* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download bright - TutorPlus
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Hayashi track wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
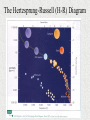
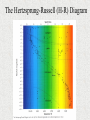
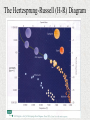
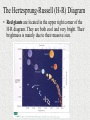
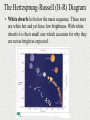
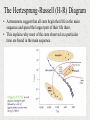
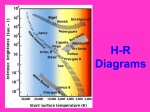
Properties of Stars Brightness of Stars • The brightness of a star observed by us depends upon – The distance of a star – The actual amount of light given off by the star (its energy) • How bright a star appears to us is called its apparent magnitude. • The actual total radiant energy given off by a star is called its luminosity and is sometimes referred to as the absolute magnitude. Brightness of Stars • The brightness of stars as viewed from Earth is often measured using the apparent magnitude scale. • The smaller the value, the brighter the star. • The Sun has a value of -27. A full moon has value -13. Star colours and Temperature • Stars come in all colours, from dull red, through orange, yellow and white to blue. • There is a direct relationship between a star’s surface temperature and its colour. Star colours and Temperature • The largest stars are the red giants – which can be hundreds of times the diameter of the sun. Betelgeuse is a red giant. • The smallest stars are white dwarfs and are about the size of Earth. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram • Between 1911 and 1913, two astronomers – one Danish (Ejnar Hertzsprung) and one American (Henry Russell) – independently developed a diagram to show the relationship between the luminosity or absolute magnitude of a star and its surface temperature as deduced from its colour. • The diagram is called the Hertzsprung-Russell or H-R diagram and is used extensively by astronomers. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram • Stars can be classified into characteristic types depending on their position on the H-R diagram. • Most stars line up along a slightly curved diagonal line called the main sequence. Our Sun is located on the main sequence. • On the main sequence, low mass stars tend to be cooler and less bright whereas high mass stars are hotter, brighter and located at the top of the sequence. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram • Red giants are located in the upper right corner of the H-R diagram. They are both cool and very bright. Their brightness is mainly due to their massive size. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram • White dwarfs lie below the main sequence. These stars are white hot and yet have low brightness. With white dwarfs it is their small size which accounts for why they are not as bright as expected. The Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram • Astronomers suggest that all stars begin their life in the main sequence and spend the largest part of their life there. • This explains why most of the stars observed at a particular time are found in the main sequence.