Celestial Sphere Lab
... ideas they proposed have since proven to be incorrect. Some of the concepts they developed are still useful today though. One of the more useful ideas proposed by the ancient Greeks is the idea of a celestial sphere. We now know that the Earth’s rotation causes the stars to appear to move around us ...
... ideas they proposed have since proven to be incorrect. Some of the concepts they developed are still useful today though. One of the more useful ideas proposed by the ancient Greeks is the idea of a celestial sphere. We now know that the Earth’s rotation causes the stars to appear to move around us ...
Star - AUSD Blogs
... magnetic tape and the thousands of photographs we are carrying back to earth. Other scientists can interpret them as easily as I can, and I am not one who would condone that tampering with the truth which often gave my order a bad name in the olden days. The crew are already sufficiently depressed: ...
... magnetic tape and the thousands of photographs we are carrying back to earth. Other scientists can interpret them as easily as I can, and I am not one who would condone that tampering with the truth which often gave my order a bad name in the olden days. The crew are already sufficiently depressed: ...
Day-26
... the mass of Jupiter. Some of these orbit close to their stars and are called hot Jupiters. It is easier to find these very large planets due to the greater “wobble” they cause for their stars. ...
... the mass of Jupiter. Some of these orbit close to their stars and are called hot Jupiters. It is easier to find these very large planets due to the greater “wobble” they cause for their stars. ...
A tour of the solar system.
... Two theories: 1. Solar system evolved from a nebula (dust cloud) ...
... Two theories: 1. Solar system evolved from a nebula (dust cloud) ...
Test#1
... A shift in the direction of an object caused by a change in the position of an observer is called a) parallax, b) precession, c) the Coriolis effect, d) epicycle motion Newton invented this to help him solve Kepler's equations a) algebra, b) calculus, c) trigonometry, d) protractor At anyone given t ...
... A shift in the direction of an object caused by a change in the position of an observer is called a) parallax, b) precession, c) the Coriolis effect, d) epicycle motion Newton invented this to help him solve Kepler's equations a) algebra, b) calculus, c) trigonometry, d) protractor At anyone given t ...
Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam
... Draw the apparent motion of stars as seen by any observer looking North, East, South or West, Define a constellation and distinguish it from an asterism, Use celestial coordinates of Right Ascension and Declination appropriately in written work and problem solving, Use the simplified celesti ...
... Draw the apparent motion of stars as seen by any observer looking North, East, South or West, Define a constellation and distinguish it from an asterism, Use celestial coordinates of Right Ascension and Declination appropriately in written work and problem solving, Use the simplified celesti ...
Star Gazing
... • The zodiacal constellations are located along the Sun’s path on Earth (Ecliptic). • The Ecliptic is also the plane of Earth’s path around the Sun. http://lifeng.lamost.org/courses/astrotoday/CHAISSON/AT301/HTML/AT30103.HTM ...
... • The zodiacal constellations are located along the Sun’s path on Earth (Ecliptic). • The Ecliptic is also the plane of Earth’s path around the Sun. http://lifeng.lamost.org/courses/astrotoday/CHAISSON/AT301/HTML/AT30103.HTM ...
Lecture 10: Stars
... compared to their distance that we almost never have the resolution to see their sizes and details directly – “point sources” & We deduce everything by measuring the amount of light (brightness) at different wavelengths (color, spectra) ...
... compared to their distance that we almost never have the resolution to see their sizes and details directly – “point sources” & We deduce everything by measuring the amount of light (brightness) at different wavelengths (color, spectra) ...
Great Discoveries in Astronomy and Astrophysics 171.112
... How did we come to know what we know about the Universe? This course will focus on key discoveries in astronomy and astrophysics from the speed of light to the speed of the expanding and now accelerating Universe, from the discovery of Neptune to the modern detection of extrasolar planets, spanning ...
... How did we come to know what we know about the Universe? This course will focus on key discoveries in astronomy and astrophysics from the speed of light to the speed of the expanding and now accelerating Universe, from the discovery of Neptune to the modern detection of extrasolar planets, spanning ...
Document
... 24. A star spends most of its life: a) As a protostar. b) In explosions lasting millions of years. c) As a red giant or supergiant. d) As a main sequence star. 25. What characteristic of a star cluster is used to determine its age? a) The number of red giants. b) The faintest stars seen in the clus ...
... 24. A star spends most of its life: a) As a protostar. b) In explosions lasting millions of years. c) As a red giant or supergiant. d) As a main sequence star. 25. What characteristic of a star cluster is used to determine its age? a) The number of red giants. b) The faintest stars seen in the clus ...
Common Misconceptions in Astronomy and History
... is unable to stop, or consume, the material completely, due to its size, a piece of it will reach the Earth's surface, where it is known as a Meteorite. Meteorites most likely originate from the asteroid belt as rock or ice-rock fragments formed through the collisions of asteroids and comets. Meteo ...
