The Zodiac - Alchemical.org
... ground. The Greeks first saw Cancer as a Turtle, then later as a crab. This constellation was first associated with the Sun on the Summer Solstice. It was later associated with the Moon in Alexander the Great’s time. ...
... ground. The Greeks first saw Cancer as a Turtle, then later as a crab. This constellation was first associated with the Sun on the Summer Solstice. It was later associated with the Moon in Alexander the Great’s time. ...
Beers_First_Stars_NIC_School
... Abstract: Numerical simulations of structure formation in the early Universe predict the formation of some fraction of stars with masses several hundred times the solar mass. No clear evidence of supernovae from such supermassive stars has, however, yet been found in the chemical compositions of Mil ...
... Abstract: Numerical simulations of structure formation in the early Universe predict the formation of some fraction of stars with masses several hundred times the solar mass. No clear evidence of supernovae from such supermassive stars has, however, yet been found in the chemical compositions of Mil ...
Document
... thus, at a certain point, the newly forming object becomes visible. At this stage the large luminous body is called a protostar. The other half of its gravitational energy remains within the protostar as heat. As contraction continues, the internal temperature of the protostar keeps rising, and when ...
... thus, at a certain point, the newly forming object becomes visible. At this stage the large luminous body is called a protostar. The other half of its gravitational energy remains within the protostar as heat. As contraction continues, the internal temperature of the protostar keeps rising, and when ...
key for the HR Diagram Lab Handout
... Geminorum have brightness of 9,000 Suns and 310 Suns respectively; these stars are much larger than Proxima and Barnard s with brightness of 0.00005 and 0.0003 Suns. The significant difference in brightness with no change in temperature means that Betelgeuse and Mu Geminorum are much larger than the ...
... Geminorum have brightness of 9,000 Suns and 310 Suns respectively; these stars are much larger than Proxima and Barnard s with brightness of 0.00005 and 0.0003 Suns. The significant difference in brightness with no change in temperature means that Betelgeuse and Mu Geminorum are much larger than the ...
Science Olympiad 2008 Reach for the Stars Division B
... full moon. It would also be about as bright as the full moon. 96. What event marks the beginning of a supernova? A) the onset of helium burning after a helium flash in a star with mass comparable to that of the Sun B) the sudden outpouring of X rays from a newly formed accretion disk C) the sudden c ...
... full moon. It would also be about as bright as the full moon. 96. What event marks the beginning of a supernova? A) the onset of helium burning after a helium flash in a star with mass comparable to that of the Sun B) the sudden outpouring of X rays from a newly formed accretion disk C) the sudden c ...
5 Understanding stars and star ClUsters
... with a negative charge that orbit the atomic nucleus. Electrons must always move in distinct orbit levels. If the electron moves to the next lower orbit it loses energy and spits out a light particle (photon) of a specific color (energy). Each different atom has different color photons, which are em ...
... with a negative charge that orbit the atomic nucleus. Electrons must always move in distinct orbit levels. If the electron moves to the next lower orbit it loses energy and spits out a light particle (photon) of a specific color (energy). Each different atom has different color photons, which are em ...
Practice Exam for 3 rd Astronomy Exam
... OB Association In the Milky Way Galaxy there are very many Giant Molecular Clouds (GMC). A typical GMC contains most hydrogen and helium gas and microscopic solid particles of ice and rocky material known collectively as “dust”. The typical GMC may be 300 ly in diameter and encompass 300,000 solar m ...
... OB Association In the Milky Way Galaxy there are very many Giant Molecular Clouds (GMC). A typical GMC contains most hydrogen and helium gas and microscopic solid particles of ice and rocky material known collectively as “dust”. The typical GMC may be 300 ly in diameter and encompass 300,000 solar m ...
DTU9ePPTChap13 - Faculty Lounge : Astronomy
... (a) Intense radiation from the supernova explosion caused three rings of gas surrounding SN 1987A to glow in this HST image. This gas was ejected from the star 20,000 years before the star detonated. All three rings lie in parallel planes. The inner ring is about 1.3 ly across. The white and colored ...
... (a) Intense radiation from the supernova explosion caused three rings of gas surrounding SN 1987A to glow in this HST image. This gas was ejected from the star 20,000 years before the star detonated. All three rings lie in parallel planes. The inner ring is about 1.3 ly across. The white and colored ...
Notes 6 - University of Northern Iowa
... can be used to directly test computer models of not only the evolutionary paths of stars but also stellar pulsation models. But not all stars in this phase are pulsating stars like Cepheids or RR Lyre, so that also needs to be explained. The region of instability is relatively narrow, and star will ...
... can be used to directly test computer models of not only the evolutionary paths of stars but also stellar pulsation models. But not all stars in this phase are pulsating stars like Cepheids or RR Lyre, so that also needs to be explained. The region of instability is relatively narrow, and star will ...
THE HR DIAGRAM
... 3. Once the core temperature reaches 10 million K, coulombic repulsion between the now ionized hydrogen atoms (protons) is overcome, and nuclear fusion commences. Hydrogen fuses to form helium nuclei, releasing energy in the process. Initially, the increased outward radiation pressure is still insu ...
... 3. Once the core temperature reaches 10 million K, coulombic repulsion between the now ionized hydrogen atoms (protons) is overcome, and nuclear fusion commences. Hydrogen fuses to form helium nuclei, releasing energy in the process. Initially, the increased outward radiation pressure is still insu ...
Here
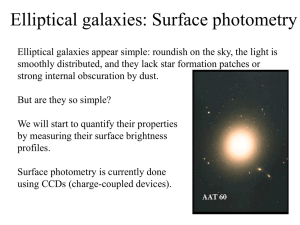
... •Fainter systems are bluer This could be explained if small E galaxies were younger or more metalpoor than the large bright ones. ...
