ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes - Faculty
... Type Ib supernovae display strong helium lines. These tyeps of supernovae are only seen in the arms of spiral galaxies near star forming regions. Hence, this implied that short-lived massive stars in binary systems are probably involved. These explosions are similar to that of a Type II supernova, o ...
... Type Ib supernovae display strong helium lines. These tyeps of supernovae are only seen in the arms of spiral galaxies near star forming regions. Hence, this implied that short-lived massive stars in binary systems are probably involved. These explosions are similar to that of a Type II supernova, o ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy - University of Texas Astronomy
... made of) were made in the big bang. Many of the helium atoms in the Universe were also made in the big bang. The other atoms were made inside of stars or during explosions of stars. When the Sun becomes a red giant, carbon and maybe oxygen will be made in its core. But the core will be the left-over ...
... made of) were made in the big bang. Many of the helium atoms in the Universe were also made in the big bang. The other atoms were made inside of stars or during explosions of stars. When the Sun becomes a red giant, carbon and maybe oxygen will be made in its core. But the core will be the left-over ...
Refuges for Life in a - University of Arizona
... (which extends halfway to the nearest star). Other stars probably have similar retinues. Infrared observations of young nearby stars indicate that most are surrounded by excess dust, consistent with the presence of Kuiper-belt objects. More recently, detection of water vapor around the highly evolve ...
... (which extends halfway to the nearest star). Other stars probably have similar retinues. Infrared observations of young nearby stars indicate that most are surrounded by excess dust, consistent with the presence of Kuiper-belt objects. More recently, detection of water vapor around the highly evolve ...
3 Exam #1
... 9. State Kepler’s laws and the implication to each. 10. Explain how you would determine mass of the sun. 11. What is escape speed? What is light, how do atoms produce light, and what does light reveal about astronomical bodies? 12. Describe the structure of a typical atom, and explain the rules whic ...
... 9. State Kepler’s laws and the implication to each. 10. Explain how you would determine mass of the sun. 11. What is escape speed? What is light, how do atoms produce light, and what does light reveal about astronomical bodies? 12. Describe the structure of a typical atom, and explain the rules whic ...
The galactic metallicity gradient Martín Hernández, Nieves Leticia
... in the life of a star is called main sequence. Once the supply of hydrogen is exhausted, the star becomes cooler, larger, and more luminous. Stars like our Sun will eventually eject their outer layers, creating planetary nebulae, and contract to become a white dwarf; highmass stars will die violentl ...
... in the life of a star is called main sequence. Once the supply of hydrogen is exhausted, the star becomes cooler, larger, and more luminous. Stars like our Sun will eventually eject their outer layers, creating planetary nebulae, and contract to become a white dwarf; highmass stars will die violentl ...
Powerpoint
... •Luminosity up the vertical axis (measured relative to the Sun) •Temperature along the horizontal axis (measured in Kelvin) The stars Vega and Sirius are brighter than the Sun, and also hotter. Where would you put them? Where would you mark the Sun on the plot? ...
... •Luminosity up the vertical axis (measured relative to the Sun) •Temperature along the horizontal axis (measured in Kelvin) The stars Vega and Sirius are brighter than the Sun, and also hotter. Where would you put them? Where would you mark the Sun on the plot? ...
Star in a Box - Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope
... •Luminosity up the vertical axis (measured relative to the Sun) •Temperature along the horizontal axis (measured in Kelvin) The stars Vega and Sirius are brighter than the Sun, and also hotter. Where would you put them? Where would you mark the Sun on the plot? ...
... •Luminosity up the vertical axis (measured relative to the Sun) •Temperature along the horizontal axis (measured in Kelvin) The stars Vega and Sirius are brighter than the Sun, and also hotter. Where would you put them? Where would you mark the Sun on the plot? ...
Cosmic future of nuclear and particle physics
... Cosmic and human made accelerators Where do the cosmic rays come from? Some of them come from the Sun and other stars. However, these are rather soft. High energy particles are produced in more violent environment such as supernovae explosions, gamma ray bursts, active galaxy nuclei, microquasars, p ...
... Cosmic and human made accelerators Where do the cosmic rays come from? Some of them come from the Sun and other stars. However, these are rather soft. High energy particles are produced in more violent environment such as supernovae explosions, gamma ray bursts, active galaxy nuclei, microquasars, p ...
SPA 302: THE EVOLUTION OF STARS LECTURE 1: BASICS OF
... Man's intrigues about the stars has over the years grown immensely and crystallized into a solid physical theory that provides scientists with a frame of reference on which to interpret many aspects about our Universe. Stars- the hot spherical balls of burning gas that light up the night sky- come i ...
... Man's intrigues about the stars has over the years grown immensely and crystallized into a solid physical theory that provides scientists with a frame of reference on which to interpret many aspects about our Universe. Stars- the hot spherical balls of burning gas that light up the night sky- come i ...
Stellar Evolution
... to type II and Ib, only difference is whether or not star sheds outer hydrogen layer before exploding ...
... to type II and Ib, only difference is whether or not star sheds outer hydrogen layer before exploding ...
Astronomy in 1936 The History of the Universe
... Ωlp calculated from rotation curve for Milky Way. ...
... Ωlp calculated from rotation curve for Milky Way. ...
HR Diagram Lab Handout
... Brightness: the number of times brighter the star is than our Sun (a fractions means it is dimmer than our Sun) Expected Lifetime: the number of years the star is expected to exist based on color and brightness Getting Started: Making the HR Diagram 1. Hand out the “stars” to each member of your ...
