The Evolution of the Solar System
... and gases all around areas. Grains of dust collided and formed bigger and bigger lumps. Some of these lumps crashed together and formed planets, drawn together under gravity. The four solid rock planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars were created. In the outer regions of the disk, the solar wind w ...
... and gases all around areas. Grains of dust collided and formed bigger and bigger lumps. Some of these lumps crashed together and formed planets, drawn together under gravity. The four solid rock planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars were created. In the outer regions of the disk, the solar wind w ...
Astronomy 1 Study Guide Key 16
... chromosphere – region of glowing red gas corona – outermost part of sun, seen during total solar eclipse 2. What do sun spots produce and how do they effect Earth? can produce solar flares that send ions and radiation out toward Earth; can cause auroras and problems with communications 3. What prote ...
... chromosphere – region of glowing red gas corona – outermost part of sun, seen during total solar eclipse 2. What do sun spots produce and how do they effect Earth? can produce solar flares that send ions and radiation out toward Earth; can cause auroras and problems with communications 3. What prote ...
Solar Furnaces
... • If M < 0.08 Msun, then T is not high enough for sustained nuclear reactions: get a “BROWN DWARF” (failed star) (But fusion does occur for a short time.) • It is held up by “degeneracy pressure” (quantum mechanical pressure). • Until the mid-1990s, no confirmed brown dwarfs had been found, but now ...
... • If M < 0.08 Msun, then T is not high enough for sustained nuclear reactions: get a “BROWN DWARF” (failed star) (But fusion does occur for a short time.) • It is held up by “degeneracy pressure” (quantum mechanical pressure). • Until the mid-1990s, no confirmed brown dwarfs had been found, but now ...
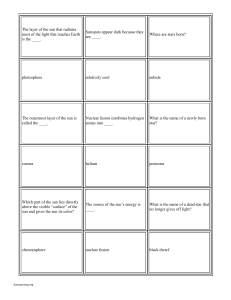
Layers of the Sun
... million degrees Fahrenheit. Enormous amounts of helium are produced here through nuclear fusion. Nuclear fusion is the process of combining two or more small nuclei to form a single, larger nucleus. Thus, creating a helium atom, neutron and energy. From the core, energy moves outward toward the Sun’ ...
... million degrees Fahrenheit. Enormous amounts of helium are produced here through nuclear fusion. Nuclear fusion is the process of combining two or more small nuclei to form a single, larger nucleus. Thus, creating a helium atom, neutron and energy. From the core, energy moves outward toward the Sun’ ...
Star Game Cards
... In the Milky Way, the most abundant gas is ____ which is also the element that fuses first to make a star. ...
... In the Milky Way, the most abundant gas is ____ which is also the element that fuses first to make a star. ...
Chapter 14 Our Star 14.1 A Closer Look at the Sun Why was the
... find the right number of neutrinos, but some have changed form ...
... find the right number of neutrinos, but some have changed form ...
Weathering, Erosion and Mass Movement
... Explore the structure of the Sun. Describe the solar activity cycle and how the Sun affects the Earth. Compare the different types of spectra. ...
... Explore the structure of the Sun. Describe the solar activity cycle and how the Sun affects the Earth. Compare the different types of spectra. ...
PHYS 1311: In Class Problems Chapter 5 Solutions Feb. 23, 2016
... overpowering luminosity, but if they observed long enough (at least 6 years), they would see the Sun “wobble” and therefore deduce a massive object must be orbiting it. If the observers happen to view the Solar System edge-on, the Sun would display simple harmonic motion. This same logic is applied ...
... overpowering luminosity, but if they observed long enough (at least 6 years), they would see the Sun “wobble” and therefore deduce a massive object must be orbiting it. If the observers happen to view the Solar System edge-on, the Sun would display simple harmonic motion. This same logic is applied ...
Slide 1
... • Every particle in the cloud attracts every other particle • As they ‘fall’ inwards, they move faster (gravitational potential energy is being converted to kinetic energy) • The particles collide with each other, sharing their ...
... • Every particle in the cloud attracts every other particle • As they ‘fall’ inwards, they move faster (gravitational potential energy is being converted to kinetic energy) • The particles collide with each other, sharing their ...
Jeopardy Midterm Review
... A fancy car is decelerating at a rate of 2 m/s/s and after 10 seconds is now going 10 m/s, state its initial velocity ...
... A fancy car is decelerating at a rate of 2 m/s/s and after 10 seconds is now going 10 m/s, state its initial velocity ...
L5 - QUB Astrophysics Research Centre
... The surface luminosity of the sun is L =3.86x1026W, and at no point in the Sun can the luminosity exceed this value (see eqn of energy production). What can you conclude from this ? As the T and v of the rising elements are determined by the difference between the actual temperature gradient and a ...
... The surface luminosity of the sun is L =3.86x1026W, and at no point in the Sun can the luminosity exceed this value (see eqn of energy production). What can you conclude from this ? As the T and v of the rising elements are determined by the difference between the actual temperature gradient and a ...
The Sun
... Since large number of neutrinos are produced in the hydrogen fusion process, working of the sun can also be studied observing those neutrinos. Neutrinos interact only very weakly interact with matter, so large detectors are used to record few neutrinos a day. Neutrinos going through a medium (water) ...
... Since large number of neutrinos are produced in the hydrogen fusion process, working of the sun can also be studied observing those neutrinos. Neutrinos interact only very weakly interact with matter, so large detectors are used to record few neutrinos a day. Neutrinos going through a medium (water) ...
Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation
... of our galaxy, the Milky Way. The sun, mass 2.0X1030kg, revolves around the center of thee galaxy with a radius of 2.2X1020 m. The period of one rotation is 2.6X108 years. a. Find the approximate mass of the galaxy. b. Assume the average star in the galaxy has the mass of the sun, find the number of ...
... of our galaxy, the Milky Way. The sun, mass 2.0X1030kg, revolves around the center of thee galaxy with a radius of 2.2X1020 m. The period of one rotation is 2.6X108 years. a. Find the approximate mass of the galaxy. b. Assume the average star in the galaxy has the mass of the sun, find the number of ...
Forces in stars
... The nuclear fusion reactions going on within the Sun generate huge amounts of energy in the form of radiation and this streams upwards through the Sun until it eventually leaves the surface and is radiated out into space. If the star is stable the gravitational forces acting inwards to the centre of ...
... The nuclear fusion reactions going on within the Sun generate huge amounts of energy in the form of radiation and this streams upwards through the Sun until it eventually leaves the surface and is radiated out into space. If the star is stable the gravitational forces acting inwards to the centre of ...
Picture - The Russell Elementary Science Experience
... What is the difference between mass and weight? How does a plant create its own food? What is the name of the process? How are volcanoes formed? How are mountains formed? How are earthquakes created? Explain the main processes in the water cycle? Where do fossil fuels come from? Give some examples o ...
... What is the difference between mass and weight? How does a plant create its own food? What is the name of the process? How are volcanoes formed? How are mountains formed? How are earthquakes created? Explain the main processes in the water cycle? Where do fossil fuels come from? Give some examples o ...