View poster
... The solution is to start considering the Moon. Therefore the dynamic range of the star sensor had to include the brighter stars in our galaxy and the very bright Moon. Ranges from magnitudes 1 to -13 need to be covered. In the lab we have shown that the dynamic range of the star sensor can include t ...
... The solution is to start considering the Moon. Therefore the dynamic range of the star sensor had to include the brighter stars in our galaxy and the very bright Moon. Ranges from magnitudes 1 to -13 need to be covered. In the lab we have shown that the dynamic range of the star sensor can include t ...
Quiz Chapter 10 Answers
... 10-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shifted into the infrared ...
... 10-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shifted into the infrared ...
Lecture 15, PPT version
... “Low-mass” stars: born with M < 2 Msun “Intermediate-mass” stars: born with 2 Msun < M < 8 Msun “High-mass” stars: born with M > 8 Msun Main Sequence lifetime of 0.2 Msun star = about 500 billion years Main Sequence lifetime of a 10 Msun star = about 100 million years ...
... “Low-mass” stars: born with M < 2 Msun “Intermediate-mass” stars: born with 2 Msun < M < 8 Msun “High-mass” stars: born with M > 8 Msun Main Sequence lifetime of 0.2 Msun star = about 500 billion years Main Sequence lifetime of a 10 Msun star = about 100 million years ...
Astronomy 112: Physics of Stars Problem set 2: Due April 29 1. Time
... 7. Polytropes: A neutron star is roughly describable as a polytrope of index 1. The radius of a typical neutron star of mass 1.4 solar masses is 10 km. What is its central density? The density of the atomic nucleus is 2.4 x 10**14 g cm−3 . Compare the value you computed to this number. Neutron stars ...
... 7. Polytropes: A neutron star is roughly describable as a polytrope of index 1. The radius of a typical neutron star of mass 1.4 solar masses is 10 km. What is its central density? The density of the atomic nucleus is 2.4 x 10**14 g cm−3 . Compare the value you computed to this number. Neutron stars ...
6.1 Sun - TeacherWeb
... A star is an object that produces its own energy including heat and light. o The planets and other objects in the solar system are not stars o They do not produce light. Sun is an averaged sized star. Larger stars produce ten million times more energy. Smaller stars produce 1 / 100th as much ene ...
... A star is an object that produces its own energy including heat and light. o The planets and other objects in the solar system are not stars o They do not produce light. Sun is an averaged sized star. Larger stars produce ten million times more energy. Smaller stars produce 1 / 100th as much ene ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... The ratio of the radii squared is 81, so the ratio of the radii must be 81 9 . The radius of the star in question is 9 times the radius of the Sun. A note is worthy here: We expected this star to be larger because it was the same temperature as the Sun, by quite a bit more luminous. What this prob ...
... The ratio of the radii squared is 81, so the ratio of the radii must be 81 9 . The radius of the star in question is 9 times the radius of the Sun. A note is worthy here: We expected this star to be larger because it was the same temperature as the Sun, by quite a bit more luminous. What this prob ...
The Life of a Star - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... • When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core • This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...
... • When the central temperature of a red giant reaches about 100 million K, helium fusion begins in the core • This process, also called the triple alpha process, converts helium to carbon and oxygen ...
Open Houses at the Campus Observatory Astronomical Horizons Lecture
... • Pressure is not greater at hotter temperature • Baseballs move because they are close together • Quantum mechanics: uncertainty relation • Speed × confinement = Planck’s constant • Pressure is greater if gas is confined to smaller region • In a smaller star, baseballs move faster • Baseballs hit w ...
... • Pressure is not greater at hotter temperature • Baseballs move because they are close together • Quantum mechanics: uncertainty relation • Speed × confinement = Planck’s constant • Pressure is greater if gas is confined to smaller region • In a smaller star, baseballs move faster • Baseballs hit w ...
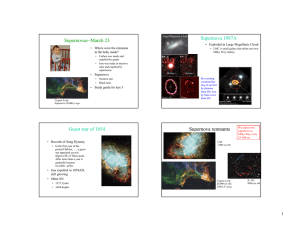
Supernovae March 23 − Supernova 1987A
... Degeneracy pressure prevents temperature from rising. Carbon burning. That is wrong; the sun will become a supernova. ...
... Degeneracy pressure prevents temperature from rising. Carbon burning. That is wrong; the sun will become a supernova. ...
A Stellar Astronomy Toolbox 9
... Where T is the temperature and k is the boltzman constant (k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K). So what is important here? The higher the average kinetic energy of a group of particles, the higher the temperature. They are directly proportional. Why does a stove burner feel hot? When a stove burner has a high tem ...
... Where T is the temperature and k is the boltzman constant (k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K). So what is important here? The higher the average kinetic energy of a group of particles, the higher the temperature. They are directly proportional. Why does a stove burner feel hot? When a stove burner has a high tem ...
Can you figure out which of the stars shown here have planets
... because it is one of the closest stars to Earth. There are actually two stars here -- one much larger and hotter than the Sun, and a much fainter "white dwarf" left over when a star like our sun used up its fuel and died. Sirius B was discovered over 150 years ago -- as it orbits around it makes Sir ...
... because it is one of the closest stars to Earth. There are actually two stars here -- one much larger and hotter than the Sun, and a much fainter "white dwarf" left over when a star like our sun used up its fuel and died. Sirius B was discovered over 150 years ago -- as it orbits around it makes Sir ...
How Bright is that star?
... Luminosity is the amount of energy a star gives off as light. Measured in Watts or Solar Units or “Sols” However for all practical purposes Absolute magnitude and Luminosity of a star measure the same thing. Absolute Magnitude Approximate Luminosity ...
... Luminosity is the amount of energy a star gives off as light. Measured in Watts or Solar Units or “Sols” However for all practical purposes Absolute magnitude and Luminosity of a star measure the same thing. Absolute Magnitude Approximate Luminosity ...
April
... Average distance from the Sun – 900 million miles Current distance from Earth – 800 million miles Diameter is approximately 65,000 miles at the poles, and 72,000 miles at the equator. Why the difference? Average rotation period is 10 – 11 hours. Orbital period around the Sun is 29.5 years. Saturn ha ...
... Average distance from the Sun – 900 million miles Current distance from Earth – 800 million miles Diameter is approximately 65,000 miles at the poles, and 72,000 miles at the equator. Why the difference? Average rotation period is 10 – 11 hours. Orbital period around the Sun is 29.5 years. Saturn ha ...