Star Life Cycle – Web Activity
... For today’s activity, you will need to visit http://aspire.cosmic-ray.org/Labs/StarLife/starlife_main.html Read the first page (don’t click on any of the “Table of Contents” items) and click on the arrow in the bottom right corner when you are finished. Below you will find questions and directions t ...
... For today’s activity, you will need to visit http://aspire.cosmic-ray.org/Labs/StarLife/starlife_main.html Read the first page (don’t click on any of the “Table of Contents” items) and click on the arrow in the bottom right corner when you are finished. Below you will find questions and directions t ...
Star Fromation and ISM
... The Formation of Stars Like the Sun At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature, until it is in equilibrium. This is stage 7: the star has reached the main sequence and will remain ...
... The Formation of Stars Like the Sun At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature, until it is in equilibrium. This is stage 7: the star has reached the main sequence and will remain ...
Deaths of Stars - Chabot College
... “Two particles cannot occupy same space with same momentum (energy)” ...
... “Two particles cannot occupy same space with same momentum (energy)” ...
Masses are much harder than distance, luminosity, or temperature
... distance, luminosity, or temperature • Since we are only ever seeing a point source, it is hard to determine how much mass is contained. ...
... distance, luminosity, or temperature • Since we are only ever seeing a point source, it is hard to determine how much mass is contained. ...
l rest
... EMR and matter interact all the time This means that matter absorbs and emits EMR Often, the means of interaction is the acceleration of an electron. But this is not the only way, and other ways are possible. The details are not crucial now As long as there is a strong interaction, matter and EMR ca ...
... EMR and matter interact all the time This means that matter absorbs and emits EMR Often, the means of interaction is the acceleration of an electron. But this is not the only way, and other ways are possible. The details are not crucial now As long as there is a strong interaction, matter and EMR ca ...
The Properties of Stars
... Usually, the spectrum will show two sets of lines that change positions as the stars move along their orbits. In the following figures, wavelength increases toward the right and only the hydrogen Balmer lines are shown. In each case, the Balmer lines observed in the laboratory are displayed on the b ...
... Usually, the spectrum will show two sets of lines that change positions as the stars move along their orbits. In the following figures, wavelength increases toward the right and only the hydrogen Balmer lines are shown. In each case, the Balmer lines observed in the laboratory are displayed on the b ...
The Lives of Stars
... neutron stars produce novae and bursters • Material from an ordinary star in a close binary can fall onto the surface of the companion white dwarf or neutron star to produce a surface layer in which thermonuclear reactions can explosively ignite • Explosive hydrogen fusion may occur in the surface l ...
... neutron stars produce novae and bursters • Material from an ordinary star in a close binary can fall onto the surface of the companion white dwarf or neutron star to produce a surface layer in which thermonuclear reactions can explosively ignite • Explosive hydrogen fusion may occur in the surface l ...
doc - Eu-Hou
... realize something: the furthest ones appear less bright than expected! At the same time, the two teams realized that only a Universe in accelerated expansion can explain this effect, and published their results in scientific papers. Their discovery implied that the Universe was filled by an energy t ...
... realize something: the furthest ones appear less bright than expected! At the same time, the two teams realized that only a Universe in accelerated expansion can explain this effect, and published their results in scientific papers. Their discovery implied that the Universe was filled by an energy t ...
Star Formation
... • Without CO molecules to provide cooling, the clouds that formed the first stars had to be considerably warmer than today’s molecular clouds • The first stars must therefore have been more massive than most of today’s stars, for gravity to overcome ...
... • Without CO molecules to provide cooling, the clouds that formed the first stars had to be considerably warmer than today’s molecular clouds • The first stars must therefore have been more massive than most of today’s stars, for gravity to overcome ...
Formation of Stars
... • The interstellar medium is not uniform, but varies by large factors in density and temperature. • The clumps in the interstellar medium are clouds or nebulae (one nebula, two nebulae). • Three types of nebulae: – Emission nebulae: photons strike atoms and excite electrons to higher energy levels, ...
... • The interstellar medium is not uniform, but varies by large factors in density and temperature. • The clumps in the interstellar medium are clouds or nebulae (one nebula, two nebulae). • Three types of nebulae: – Emission nebulae: photons strike atoms and excite electrons to higher energy levels, ...
Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam
... List in chronological order the mechanisms of energy production in Sun-like stars. List in chronological order the stages of evolution in Sun-like stars. ...
