June 2017
... expected that hotter (bluer) stars are more luminous. However, there are exceptions, such as the Red Giants (for example, Betelgeuse) and White Dwarf stars. Giant stars have diameters many 70 times that of the Sun. The diagonal band is called the Main Sequence but must not be seen as an evolutionary ...
... expected that hotter (bluer) stars are more luminous. However, there are exceptions, such as the Red Giants (for example, Betelgeuse) and White Dwarf stars. Giant stars have diameters many 70 times that of the Sun. The diagonal band is called the Main Sequence but must not be seen as an evolutionary ...
The classification of stellar spectra
... the MAIN SEQUENCE, with increasing L as T increases - a relatively cool star can be quite luminous if it has a large enough radius (10-100 R): RED GIANTS and SUPERGIANTS - a relatively hot star can have very low luminosity, if its radius is very small (0.01 R): WHITE DWARFS ...
... the MAIN SEQUENCE, with increasing L as T increases - a relatively cool star can be quite luminous if it has a large enough radius (10-100 R): RED GIANTS and SUPERGIANTS - a relatively hot star can have very low luminosity, if its radius is very small (0.01 R): WHITE DWARFS ...
Assignment 7 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... ____ 19. Stars that do not have what it takes to succeed as a star (i.e. do not have enough mass to fuse hydrogen into helium at their centers) are called: a. extras b. red giants c. spectroscopic stars d. brown dwarfs e. main sequence stars ____ 20. Which of the following has the smallest mass? a ...
... ____ 19. Stars that do not have what it takes to succeed as a star (i.e. do not have enough mass to fuse hydrogen into helium at their centers) are called: a. extras b. red giants c. spectroscopic stars d. brown dwarfs e. main sequence stars ____ 20. Which of the following has the smallest mass? a ...
Draft Science Cases for KPAO
... coronographs. Being critically sampled is crucial and with 120nm rms error, the Strehl ratio will be 0.89 at K band, 0.81 at H band and 0.70 at J band (see Figure 2: Predicted KPAO Strehlfor different rms wavefront error goals.). Assuming a NIR imager extends down to 1 micron, then the required pixe ...
... coronographs. Being critically sampled is crucial and with 120nm rms error, the Strehl ratio will be 0.89 at K band, 0.81 at H band and 0.70 at J band (see Figure 2: Predicted KPAO Strehlfor different rms wavefront error goals.). Assuming a NIR imager extends down to 1 micron, then the required pixe ...
Chapter 17 Star Stuff
... • This double-shell burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses ...
... • This double-shell burning stage never reaches equilibrium—fusion rate periodically spikes upward in a series of thermal pulses ...
Chapter 17 Star Stuff How does a star`s mass affect nuclear fusion
... Stellar Mass and Fusion • The mass of a main sequence star determines its core pressure and temperature • Stars of higher mass have higher core temperature and more rapid fusion, making those stars both more luminous and shorter-lived • Stars of lower mass have cooler cores and slower fusion rates, ...
... Stellar Mass and Fusion • The mass of a main sequence star determines its core pressure and temperature • Stars of higher mass have higher core temperature and more rapid fusion, making those stars both more luminous and shorter-lived • Stars of lower mass have cooler cores and slower fusion rates, ...
Educator`s Guide for Dark Star Adventure
... 2. Bring a ball to the edge of that table and let the ball drop. Have students notice the path and landing point of the ball (it should fall directly below the edge of the table) on the chart paper. 3. Push the ball so that it slowly rolls across the table and let it drop. Have students notice the p ...
... 2. Bring a ball to the edge of that table and let the ball drop. Have students notice the path and landing point of the ball (it should fall directly below the edge of the table) on the chart paper. 3. Push the ball so that it slowly rolls across the table and let it drop. Have students notice the p ...
HR Diagram - TeacherWeb
... 3. Classify: Click Move all and then Sort stars. Click the Tools palette at lower left and click Screen shot. Right click the image, click Copy Image, and paste a screenshot of the diagram in a blank document that you will turn in with this worksheet. Circle stars that you think belong in a group to ...
... 3. Classify: Click Move all and then Sort stars. Click the Tools palette at lower left and click Screen shot. Right click the image, click Copy Image, and paste a screenshot of the diagram in a blank document that you will turn in with this worksheet. Circle stars that you think belong in a group to ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
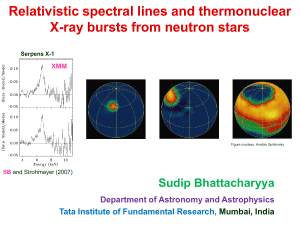
Broad Relativistic Iron Lines from Neutron Star LMXBs
... These lines are nature-given tool to measure the black hole spin and to probe the strong gravity regime. ...