... Brightness: the number of times brighter the star is than our Sun (a fractions means it is dimmer than our Sun) Expected Lifetime: the number of years the star is expected to exist based on color and brightness Getting Started: Making the HR Diagram 1. Hand out the “stars” to each member of your ...
Nobel Prize in Physics 2002: Riccardo Giaconni
... firm conclusions about the X-ray background glow of the Universe - which was one of Giaconni's initial discoveries - but it is believed that it was produced about ten billion years ago. When the homogeneously distributed gas in the early Universe formed clumps to collapse into galaxies, the radiatio ...
... firm conclusions about the X-ray background glow of the Universe - which was one of Giaconni's initial discoveries - but it is believed that it was produced about ten billion years ago. When the homogeneously distributed gas in the early Universe formed clumps to collapse into galaxies, the radiatio ...
Where to Look: Habitable Zones
... Fred Hoyle: “The chance that higher life forms might have emerged in this way is comparable to the chance that a tornado sweeping through a junkyard might assemble a Boeing 747 from the materials therein.” ...
... Fred Hoyle: “The chance that higher life forms might have emerged in this way is comparable to the chance that a tornado sweeping through a junkyard might assemble a Boeing 747 from the materials therein.” ...
ASTRONOMY 120
... How do astronomers test the theory of stellar evolution? (3 points) Stars change so slowly over time, that we have no hope of observing the changes they go through directly in a human lifetime or even in all of human history. However, we have a galaxy full of many stars at different stages of develo ...
... How do astronomers test the theory of stellar evolution? (3 points) Stars change so slowly over time, that we have no hope of observing the changes they go through directly in a human lifetime or even in all of human history. However, we have a galaxy full of many stars at different stages of develo ...
White Dwarfs and the age of the Universe
... • if we know the temperature and luminosity of a white dwarf, we know its size • if we know temperature, luminosity, and size now, we know the rate at which it is cooling today ...
... • if we know the temperature and luminosity of a white dwarf, we know its size • if we know temperature, luminosity, and size now, we know the rate at which it is cooling today ...
ASTROPHYSICS UNIVERSE - Physics
... of their life cycles. In these stars, there is less hydrogen fusion occurring in the core. The reduced fusion leads to reduced radiation pressure from the core and leads to gravitational collapse (within the core). The core then starts to fuse Helium, and fusion that is still occurring happens in a ...
... of their life cycles. In these stars, there is less hydrogen fusion occurring in the core. The reduced fusion leads to reduced radiation pressure from the core and leads to gravitational collapse (within the core). The core then starts to fuse Helium, and fusion that is still occurring happens in a ...
Assignment 8 - utoledo.edu
... c. planetary nebulae expand rapidly and soon become too faint to be visible d. planetary nebulae quickly fall back onto the star produced them e. while most stars are lowmass when they are born, throughout their lives they gather more and more material; so few stars are lowmass when they die ____ ...
... c. planetary nebulae expand rapidly and soon become too faint to be visible d. planetary nebulae quickly fall back onto the star produced them e. while most stars are lowmass when they are born, throughout their lives they gather more and more material; so few stars are lowmass when they die ____ ...
T Einstein’s Mirage Paul L. Schechter
... to be a close pair of virtually identical quasars was observed. Quasars are very bright distant sources, so light from them sometimes passes near galaxies on its way to us. The suspicion that they were the multiple images of a single quasar expected for a gravitational mirage was confirmed Perhaps t ...
... to be a close pair of virtually identical quasars was observed. Quasars are very bright distant sources, so light from them sometimes passes near galaxies on its way to us. The suspicion that they were the multiple images of a single quasar expected for a gravitational mirage was confirmed Perhaps t ...
Interstellar medium, birth and life of stars
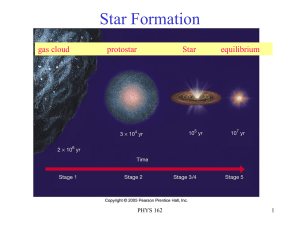
... In the final stages of pre–main-sequence contraction, when hydrogen fusion is about to begin in the core, the pre–main-sequence star may undergo vigorous chromospheric activity that ejects large amounts of matter into space. G, K, and M stars at this stage are called T Tauri stars. A collection ...
... In the final stages of pre–main-sequence contraction, when hydrogen fusion is about to begin in the core, the pre–main-sequence star may undergo vigorous chromospheric activity that ejects large amounts of matter into space. G, K, and M stars at this stage are called T Tauri stars. A collection ...
What does X-ray light show us?
... produced by the hottest regions of the universe. They are also produced by such violent events as supernova explosions or the destruction of atoms, and by less dramatic events, such as the decay of radioactive material in space. Things like supernova explosions (the way massive stars die), neutron s ...
... produced by the hottest regions of the universe. They are also produced by such violent events as supernova explosions or the destruction of atoms, and by less dramatic events, such as the decay of radioactive material in space. Things like supernova explosions (the way massive stars die), neutron s ...
Lecture 15 Star Formation and Evolution 3/7
... • test out model of stellar evolution using Star Clusters • HR diagram of a cluster gives “snapshot” of stars with the same age but different masses • Birth Main Sequence Red Giant “live+die” faster if higher mass • tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...
... • test out model of stellar evolution using Star Clusters • HR diagram of a cluster gives “snapshot” of stars with the same age but different masses • Birth Main Sequence Red Giant “live+die” faster if higher mass • tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...