruling childbirth. They kept track of synodic- lunation’s (intervals of full moons). They were able to calculate that there were 149 moons in 4 ...
Document
... interesting feature obtained so far. It has a direct bearing on the current search for extra-solar planetary systems, one of the most challenging astronomical activities. While spectroscopic, astrometric and photometric studies may only provide indirect evidence for planets around other stars, coron ...
... interesting feature obtained so far. It has a direct bearing on the current search for extra-solar planetary systems, one of the most challenging astronomical activities. While spectroscopic, astrometric and photometric studies may only provide indirect evidence for planets around other stars, coron ...
GST 2420 Final Exam topics
... What do you know about what is happening and when this event took place? How do you know? What does this tell us about the possibilities of studying some past events in astronomy? 12. What is a black hole? Describe how they are formed and their characteristics. What effects do they have on matter, s ...
... What do you know about what is happening and when this event took place? How do you know? What does this tell us about the possibilities of studying some past events in astronomy? 12. What is a black hole? Describe how they are formed and their characteristics. What effects do they have on matter, s ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... Structure of the Milky Way The energy for the state where the spins are parallel is higher than for the state where the spins are anti-parallel The hydrogen atom, if it is in the spin parallel state, can make a transition to the spin anti-parallel state releasing energy When a transition does a occ ...
... Structure of the Milky Way The energy for the state where the spins are parallel is higher than for the state where the spins are anti-parallel The hydrogen atom, if it is in the spin parallel state, can make a transition to the spin anti-parallel state releasing energy When a transition does a occ ...
Chaper 1 part b
... 2. REVOLUTION=the movement of the Earth in orbit around the sun. It takes one year for the Earth to complete one revolution. 3. PRECESSION=the slow conical (top-like) motion of the Earth’ Earth’s axis of rotation. It takes 26,000 years for the Earth to complete one cycle of precession. ...
... 2. REVOLUTION=the movement of the Earth in orbit around the sun. It takes one year for the Earth to complete one revolution. 3. PRECESSION=the slow conical (top-like) motion of the Earth’ Earth’s axis of rotation. It takes 26,000 years for the Earth to complete one cycle of precession. ...
PHY299B Poster-Justin Hudson-v2
... dips in brightness during the phase is when the brightest star is blocked by the other creating the eclipsing effect like when Earth experiences a solar eclipse. The smaller dips in brightness is when the brighter star blocks out the light from the other star when passing in front of it. • From thes ...
... dips in brightness during the phase is when the brightest star is blocked by the other creating the eclipsing effect like when Earth experiences a solar eclipse. The smaller dips in brightness is when the brighter star blocks out the light from the other star when passing in front of it. • From thes ...
Chapter 16
... Galileo drew detailed diagrams of Earth's moon, observing valleys and mountains and craters. ...
... Galileo drew detailed diagrams of Earth's moon, observing valleys and mountains and craters. ...
Characteristics of stars
... • Many stars are about the size of the sun, which is a medium sized star. • White dwarfs are about the size of Earth. • Neutron stars are about 20KM (smallest) • Giant stars and super giant stars. If our sun were a super giant star it would fill our solar system as far out as Jupiter. ...
... • Many stars are about the size of the sun, which is a medium sized star. • White dwarfs are about the size of Earth. • Neutron stars are about 20KM (smallest) • Giant stars and super giant stars. If our sun were a super giant star it would fill our solar system as far out as Jupiter. ...
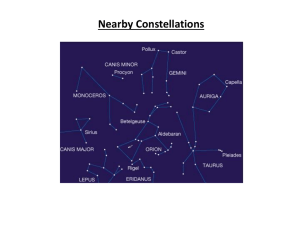
Nearby Constellations
... Stars/Constellations This several-hour-long time exposure, taken from tropical northern Australia, shows the clockwise motion of the southern stars around the South Celestial Pole. (Photo by David Miller/DMI.) ...
... Stars/Constellations This several-hour-long time exposure, taken from tropical northern Australia, shows the clockwise motion of the southern stars around the South Celestial Pole. (Photo by David Miller/DMI.) ...
History of the Universe and Solar System
... When a red giant has exhausted its fuel, it collapses inward by gravity. This collapse releases so much energy through fusion that the star explodes as a supernova. Explosive nucleosynthesis produces all the elements heavier than iron (57-260) plus all radioactive elements (except C14). ...
... When a red giant has exhausted its fuel, it collapses inward by gravity. This collapse releases so much energy through fusion that the star explodes as a supernova. Explosive nucleosynthesis produces all the elements heavier than iron (57-260) plus all radioactive elements (except C14). ...