... These lines are nature-given tool to measure the black hole spin and to probe the strong gravity regime. ...
Nucleosynthesis and the death of stars
... Hotter fusion and heavier elements • Could stars in principle live forever simply by contracting gravitationally and increasing their temperature to ignite the next heavier source of nuclear fuel whenever they run out? – No. The strong interaction’s range is smaller than the diameters of all but th ...
... Hotter fusion and heavier elements • Could stars in principle live forever simply by contracting gravitationally and increasing their temperature to ignite the next heavier source of nuclear fuel whenever they run out? – No. The strong interaction’s range is smaller than the diameters of all but th ...
On the nature of early-type emission line objects in NGC6611
... Herbig & Dahm (2001) only found a small number of these. It is however worth noticing that the two first studies were carried out using slit spectrographs, while Herbig & Dahm (2001) used a slitless instrument not sensitive to the surrounding emission originating from the Eagle nebula. In order to f ...
... Herbig & Dahm (2001) only found a small number of these. It is however worth noticing that the two first studies were carried out using slit spectrographs, while Herbig & Dahm (2001) used a slitless instrument not sensitive to the surrounding emission originating from the Eagle nebula. In order to f ...
5 – Stellar Structure I
... For our stars – which are isolated, static, and spherically symmetric – there are four basic equations to describe structure. All physical quantities depend on the distance from the center of the star alone 1) Equation of hydrostatic equilibrium: at each radius, forces due to pressure differences b ...
... For our stars – which are isolated, static, and spherically symmetric – there are four basic equations to describe structure. All physical quantities depend on the distance from the center of the star alone 1) Equation of hydrostatic equilibrium: at each radius, forces due to pressure differences b ...
A new low proper motion catalogue of bright M
... Low mass stars have become of interest in recent years for their applications to exoplanet research especially because of their unique properties of having short orbital periods for planets lying in the habitable zone as well as favourable contrast ratios between the planet and the host star. Though ...
... Low mass stars have become of interest in recent years for their applications to exoplanet research especially because of their unique properties of having short orbital periods for planets lying in the habitable zone as well as favourable contrast ratios between the planet and the host star. Though ...
what are stars made of?
... Stars begin their lives as main sequence stars. They burn hydrogen in their cores, creating nuclear fusion. Some of these stars are average in size and some are huge. Main sequence stars are grouped by astronomers according to the colours they give out. Stars that look blue and white are the hottest ...
... Stars begin their lives as main sequence stars. They burn hydrogen in their cores, creating nuclear fusion. Some of these stars are average in size and some are huge. Main sequence stars are grouped by astronomers according to the colours they give out. Stars that look blue and white are the hottest ...
Stellar Astrophysics: Introduction Q. Daniel Wang Astronomy Department University of Massachusetts
... where M is any constant. We then obtain, for example, M αr −1 ...
... where M is any constant. We then obtain, for example, M αr −1 ...
Lec09_ch11_lifecycleofstars
... prevents further collapse (or must wait until nebula cools) – If nebula cool enough, Jeans instability allows gravity to overtake thermal energy ...
... prevents further collapse (or must wait until nebula cools) – If nebula cool enough, Jeans instability allows gravity to overtake thermal energy ...
Pre-Final Quiz Answers
... In the mid-1970s, Vera Rubin discovered that stars orbiting around galaxies did not show orbital speeds that corresponded to the expectation of a Newtonian gravitational rule. Her work confirmed what new understanding of the character of galaxies? Galaxies contain more interior mass than we can see; ...
... In the mid-1970s, Vera Rubin discovered that stars orbiting around galaxies did not show orbital speeds that corresponded to the expectation of a Newtonian gravitational rule. Her work confirmed what new understanding of the character of galaxies? Galaxies contain more interior mass than we can see; ...
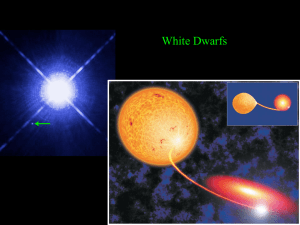
Whiteq
... mass of the sun. However, it is believed that the progenitor star can be as much as 4 times as massive as the sun, because during the end of their nuclear fuel burning stage most stars eject a large portion of their mass. In the case of low mass stars, this leads to a planetary nebula. A small minor ...
... mass of the sun. However, it is believed that the progenitor star can be as much as 4 times as massive as the sun, because during the end of their nuclear fuel burning stage most stars eject a large portion of their mass. In the case of low mass stars, this leads to a planetary nebula. A small minor ...