* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - MIT
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Celestial spheres wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
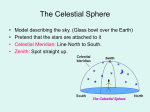
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy 101, Exam #1 (Practice questions) Name____________________________________ ID #__________________________ No notes, No books; 1) The planet Mars never passes through which of these constellations as seen from Earth? A) Virgo B) Capricorn C) Leo D) Ursa Minor E) Aquarius 2) Which of these planets takes the shortest time to travel one full orbit around the Sun? A) Mars B) Venus C) Jupiter D) Earth E) Saturn 3) There are 40 galaxies in the Local Group of galaxies. Each galaxy contains 1 x 1011 stars. How many stars are in the Local Group. A) 4.0 x 1011 B) 4.0 x 1012 C) 4.0 x 1013 D) 2.5 x 1010 E) 2.5 x 1011 4) In 13,000 years (in 15,000 AD), the north celestial pole will be closest to which of these stars? A) B) C) D) E) Polaris Vega Betelgeuse Rigel Orion 5) The altitude of the celestial pole in your sky is equal to … A) B) C) D) E) your longitude. your latitude. your fall equinox. your spring equinox. your summer solstice. Astronomy 101, Exam #1 (Practice questions) 6) The point directly above your head is called the … A) B) C) D) E) horizon. zenith. latitude longitude. declination. 7) How many astronomical units is the Earth from the Sun? A) B) C) D) E) 10 2 1 0.5 0.1 8) The plane of the ecliptic is … A) an extension of the celestial equator B) inclined at an angle of 60 degrees to the celestial equator. C) inclined at an angle of 48.3 degrees to the celestial equator. D) inclined at an angle of 23.5 degrees to the celestial equator. E) inclined at an angle of 4.3 degrees to the celestial equator. 9) The celestial equator is … A) an extension of the Earth’s equator. B) inclined at an angle of 60 degrees to the Earth’s equator. C) inclined at an angle of 48.3 degrees to the Earth’s equator. D) inclined at an angle of 23.5 degrees to the Earth’s equator. E) inclined at an angle of 4.3 degrees to the Earth’s equator. Astronomy 101, Exam #1 (Practice questions) 10) Seasons on the Earth are a consequence of … A) the varying distance between the Earth and the Sun during the year. B) the varying speed of the Earth in its orbit about the Sun. C) the precession of the Earth's rotation axis. D) the tilt of the Earth's rotation axis relative to the ecliptic. E) the tilt of the Moon's orbital plane relative to the ecliptic. 11) If you are standing at the Earth's north pole, which of the following will be directly overhead? A) the celestial equator B) the ecliptic C) the zodiac D) the north celestial pole E) the Sun 12) Why is it so difficult to detect stellar parallax? A) Because the stars are so close to the Earth. B) Because the stars are at enormous distances compared to the distance between the Earth and Sun. C) Because it is hidden by the Moon. D) There is no stellar parallax because the Earth does not move. E) There is no stellar parallax because the Earth orbits the Sun. 13) The moons of Jupiter were discovered by … A) Tycho Brahe. B) Galileo Galilei. C) Nicolas Copernicus. D) Aristotle. E) Johannes Kepler. 14) A planet is 3 Astronomical Units from the Sun. What is the planet’s orbital period around the Sun? A) the square of 3, which equals 9 years B) the square root of 3, which equals 1.7 years C) the square root of 27, which equals 5.2 years D) the square of 9, which equals 81 years E) the cube of 3, which equals 27 years Astronomy 101, Exam #1 (Practice questions) 15) During its orbit when a planet is at aphelion, it is … A) B) C) D) E) at its closest point to the Sun. at its farthest point from the Sun. in total shadow. in partial shadow. in conjunction with the Sun and another planet. 16) A galaxy is 3,000 light years away and we observe light from that galaxy. We are looking at the galaxy as it appeared … A) B) C) D) E) a few minutes ago. 9 x 1011 years ago. 6,000 years ago. 3,000 years ago. 1,500 years ago. 17) Which of the following is not one of, nor a direct consequence of, Kepler's Laws? A) More distant planets orbit the Sun at slower speeds. B) The orbit of each planet about the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus. C) The force of attraction between any two objects decreases with the square of the distance between their centers. D) As a planet moves around its orbit, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times. E) A planet or