Content Standards/Performance Indicators: Key Pre
... Understanding the solar system helps you understand Earth’s position in space. The Sun is the star that provides energy for life on Earth. That Earth is part of the Milky Way galaxy. ...
... Understanding the solar system helps you understand Earth’s position in space. The Sun is the star that provides energy for life on Earth. That Earth is part of the Milky Way galaxy. ...
The Sun and Stardust
... How are other elements made? Massive stars burn their hydrogen (and helium and carbon-nitrogen-oxygen) very quickly. At the end of their life heavier (metals) are formed such as vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and nickel etc. Then massive stars (about ten times more massive than the Su ...
... How are other elements made? Massive stars burn their hydrogen (and helium and carbon-nitrogen-oxygen) very quickly. At the end of their life heavier (metals) are formed such as vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and nickel etc. Then massive stars (about ten times more massive than the Su ...
Galaxies
... concentration (3%) heavy elements Population II – red, old, found in bulge and halo, elliptical orbits, low concentration of heavy elements Probably smooth transition between end members (i.e. the sun). ? Population III ? – pure H and He ...
... concentration (3%) heavy elements Population II – red, old, found in bulge and halo, elliptical orbits, low concentration of heavy elements Probably smooth transition between end members (i.e. the sun). ? Population III ? – pure H and He ...
The Sun and the Stars
... • While all stars appear as a faint white light from a distance they can be bluish, bluish-white, yellow, orangish, or reddish depending on their surface temperature • Scientists use a powerful telescope to analyze the colour of the star and then its surface temperature. Since the Sun is yellow, we ...
... • While all stars appear as a faint white light from a distance they can be bluish, bluish-white, yellow, orangish, or reddish depending on their surface temperature • Scientists use a powerful telescope to analyze the colour of the star and then its surface temperature. Since the Sun is yellow, we ...
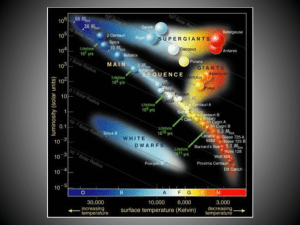
The HR Diagram
... Color and Stars Think of a candle • Hottest part is blue • Red is the cool part at the top ...
... Color and Stars Think of a candle • Hottest part is blue • Red is the cool part at the top ...
1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light... limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of...
... 1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer p ...
... 1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer p ...
Solving the Mystery of Massive Star Birth
... As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new ...
... As the cloud gets smaller, it gets clumpy. The clumps may eventually become so compact that they begin to heat up, growing hotter and hotter, until eventually they begin “burning” at their core. When the temperature at the core reaches a scorching 10 million degrees, the clump officially becomes a new ...
Main Sequence Star
... a) Size of giants depends on the initial mass b) Could be a super red giant like Betelgeuse ...
... a) Size of giants depends on the initial mass b) Could be a super red giant like Betelgeuse ...
Lifecycle of a Star
... Massive main sequence stars fuse hydrogen much faster than small or medium stars ...
... Massive main sequence stars fuse hydrogen much faster than small or medium stars ...
Lecture Summary (11/22)
... as it passes through concentrations of gas and dust. There are advantages to using infrared telescopes to probe the interstellar medium. Our Sun formed in a nebula 4.6 billion years ago. Stars like the Sun are born as protostars in regions where the ISM collapses. There are many examples of star-for ...
... as it passes through concentrations of gas and dust. There are advantages to using infrared telescopes to probe the interstellar medium. Our Sun formed in a nebula 4.6 billion years ago. Stars like the Sun are born as protostars in regions where the ISM collapses. There are many examples of star-for ...
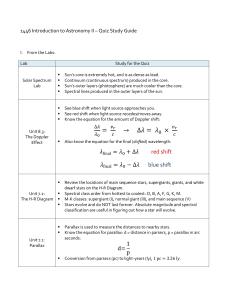
red shift blue shift
... Review the locations of main sequence stars, supergiants, giants, and white dwarf stars on the H-R Diagram. Spectral class order from hottest to coolest: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. M-K classes: supergiant (I), normal giant (III), and main sequence (V) Stars evolve and do NOT last forever. Absolute magnitu ...
... Review the locations of main sequence stars, supergiants, giants, and white dwarf stars on the H-R Diagram. Spectral class order from hottest to coolest: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. M-K classes: supergiant (I), normal giant (III), and main sequence (V) Stars evolve and do NOT last forever. Absolute magnitu ...
