* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics-Y11-LP3 - All Saints` Catholic High School
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
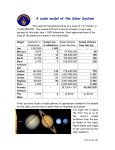
All Saints’ Catholic High School & Specialist Language College Learning Programme 1 (LP1) Subject: P7.1 Year group: 11 During this half term I will be learning … LP 4/ 1 LP4 Homework Research Based HW • recall that Cepheid variable stars pulse in brightness, with a period related to their luminosity • recall that and explain qualitatively how this relationship enables astronomers to estimate the distance to Cepheid variable stars • understand the role of observations of Cepheid variable stars in establishing the scale of the Universe and the nature of most spiral nebulas as distant galaxies • describe some of the new information that telescopes revealed about the Milky Way and objects beyond the Milky Way • recall the main issue in the Curtis–Shapley debate • recall that Hubble’s observations of Cepheid variables in one spiral nebula indicated that it was much further away than any star in the Milky Way, and so he concluded that this nebula was a separate galaxy LP4/2 • calculate distances in parsecs from values in light years and angles of parallax • appreciate that typical interstellar distances are a few parsecs Revision tasks • calculate distances in parsecs from values in light years and angles of parallax • appreciate that typical interstellar distances are a few parsecs LP4/3 • explain how data about supernovae can be used to estimate distances to other galaxies • use data to plot a graph of velocity against distance and get a value of the Hubble constant • appreciate that, as new data is collected, the value for the Hubble constant is reviewed • use a spreadsheet to make charts and analyse data • explain that observations support the big bang theory • H: explain that observations suggest that space is expanding Exam questions All Saints’ Catholic High School & Specialist Language College Learning Programme 1 (LP1) LP4/4 • describe how all hot objects (including stars) emit a continuous range of electromagnetic radiation, whose luminosity and peak frequency increases with temperature Research Based HW • describe how specific spectral lines in the spectrum of a star provide evidence of the chemical elements present in it • use data on the spectrum of a star, together with data on the line spectra of elements, to identify elements present in it LP4/5 Revision tasks • recall that the removal of electrons from atoms is called ionisation • explain how electron energy levels within atoms give rise to line spectra • describe how hydrogen nuclei can fuse to produce helium nuclei and release energy • show how the process of nuclear fusion can provide an explanation for the Sun’s energy source • H: explain how Einstein’s equation E = mc2 is used to calculate the energy released during nuclear Fusion • describe how specific spectral lines in the spectrum of a star provide evidence of the chemical elements present in it • use data on the spectrum of a star, together with data on the line spectra of elements, to identify elements present in it LP4/6 Exam questions All Saints’ Catholic High School & Specialist Language College Learning Programme 1 (LP1) • use the kinetic theory of gases to explain why the Exam style questions pressure of a fixed mass of gas increases when the volume is reduced, if its temperature is constant • use the relationship P x V = constant • recall that –273 °C is the absolute zero of temperature • be able to convert temperatures in K to temperatures in °C (and vice versa) • describe and explain the processes that take place in a star • explain why the core of a star is where most nuclear fusion takes place • explain how energy is transported from core to surface • describe how energy is radiated into space from the star’s surface LP4/7 • describe and explain the processes that take place in a star • explain why the core of a star is where most nuclear fusion takes place • explain how energy is transported from core to surface • describe how energy is radiated into space from the star’s surface • explain the theory of formation of red giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs • explain what a supernova is and what a neutron star is and look at examples • explain what a black hole is, how it is formed, and look at evidence of their existence • how nuclei with masses greater those of than iron are formed in a supernova explosion All Saints’ Catholic High School & Specialist Language College Learning Programme 1 (LP1) LP1/3 o LP 1 4 5 6 7 8 Data task