comet in a non-circular orbit travels faster when it is nearer to the Sun and slower when it is farther from the Sun. 18) We describe a location on the Earth's surface by stating its … A) altitude and direction (or azimuth) B) meridian and longitude C) latitude and direction D) latitude and longitude E) right ascencion and declination 19) When traveling north from the United States into Canada, you'll see the North Star (Polaris) getting … A) dimmer. B) lower in the sky. C) brighter. D) higher in the sky. E) larger. Astronomy 101, Exam #1 (Practice questions) 20) No star corresponds to the South Celestial Pole. How would you find it if you were in the southern hemisphere? A) Know that two stars in the Big Dipper (which is part of Ursa Major) point to the South Celestial Pole. B) Know that the South Celestial Pole is between the constellations Cancer and Virgo. C) Know that the Southern Cross (the constellation Crux) points toward the South Celestial Pole and is four cross lengths away. D) Know that the South Celestial Pole appears to be in the center of the constellation Hercules. E) Know that the stars that appear to be part of Orion’s belt in the constellation Orion point directly at the South Celestial Pole. 21) The constellations in the zodiac are found spread along the … A) B) C) D) E) celestial equator. Tropic of Cancer. celestial poles. meridian. ecliptic. 22) Kepler found that a planets' orbit about the Sun is … A) a circle with the Sun at the center. B) an ellipse with the Sun at the center. C) an ellipse with the Sun at one foci. D) a circle with the Sun outside the circle. E) an ellipse with the Sun outside the ellipse. 23) During the period each year when we see Mars undergoing apparent retrograde motion in our sky, what is really going on in space? A) Mars is moving around the Sun in the opposite direction from which Earth is moving around the Sun. B) Earth is catching up with and passing by Mars in their respective orbits. C) The Earth and Mars are getting closer together. D) Earth and Mars are on opposite sides of the Sun. E) The Earth and Mars are getting farther apart. Astronomy 101, Exam #1 (Practice questions) 24) What is the ecliptic? A) The shape of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. B) The path on the Earth traced by the Moon's shadow during a solar eclipse. C) It is a half-circle extending from your horizon due north, through your zenith, to your horizon due south. D) The path the Sun appears to trace around the celestial sphere each year. E) An extension of the meridian out into space. 25) What is the celestial sphere? A) The celestial sphere is a model that shows the true locations of the Sun and a few thousand of the nearest stars. B) It is a model of how the stars are arranged in the sky relative to our Sun, which is in the middle of the sphere. C) The celestial sphere is a representation of how the sky looks as seen from Earth. D) The perimeter of the Milky Way Galaxy. E) The area enveloped by the corona of the Sun. 26) Which of the following statements does NOT use the term "angular size" or "angular distance" correctly? A) The angular size of the Sun is about the same as that of the Moon. B) You can use your outstretched hand against the sky to estimate angular sizes and angular distances. C) The angular distance between those two bright stars in the sky is about 2 meters. D) The angular distance between those two houses in the distance is 30 degrees. E) The angular distance between these two binary stars is 10 arcseconds. Astronomy 101, Exam #1 (Practice questions) 27) During a solar eclipse, the umbra is the … A) B) C) D) E) region where sunlight is only partially blocked. time it takes the eclipse to pass over you. the distance from the Earth to the Sun. the distance from the Earth to the Moon. region where sunlight is fully blocked. 28) You have decided to move to an uninhabited planet on the other side of the Milky Way Galaxy. How many constellations will be observable from that planet? A) B) C) D) 88 44 22 The number of constellations appearing in the sky is rather arbitrary and you will have to identify your own constellations when you get there. E) 1,000 29) The diameter of the Milky Way Galaxy is approximately … A) B) C) D) E) 100,000 light years 100,000 meters 100,000 kilometers 100,000 parsecs 100,000 centimeters 30) A proton has a mass of 1.67 x 10-27 kg. What is the mass of 3 x 108 protons? A) 4.67 x 10--35 kg B) 4.67 x 10-20 kg C) 4.67 x 10-19 kg D) 5.01 x 10-19 kg E) 5.01 x 10-35 kg