Red Dwarfs and Barnard`s star. Their origin and significance to
... eye; however, it is much brighter in the infrared than it is in visible light. Barnard’s star is thought to be 10 billion years old and older than our galaxy. It must have been captured from elsewhere. Bernard’s star is travelling towards us at a very high speed. It will become closer to us than Pro ...
... eye; however, it is much brighter in the infrared than it is in visible light. Barnard’s star is thought to be 10 billion years old and older than our galaxy. It must have been captured from elsewhere. Bernard’s star is travelling towards us at a very high speed. It will become closer to us than Pro ...
Regents Earth Science – Unit 5: Astronomy
... Red Giants eventually expel their outer layers of gas (Planetary Nebula stage) and leave behind their exposed hot, small core this core is a White Dwarf star white dwarfs cool over time and become Black Dwarf stars high mass stars evolve to become Supergiant stars Supergiants will explode in an even ...
... Red Giants eventually expel their outer layers of gas (Planetary Nebula stage) and leave behind their exposed hot, small core this core is a White Dwarf star white dwarfs cool over time and become Black Dwarf stars high mass stars evolve to become Supergiant stars Supergiants will explode in an even ...
Theoretical Modeling of Massive Stars Mr. Russell University of Delaware
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
Outer Space Study Guide
... This is another exciting theme to learn about. In the next few years ordinary people can travel to space thanks to Virgin Galactic’s idea. Anyone can view space from their computer thanks to the ISS. LINK. To top things off you can even explore Mars from home. LINK Scientist have estimated Earth to ...
... This is another exciting theme to learn about. In the next few years ordinary people can travel to space thanks to Virgin Galactic’s idea. Anyone can view space from their computer thanks to the ISS. LINK. To top things off you can even explore Mars from home. LINK Scientist have estimated Earth to ...
The Lives of Stars
... Astronomers speculate that stars form from gas and dust clouds called nebulae Gravity pulls the material togethe Accumulating gas increases temperature At 10,000,000 degrees nuclear fusion begins (transformation of hydrogen into helium) ...
... Astronomers speculate that stars form from gas and dust clouds called nebulae Gravity pulls the material togethe Accumulating gas increases temperature At 10,000,000 degrees nuclear fusion begins (transformation of hydrogen into helium) ...
red shift summary sheet
... energy and matter found today in the universe expanded from tiny point and formed the galaxies, stars, planets, asteroids, gases, dust and energy. Even today the universe is still expanding. In fact one example of how we can prove this is by looking at a phenomenon called red shift. It was discovere ...
... energy and matter found today in the universe expanded from tiny point and formed the galaxies, stars, planets, asteroids, gases, dust and energy. Even today the universe is still expanding. In fact one example of how we can prove this is by looking at a phenomenon called red shift. It was discovere ...
File
... Stars like the Sun run out of hydrogen after about ____ billion years... core collapses under _____________ pressure core heats up and ________ begins to fuse into other elements (carbon) outer surface expands up to _____ times huge size mean low temperature... it is now a ______ ________. ...
... Stars like the Sun run out of hydrogen after about ____ billion years... core collapses under _____________ pressure core heats up and ________ begins to fuse into other elements (carbon) outer surface expands up to _____ times huge size mean low temperature... it is now a ______ ________. ...
Click here
... The Universe - 93 billion light years in _____________________________________ o Virgo Supercluster: 110 million light years in diameter. This is a group of about 100 galaxy groups. The Local Group - ________________ million light years in diameter. This is a group of over 50 galaxies. The Milky ...
... The Universe - 93 billion light years in _____________________________________ o Virgo Supercluster: 110 million light years in diameter. This is a group of about 100 galaxy groups. The Local Group - ________________ million light years in diameter. This is a group of over 50 galaxies. The Milky ...
X-ray Binaries and Cygnus X-1
... An X-ray binary is a system made up of a normal star and a compact object rotating about a common center of mass. The compact object pulls mass off of the outer atmospheres of the normal star and the particles spiral down toward the compact object, creating an accretion disk. Because of the internal ...
... An X-ray binary is a system made up of a normal star and a compact object rotating about a common center of mass. The compact object pulls mass off of the outer atmospheres of the normal star and the particles spiral down toward the compact object, creating an accretion disk. Because of the internal ...
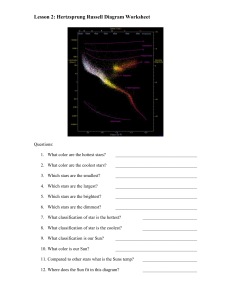
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...