... is unable to stop, or consume, the material completely, due to its size, a piece of it will reach the Earth's surface, where it is known as a Meteorite. Meteorites most likely originate from the asteroid belt as rock or ice-rock fragments formed through the collisions of asteroids and comets. Meteo ...
04 Lines in the Sky
... Lines in the Sky • In order to use the sky to measure time you need to measure the location of objects in the sky. We will look at two methods of measuring locations in the sky. • Both methods require measuring angles. • These methods have long been used not only for timekeeping but for navigation a ...
... Lines in the Sky • In order to use the sky to measure time you need to measure the location of objects in the sky. We will look at two methods of measuring locations in the sky. • Both methods require measuring angles. • These methods have long been used not only for timekeeping but for navigation a ...
Document
... If the star is very massive, roughly 3 or more times the mass of our Sun, the final object produced may be a black hole. ...
... If the star is very massive, roughly 3 or more times the mass of our Sun, the final object produced may be a black hole. ...
Kinesthetic Astronomy: Earth`s Rotation
... planet Pluto. In reality Polaris is about 876,000 times more distant from our sun than Pluto. Many people have not perceived that stars (at all but polar latitudes) appear to rise and set just as the Sun does (due to Earth’s rotation about its north-south axis). For some urban dwellers, even sunri ...
... planet Pluto. In reality Polaris is about 876,000 times more distant from our sun than Pluto. Many people have not perceived that stars (at all but polar latitudes) appear to rise and set just as the Sun does (due to Earth’s rotation about its north-south axis). For some urban dwellers, even sunri ...
Document
... means of the sky, but the motions of objects in the sky predicted the changing of the seasons, etc. ...
... means of the sky, but the motions of objects in the sky predicted the changing of the seasons, etc. ...
The Life of a Star - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster • A stellar association is a group ...
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster • A stellar association is a group ...
solution
... statistical mechanics. Combined with this is the rapid pace of development in computational physics and the computing power that can fit in the palm of your hand – we can now simulate much of stellar evolution to make predictions about what we observe. This allows us to more than speculate about the ...
... statistical mechanics. Combined with this is the rapid pace of development in computational physics and the computing power that can fit in the palm of your hand – we can now simulate much of stellar evolution to make predictions about what we observe. This allows us to more than speculate about the ...
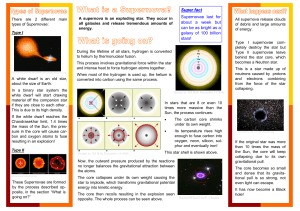
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... gravitational pull. The core becomes so small and dense that its gravitational pull is so strong, not even light can escape. ...
... gravitational pull. The core becomes so small and dense that its gravitational pull is so strong, not even light can escape. ...
L5 - QUB Astrophysics Research Centre
... (surface)~10-4 kg m-3. Much smaller than mean density (mean)~1.4103 kg m-3 (which we derived). We know the surface temperature (Teff=5780K) is much smaller than its minimum mean temperature (2106 K). Thus we make two approximations for the surface boundary conditions: = T = 0 at r=rs i.e. that ...
... (surface)~10-4 kg m-3. Much smaller than mean density (mean)~1.4103 kg m-3 (which we derived). We know the surface temperature (Teff=5780K) is much smaller than its minimum mean temperature (2106 K). Thus we make two approximations for the surface boundary conditions: = T = 0 at r=rs i.e. that ...
Lecture 9
... • Absolute magnitude describes stellar luminosities – Its what the stars apparent magnitude would be if it were 10 parsecs away ...
... • Absolute magnitude describes stellar luminosities – Its what the stars apparent magnitude would be if it were 10 parsecs away ...
Reminder: Assignments are due back to teachers within 2 school days.
... hydrogen and helium fuel has been burned, the delicate balance between the outer nuclear radiation.pressure and the stable gravitational force becomes disturbed and slow contraction begins. As compression increases, a very dense plasma forms. If the initial star had mass of less than 1.4 solar masse ...
... hydrogen and helium fuel has been burned, the delicate balance between the outer nuclear radiation.pressure and the stable gravitational force becomes disturbed and slow contraction begins. As compression increases, a very dense plasma forms. If the initial star had mass of less than 1.4 solar masse ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... The average apparent magnitude of a Cepheid star is m 5.8 and the period of variation of its luminosity is 12 days. Using the relation M 2.83log10 T 1.81 between period T (in days) and average absolute magnitude M calculate the distance to this star. ...
... The average apparent magnitude of a Cepheid star is m 5.8 and the period of variation of its luminosity is 12 days. Using the relation M 2.83log10 T 1.81 between period T (in days) and average absolute magnitude M calculate the distance to this star. ...
Stars and H
... • Stellar Evolution/H-R Diagram Simulation http://instruct1.cit.cornell.edu/courses/astro101/java/evolve/evolve.htm ...
... • Stellar Evolution/H-R Diagram Simulation http://instruct1.cit.cornell.edu/courses/astro101/java/evolve/evolve.htm ...