Exam #: Printed Name: Signature: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT
... The surface temperature of the Sun is 6000 K. The sunlight striking the Earth’s surface has a power per unit area of 1300 W/m2 . a) What is the typical energy of a photon emitted from the Sun? b) Estimate (to within an order of magnitude) the number of photons per second from the Sun that strike the ...
... The surface temperature of the Sun is 6000 K. The sunlight striking the Earth’s surface has a power per unit area of 1300 W/m2 . a) What is the typical energy of a photon emitted from the Sun? b) Estimate (to within an order of magnitude) the number of photons per second from the Sun that strike the ...
Night Sky Checklist July–August–September Unaided Eye Astronomy
... Altair, and Deneb form its corners, and are three of the 20 brightest stars in the night sky. Lyra¸ the Harp¸ is a small constellation that is surprisingly easy to find because it is dominated by the bright star Vega, one of the corners of the summer Triangle. Aquila, the Eagle, is a fairly shapeles ...
... Altair, and Deneb form its corners, and are three of the 20 brightest stars in the night sky. Lyra¸ the Harp¸ is a small constellation that is surprisingly easy to find because it is dominated by the bright star Vega, one of the corners of the summer Triangle. Aquila, the Eagle, is a fairly shapeles ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 4 Notes: Energy and
... named after the 19th century physicists Kelvin (of the Kelvin temperature scale) and Helmholtz, who first pointed out its importance. The meaning of tKH is that it is the time for which a star could be powered by gravity alone without its radius changing very much. Similarly, if we have a star that ...
... named after the 19th century physicists Kelvin (of the Kelvin temperature scale) and Helmholtz, who first pointed out its importance. The meaning of tKH is that it is the time for which a star could be powered by gravity alone without its radius changing very much. Similarly, if we have a star that ...
B - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... massive star? A. passage of a shock wave through the star’s envelope B. *helium flash in the star’s core, when 3 helium nuclei combine C. photodisintegration of nuclei by gamma rays D. collapse of the star’s core 12. Approximately how far is the Sun from the center of our galaxy? A. 49 kpc B. 2 kpc ...
... massive star? A. passage of a shock wave through the star’s envelope B. *helium flash in the star’s core, when 3 helium nuclei combine C. photodisintegration of nuclei by gamma rays D. collapse of the star’s core 12. Approximately how far is the Sun from the center of our galaxy? A. 49 kpc B. 2 kpc ...
Powerpoint
... Remember 1" (arcsecond) = 1/60 arcmin = 1/3600 degrees If the angle is 0.5", the distance is 2 pc. ...
... Remember 1" (arcsecond) = 1/60 arcmin = 1/3600 degrees If the angle is 0.5", the distance is 2 pc. ...
Slide 1 - Physics @ IUPUI
... somewhere. • Where does the energy the pulsars emit come from? • A) heat • B) nuclear fusion • C) gravity • D) Spin ...
... somewhere. • Where does the energy the pulsars emit come from? • A) heat • B) nuclear fusion • C) gravity • D) Spin ...
the lives of stars
... star, has been a main sequence star for about 5 billion years. It will continue to shine without changing for about 5 billion more years. Really large stars burn through their supply of hydrogen very quickly, so they ‘live fast and die young’! These very large stars may only be on the main sequence ...
... star, has been a main sequence star for about 5 billion years. It will continue to shine without changing for about 5 billion more years. Really large stars burn through their supply of hydrogen very quickly, so they ‘live fast and die young’! These very large stars may only be on the main sequence ...
Big Bang and Life Cycle of Stars
... Small nebulas, produce small cool stars that are long lived. Less gravitational force, but strong enough for the core to produce fusion. These are the red, dim stars in the lower right corner of RH diagram. ...
... Small nebulas, produce small cool stars that are long lived. Less gravitational force, but strong enough for the core to produce fusion. These are the red, dim stars in the lower right corner of RH diagram. ...
Space Exploration Review Notes
... planets are small, rocky (terrestrial), dense, few or no moons. The outer planets are large, gaseous (gas giants or Jovian), low density, numerous moons, most have rings. Planetary data tables like the one on the next page compare planet criteria such as period of rotation (day), distance from the ...
... planets are small, rocky (terrestrial), dense, few or no moons. The outer planets are large, gaseous (gas giants or Jovian), low density, numerous moons, most have rings. Planetary data tables like the one on the next page compare planet criteria such as period of rotation (day), distance from the ...
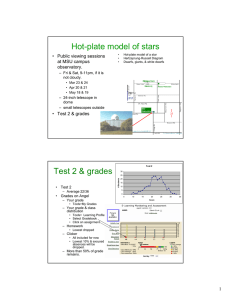
Hot-plate model of stars Test 2 & grades • Public viewing sessions
... surface temperature (1905) & discovered a surprise. Sirius A is slightly larger than the sun. Sirius B is 100 1 times smaller. The same size as the Earth! Stars come in 3 sizes. ...
... surface temperature (1905) & discovered a surprise. Sirius A is slightly larger than the sun. Sirius B is 100 1 times smaller. The same size as the Earth! Stars come in 3 sizes. ...
Document
... Planetary nebulae: Fate of low mass stars • The hot core lights up the expanding envelope, for about 20,000 years. ...
... Planetary nebulae: Fate of low mass stars • The hot core lights up the expanding envelope, for about 20,000 years. ...