... List in chronological order the mechanisms of energy production in Sun-like stars. List in chronological order the stages of evolution in Sun-like stars. ...
bright - TutorPlus
... The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram • Between 1911 and 1913, two astronomers – one Danish (Ejnar Hertzsprung) and one American (Henry Russell) – independently developed a diagram to show the relationship between the luminosity or absolute magnitude of a star and its surface temperature as deduced ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram • Between 1911 and 1913, two astronomers – one Danish (Ejnar Hertzsprung) and one American (Henry Russell) – independently developed a diagram to show the relationship between the luminosity or absolute magnitude of a star and its surface temperature as deduced ...
Death of the Stars
... But when this particle – antiparticle pair creation occurs right along the boundary of the event horizon, one of the pair might be caught by the black hole whereas other one escapes and can be observed by outside sources. ...
... But when this particle – antiparticle pair creation occurs right along the boundary of the event horizon, one of the pair might be caught by the black hole whereas other one escapes and can be observed by outside sources. ...
Galaxies Galaxies M81
... the Milky Way located about 180,000 light years from the sun. The LMC is about 60,000 light years across. The bright reddish feature in the upper right is the “Tarantula Nebula” a region of star formation in the LMC. (NOAO/AURA Photo) ...
... the Milky Way located about 180,000 light years from the sun. The LMC is about 60,000 light years across. The bright reddish feature in the upper right is the “Tarantula Nebula” a region of star formation in the LMC. (NOAO/AURA Photo) ...
ASTR120 Homework 6 − Solutions
... a. Since Enceladus and Dione have a 1 : 2 ratio of orbital periods, the time between successive oppositions would be the orbital period of Dione -- 65.7 hours b. For this part, we want to use the small angle formula. According to the text, the linear diameter of Dione is 1.0 x 106 m. Enceladus is 2. ...
... a. Since Enceladus and Dione have a 1 : 2 ratio of orbital periods, the time between successive oppositions would be the orbital period of Dione -- 65.7 hours b. For this part, we want to use the small angle formula. According to the text, the linear diameter of Dione is 1.0 x 106 m. Enceladus is 2. ...
Star Birth: The Formation of Stars Jonathan Rowles
... A star is a luminous ball of gas. They produce energy by the nuclear fusion of hydrogen to form helium. They range in size from 0.08 times the mass of the Sun to up to 120 Solar masses. They can have lifetimes ranging from a few million years to the age of the universe. ...
... A star is a luminous ball of gas. They produce energy by the nuclear fusion of hydrogen to form helium. They range in size from 0.08 times the mass of the Sun to up to 120 Solar masses. They can have lifetimes ranging from a few million years to the age of the universe. ...
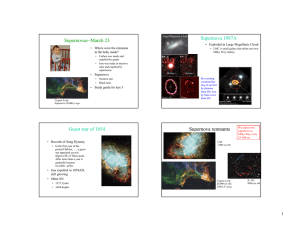
Supernovae March 23 − Supernova 1987A
... Pre-existing circumstellar ring lit up first by photons from SN, now by blast wave from SN. ...
... Pre-existing circumstellar ring lit up first by photons from SN, now by blast wave from SN. ...
Life Histories Of Some Stars
... In this activity, you can see that the very massive stars live much shorted “lives” compared to the smaller, less massive stars. Why is that? Large stars, like all stars, form inside giant gaseous nebulae. An example of such a nebula is the Great Nebula in Orion (see photo). Inside nebulae, particle ...
... In this activity, you can see that the very massive stars live much shorted “lives” compared to the smaller, less massive stars. Why is that? Large stars, like all stars, form inside giant gaseous nebulae. An example of such a nebula is the Great Nebula in Orion (see photo). Inside nebulae, particle ...
Physics-Y11-LP3 - All Saints` Catholic High School
... • describe and explain the processes that take place in a star • explain why the core of a star is where most nuclear fusion takes place • explain how energy is transported from core to surface • describe how energy is radiated into space from the star’s surface • explain the theory of formation of ...
... • describe and explain the processes that take place in a star • explain why the core of a star is where most nuclear fusion takes place • explain how energy is transported from core to surface • describe how energy is radiated into space from the star’s surface • explain the theory of formation of ...
88K PDF file
... A lot of you overstated the situation. I didn’t take off for this if you got the basic point that the gas which has gone through stars will have more Helium. Some of you, however, stated that all of the Hydrogen would be converted to Helium. This is not correct; as I mentioned in class, at its curre ...
... A lot of you overstated the situation. I didn’t take off for this if you got the basic point that the gas which has gone through stars will have more Helium. Some of you, however, stated that all of the Hydrogen would be converted to Helium. This is not correct; as I mentioned in class, at its curre ...