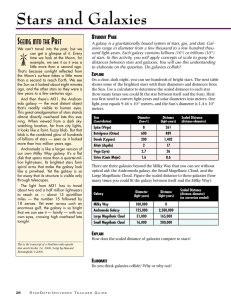
What are stars?
... - We know now that the stars in a constellation are not necessarily very close together, but appear to be due to our line of sight - Examples – Orion, Ursa Major (Big Dipper) ...
... - We know now that the stars in a constellation are not necessarily very close together, but appear to be due to our line of sight - Examples – Orion, Ursa Major (Big Dipper) ...
Answer titese questions on a piece of loose leaf paper.
... 13. Within the main sequence, surface temperatures increase as absolute brightness ...
... 13. Within the main sequence, surface temperatures increase as absolute brightness ...
22 October: The Formation of Stars
... (spectral class O), we know they are young. • With fairly simple observations, we can find groups of O and B stars (OB associations) ...
... (spectral class O), we know they are young. • With fairly simple observations, we can find groups of O and B stars (OB associations) ...
Lecture 7 Stars and Galaxies and Nebula, (Oh My!) Feb 18 2003
... Outer layers of gas are blown off from the core of a star. The core often goes on to become a white dwarf. The eject gas is illuminated by the remaining star. This is the fate of most stars, including our own Sun. ...
... Outer layers of gas are blown off from the core of a star. The core often goes on to become a white dwarf. The eject gas is illuminated by the remaining star. This is the fate of most stars, including our own Sun. ...
Stars and Galaxies
... And then there’s M31, the Andromeda galaxy — the most distant object that’s readily visible to human eyes. This great amalgamation of stars stands almost directly overhead late this evening. When viewed from a dark skywatching location, far from city lights, it looks like a faint, fuzzy blob. But th ...
... And then there’s M31, the Andromeda galaxy — the most distant object that’s readily visible to human eyes. This great amalgamation of stars stands almost directly overhead late this evening. When viewed from a dark skywatching location, far from city lights, it looks like a faint, fuzzy blob. But th ...
F03HW09
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
2nd Semester Exam Study Guide
... - light shifted toward the blue end of the spectrum; shows that the star is moving toward Earth 6. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe is expanding and galaxies are moving away from the Milky Way galaxy. 7. After the Big Bang occurred, many atoms of hydrogen and helium formed when tempera ...
... - light shifted toward the blue end of the spectrum; shows that the star is moving toward Earth 6. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe is expanding and galaxies are moving away from the Milky Way galaxy. 7. After the Big Bang occurred, many atoms of hydrogen and helium formed when tempera ...
Lecture 1 The Big Picture: Origin of the Earth
... you. The greater the star’s speed, the greater the spectral shift. [by Declan DePaor] ...
... you. The greater the star’s speed, the greater the spectral shift. [by Declan DePaor] ...
Stars and Galaxies
... • Stars more massive than our Sun may be main sequence stars for only 10 million years • Stars less massive than our Sun may be main sequence stars for 100’s of billions of years • Remember: the larger the star the shorter the life span, the smaller the star the longer the life span ...
... • Stars more massive than our Sun may be main sequence stars for only 10 million years • Stars less massive than our Sun may be main sequence stars for 100’s of billions of years • Remember: the larger the star the shorter the life span, the smaller the star the longer the life span ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What force causes particles of stellar dust to become attracted to each other ? ____gravity_____ The most widely held astronomical theory about the origin of the universe is the ...
... What force causes particles of stellar dust to become attracted to each other ? ____gravity_____ The most widely held astronomical theory about the origin of the universe is the ...
The Hot-plate Model of a Star Model of Stars— 3 Oct
... hot-plate get to my hand? What are two ways to make a hot plate produce more energy per second? (The same question applies to a star: What are two ways to make a star brighter or more luminous?) What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? ...
... hot-plate get to my hand? What are two ways to make a hot plate produce more energy per second? (The same question applies to a star: What are two ways to make a star brighter or more luminous?) What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? ...
Review
... B) The gas planets are farther from the Sun than the four inner planets C) All the planets orbit in the same direction D) The orbits of Pluto and the other distant dwarf planets are tilted in different directions. 30) Planets orbiting other stars are hard to detect because they A) only reflect light ...
... B) The gas planets are farther from the Sun than the four inner planets C) All the planets orbit in the same direction D) The orbits of Pluto and the other distant dwarf planets are tilted in different directions. 30) Planets orbiting other stars are hard to detect because they A) only reflect light ...
Supernovae, Neutron Stars, Black Holes
... Triggering the Formation of the Solar System --- New data from meteorites indicates that formation of the Solar System was triggered by a supernova. Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology One of the most amazing discoveries in space science is the unambiguous ev ...
... Triggering the Formation of the Solar System --- New data from meteorites indicates that formation of the Solar System was triggered by a supernova. Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology One of the most amazing discoveries in space science is the unambiguous ev ...
15 Billion
... of Moon. Oldest fossils are about 3.8 by old. f. Mathematical models predict that stars the size of the Sun will undergo nuclear fusion in their core. g. All galaxies are red-shifting, i.e., the universe is expanding. Cosmic background radiation, a remnant of the big bang, is observed. h. Hubble spa ...
... of Moon. Oldest fossils are about 3.8 by old. f. Mathematical models predict that stars the size of the Sun will undergo nuclear fusion in their core. g. All galaxies are red-shifting, i.e., the universe is expanding. Cosmic background radiation, a remnant of the big bang, is observed. h. Hubble spa ...
Stars and the Sun
... • Runs out of He, core shrinks, outer layers float into space (planetary nebula) • Core left over, small and hot (white dwarf) • Eventually fuses up to carbon, ends as small cold ball of carbon (black dwarf) ...
... • Runs out of He, core shrinks, outer layers float into space (planetary nebula) • Core left over, small and hot (white dwarf) • Eventually fuses up to carbon, ends as small cold ball of carbon (black dwarf) ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... Along the main sequence, stars of greater magnitude are hotter (have more energy) c. How is a star’s luminosity related to its energy? For main-sequence stars, the luminosity increases with temperature. For the giants and super-giants, large (high magnitude) and luminous stars are actually quite coo ...
... Along the main sequence, stars of greater magnitude are hotter (have more energy) c. How is a star’s luminosity related to its energy? For main-sequence stars, the luminosity increases with temperature. For the giants and super-giants, large (high magnitude) and luminous stars are actually quite coo ...