... •Fainter systems are bluer This could be explained if small E galaxies were younger or more metalpoor than the large bright ones. ...
THE INNER CORE OF A NEUTRON STAR Part 1
... star composition makes it so heavy that its density is at least twice the mass of Earth’s Sun. Current thinking subscribes to the possibility that a neutron star is primarily made up of almost entirely sub-atomic particles without net electrical charge. Neutron stars are very hot and are supported a ...
... star composition makes it so heavy that its density is at least twice the mass of Earth’s Sun. Current thinking subscribes to the possibility that a neutron star is primarily made up of almost entirely sub-atomic particles without net electrical charge. Neutron stars are very hot and are supported a ...
HD 140283: A Star in the Solar Neighborhood that Formed Shortly
... luminosity by 0.7–1.0 Gyr (Imbriani et al. 2004). Although it is unlikely that there will be further significant revisions to basic stellar physics, because most of the ingredients of stellar ...
... luminosity by 0.7–1.0 Gyr (Imbriani et al. 2004). Although it is unlikely that there will be further significant revisions to basic stellar physics, because most of the ingredients of stellar ...
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Deep Sky Objects
... Nebulae are very important in astronomy because they are the key to understanding the birth of stars. All stars, including the sun, formed from nebulae like the Orion Nebula. Astronomers have also found, however, that certain types of nebulae mark the death of stars (see slides #62 and 63). In old a ...
... Nebulae are very important in astronomy because they are the key to understanding the birth of stars. All stars, including the sun, formed from nebulae like the Orion Nebula. Astronomers have also found, however, that certain types of nebulae mark the death of stars (see slides #62 and 63). In old a ...
DP11 Foundations of Astronomy
... prevent its own collapse. If it has a mass of less than 0.08 solar masses, nothing else will happen – it will contract and cool over billions of years, shining extremely faintly. It will be a brown dwarf. ...
... prevent its own collapse. If it has a mass of less than 0.08 solar masses, nothing else will happen – it will contract and cool over billions of years, shining extremely faintly. It will be a brown dwarf. ...
GRB Progenitors and their environments
... of the accretion rate onto the disk might be doable – timing in the engine. • For massive star long-duration burst progenitors, engine perturbations will be difficult to predict. But we can differentiate the surrounding environment – ongoing work on both CE and wind/LBV phases. ...
... of the accretion rate onto the disk might be doable – timing in the engine. • For massive star long-duration burst progenitors, engine perturbations will be difficult to predict. But we can differentiate the surrounding environment – ongoing work on both CE and wind/LBV phases. ...
THE PHYSICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF THE STARS 1
... them the universe as a whole. As it is well known, stars are formed in groups from the gravitational collapse of giant and cold clouds of molecular gas, take long episodes of production of energy through thermonuclear reactions in their interior with a length that depends on the mass, and die as hig ...
... them the universe as a whole. As it is well known, stars are formed in groups from the gravitational collapse of giant and cold clouds of molecular gas, take long episodes of production of energy through thermonuclear reactions in their interior with a length that depends on the mass, and die as hig ...
File
... light emitted from far nebulae are absorbed by foreground gas and dust in the space and cannot reach to the Solar System. Light emitted from nearby nebulae, where there is not much foreground gas and dust, can reach to the Solar System. Thus visible objects in the Milky Way Galaxy are located near t ...
... light emitted from far nebulae are absorbed by foreground gas and dust in the space and cannot reach to the Solar System. Light emitted from nearby nebulae, where there is not much foreground gas and dust, can reach to the Solar System. Thus visible objects in the Milky Way Galaxy are located near t ...
Glossary Topics - Home - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... layers. Such stars also become blue and red supergiants. As they build up an iron core, they too explode as supernovae. The remaining core then begins to collapse. If the core is larger than five solar masses, collapse continues until it becomes a black hole. If the core is less than five solar mass ...
... layers. Such stars also become blue and red supergiants. As they build up an iron core, they too explode as supernovae. The remaining core then begins to collapse. If the core is larger than five solar masses, collapse continues until it becomes a black hole. If the core is less than five solar mass ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... When the inner core consisting mainly of neutrons becomes degenerate, the collapse is suddenly stopped, the core bounces back and an energetic shock wave is generated. This shock wave travels outwards from the core but is blocked by the massive and dense ’iron cap’, the outer core, which is in free ...
... When the inner core consisting mainly of neutrons becomes degenerate, the collapse is suddenly stopped, the core bounces back and an energetic shock wave is generated. This shock wave travels outwards from the core but is blocked by the massive and dense ’iron cap’, the outer core, which is in free ...
1 Stars
... This type of star is made almost entirely of neutrons. A neutron star has more mass than the Sun, yet it is only a few kilometers in diameter. If the core remaining after a supernova is more than about 5 times the mass of the Sun, the core collapses to become a black hole. Black holes are so dense t ...
... This type of star is made almost entirely of neutrons. A neutron star has more mass than the Sun, yet it is only a few kilometers in diameter. If the core remaining after a supernova is more than about 5 times the mass of the Sun, the core collapses to become a black hole. Black holes are so dense t ...
No Slide Title
... Looking to the Future The participants in NUVA have realized with great concern that no firm plans exist to maintain an Ultraviolet observing capability for astrophysics for the future. This is despite the fact that the range of important astrophysical issues in astrophysics which require observatio ...
... Looking to the Future The participants in NUVA have realized with great concern that no firm plans exist to maintain an Ultraviolet observing capability for astrophysics for the future. This is despite the fact that the range of important astrophysical issues in astrophysics which require observatio ...