Goal: To understand how Saturn formed and what its core is like
... • This distance is called the tar line. • There is a lot more carbon than there is iron and silicon in the cloud forming the sun. • So, even though there is less material overall to form a planet at this distance a much larger percentage of it becomes solid. • This allows you to build much larger pl ...
... • This distance is called the tar line. • There is a lot more carbon than there is iron and silicon in the cloud forming the sun. • So, even though there is less material overall to form a planet at this distance a much larger percentage of it becomes solid. • This allows you to build much larger pl ...
Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry
... – Our Sun is actually a Star – Are formed from clouds of dust and gas, or nebulas, and go through different stages as they age – Located at various distances from Earth • We use the light-year to describe this distance • A light-year (ly) is the distance that light travels in one year ...
... – Our Sun is actually a Star – Are formed from clouds of dust and gas, or nebulas, and go through different stages as they age – Located at various distances from Earth • We use the light-year to describe this distance • A light-year (ly) is the distance that light travels in one year ...
Earths Place in the Universe
... their life cycles and that visual, radio, and X-ray telescopes may be used to collect data that reveal those differences. ...
... their life cycles and that visual, radio, and X-ray telescopes may be used to collect data that reveal those differences. ...
Introduction to the HR Diagram
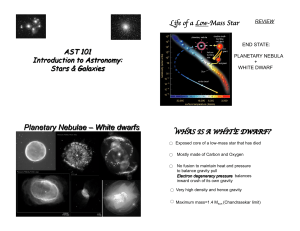
... located in the upper right-hand corner of the H-R diagram. As the central core of a main sequence star with a mass from ~0.8 to 8 solar masses runs out of hydrogen, radiation pressure no longer balances gravity and the star begins to collapse. There is still hydrogen in the outer layers surrounding ...
... located in the upper right-hand corner of the H-R diagram. As the central core of a main sequence star with a mass from ~0.8 to 8 solar masses runs out of hydrogen, radiation pressure no longer balances gravity and the star begins to collapse. There is still hydrogen in the outer layers surrounding ...
Dark blue dot not so dark
... “This can happen if there is enough gas in the cloud core to provide resistance,” said the paper’s lead author, Bo Reipurth of the Institute for Astronomy at the University of Hawaii at Manoa. “Sometimes there is so much gas in the core that the two close stars spiral all the way in and collide with ...
... “This can happen if there is enough gas in the cloud core to provide resistance,” said the paper’s lead author, Bo Reipurth of the Institute for Astronomy at the University of Hawaii at Manoa. “Sometimes there is so much gas in the core that the two close stars spiral all the way in and collide with ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... 25.1 Properties of Stars Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram A Hertzsprung–Russell diagram shows the relationship between the absolute magnitude and temperature of stars. A main-sequence star is a star that falls into the main sequence category on the H–R diagram. This category contains the majority of ...
... 25.1 Properties of Stars Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram A Hertzsprung–Russell diagram shows the relationship between the absolute magnitude and temperature of stars. A main-sequence star is a star that falls into the main sequence category on the H–R diagram. This category contains the majority of ...
Where is the rest of the universe?
... those much closer in. This implies that the galaxy is surrounded by a massive spherical distribution of unseen matter, which adds to its total mass. • The gravitational centers of galaxy clusters do not lie at their expected place, but are offset. This implies that there is much more unseen matter p ...
... those much closer in. This implies that the galaxy is surrounded by a massive spherical distribution of unseen matter, which adds to its total mass. • The gravitational centers of galaxy clusters do not lie at their expected place, but are offset. This implies that there is much more unseen matter p ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412 - Queen's University Belfast
... Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram, more exactly in the log(L/L) vs. log(Teff/K) plane. The evolution is followed from the initial main sequence (also called zero age main sequence, ZAMS) up to the end of the core carbon burning phase for the most massive stars, to the early asymptotic giant branch ...
... Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram, more exactly in the log(L/L) vs. log(Teff/K) plane. The evolution is followed from the initial main sequence (also called zero age main sequence, ZAMS) up to the end of the core carbon burning phase for the most massive stars, to the early asymptotic giant branch ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • These lumps tend to condense into stars • That is why stars tend to be found in clusters ...
... • These lumps tend to condense into stars • That is why stars tend to be found in clusters ...
Chapter 15 Test Study Sheet
... California Science Standard 8.4: The structure and composition of the universe can be learned from studying stars and galaxies and their evolution. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know galaxies are clusters of billions of stars and may have different shapes. Know how scienti ...
... California Science Standard 8.4: The structure and composition of the universe can be learned from studying stars and galaxies and their evolution. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know galaxies are clusters of billions of stars and may have different shapes. Know how scienti ...
No Slide Title
... of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri is the closest star. Most stars are too dista ...
... of an object due to the movement of the observer. Remember looking at your finger through the left and then right eye? One parsec is the distance an object must be in order to have a parallax of one arc second. One parsec = 3.3 light years Alpha Centauri is the closest star. Most stars are too dista ...
Our Universe
... •Our Sun has around 5 Billion years remaining. It is predicted to only exist for 10 Billion total years. ...
... •Our Sun has around 5 Billion years remaining. It is predicted to only exist for 10 Billion total years. ...
Neutron Star - Perry Local Schools
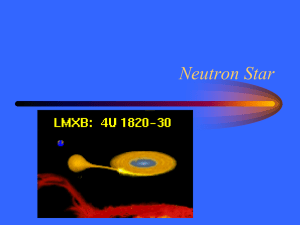
... of 1.4 to 3 solar masses, the remnant can become a neutron star. – If the leftover core has a mass that is greater than three solar masses, it will collapse to form a black ...
... of 1.4 to 3 solar masses, the remnant can become a neutron star. – If the leftover core has a mass that is greater than three solar masses, it will collapse to form a black ...
Neutron Star
... • The balance point to maintain degenerate matter is 1.4 M. • When the mass of the core is greater than 1.4 M, electrons cannot support the gravitational force. • This is the Chandrasekar limit: beyond that it’s supernova. ...
... • The balance point to maintain degenerate matter is 1.4 M. • When the mass of the core is greater than 1.4 M, electrons cannot support the gravitational force. • This is the Chandrasekar limit: beyond that it’s supernova. ...
Into the sub-mm
... pilot study of a SCUBA survey of Lynds Class 6 Clouds. The goals of their unbiased survey is to constrain star formation models by identifying complete samples of protostellar condensations for further study so as to measure star formation efficiencies, determine mass accretion rates and the minimum ...
... pilot study of a SCUBA survey of Lynds Class 6 Clouds. The goals of their unbiased survey is to constrain star formation models by identifying complete samples of protostellar condensations for further study so as to measure star formation efficiencies, determine mass accretion rates and the minimum ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.