H-R Diagram - SFA Physics
... the sun and the majority of these stars are considered to be the most common types of stars in the galaxy. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 to Figure 3. ...
... the sun and the majority of these stars are considered to be the most common types of stars in the galaxy. Transfer the main sequence curve from Figure 1 to Figure 3. ...
5Stars_Part_Two
... Pulsars: 1. Pulsars emit pulses some as short as 1/40th of a second. 2. There are many things they could not be. 3. The only thing small enough, and rotating fast enough was a neutron star ...
... Pulsars: 1. Pulsars emit pulses some as short as 1/40th of a second. 2. There are many things they could not be. 3. The only thing small enough, and rotating fast enough was a neutron star ...
PH607 – Galaxies 1
... Radio: The majority of the bright emission seen in the image is from hot, ionized regions, or is produced by energetic electrons moving in magnetic fields Near Infrared: Most of the emission at these wavelengths is from relatively cool giant K stars in the disk and bulge X-rays: extended soft X-ray ...
... Radio: The majority of the bright emission seen in the image is from hot, ionized regions, or is produced by energetic electrons moving in magnetic fields Near Infrared: Most of the emission at these wavelengths is from relatively cool giant K stars in the disk and bulge X-rays: extended soft X-ray ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY Dr. Uri Griv •
... Explanation: How could a galaxy become shaped like a ring? The rim of the blue galaxy pictured on the right is an immense ring-like structure 150,000 light years in diameter composed of newly formed, extremely bright, massive stars. That galaxy, AM 0644-741, is known as a ring galaxy and was caused ...
... Explanation: How could a galaxy become shaped like a ring? The rim of the blue galaxy pictured on the right is an immense ring-like structure 150,000 light years in diameter composed of newly formed, extremely bright, massive stars. That galaxy, AM 0644-741, is known as a ring galaxy and was caused ...
No Slide Title
... show that the Milky Way has a central bar extending to R=2-3 kpc. It is a Sbc galaxy or SABbc( r) - there can be no perfect agreement when looking at multiwavelength data! ...
... show that the Milky Way has a central bar extending to R=2-3 kpc. It is a Sbc galaxy or SABbc( r) - there can be no perfect agreement when looking at multiwavelength data! ...
Chpt14b
... Astronomers still can’t explain well why we have spiral arms in galaxies. The stars, gas, and dust in the galaxy all obey Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. Thus the inner matterial rotates faster than the outer matterial. If spiral arms were tied to the galaxy then after a few 100,000,000 years the ...
... Astronomers still can’t explain well why we have spiral arms in galaxies. The stars, gas, and dust in the galaxy all obey Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. Thus the inner matterial rotates faster than the outer matterial. If spiral arms were tied to the galaxy then after a few 100,000,000 years the ...
(HR) Diagrams
... show how a star such as the sun (a G2 star while it is on the main sequence) evolves through the following stages: a. protostar (which may have formed in a Bok globule) to main sequence star b. main sequence star to red giant to helium flash c. ejecting a planetary nebula (which exposes an interior ...
... show how a star such as the sun (a G2 star while it is on the main sequence) evolves through the following stages: a. protostar (which may have formed in a Bok globule) to main sequence star b. main sequence star to red giant to helium flash c. ejecting a planetary nebula (which exposes an interior ...
Final Exam Practice Part I
... 26. When a massive, dying star blows itself apart, if the remaining mass is less than three times the mass of the sun, the leftover material will form a ______. 28. Cosmologists think the material in our bodies was once part of a massive star. Explain how it went from a star to our bodies. 29. Descr ...
... 26. When a massive, dying star blows itself apart, if the remaining mass is less than three times the mass of the sun, the leftover material will form a ______. 28. Cosmologists think the material in our bodies was once part of a massive star. Explain how it went from a star to our bodies. 29. Descr ...
Stella Finger Prints
... Analyze and predict trends from data. Background: Now that you know how astronomers use light to collect information from the universe, let’s look at stars by themselves. All stars start out in a specific place, called a nebula (plural is nebulae). Nebulae are large areas of gas and dust where sta ...
... Analyze and predict trends from data. Background: Now that you know how astronomers use light to collect information from the universe, let’s look at stars by themselves. All stars start out in a specific place, called a nebula (plural is nebulae). Nebulae are large areas of gas and dust where sta ...
How are galaxies classified
... A: If the star is massive enough, the collapse of the star will trigger a violent explosion known as a supernova. A: Supernovas are very bright and can cause a brief (few months) burst of radiation that can outshine an entire galaxy. A: During this explosion, a supernova can give off as much energy ...
... A: If the star is massive enough, the collapse of the star will trigger a violent explosion known as a supernova. A: Supernovas are very bright and can cause a brief (few months) burst of radiation that can outshine an entire galaxy. A: During this explosion, a supernova can give off as much energy ...
Northam Sky July 2009
... Around mid July just after sunset in Northam if you look due east and about 25 degrees above the horizon you'll see an S shaped collection of stars know as the constellation of Scorpio the scorpion. From the five stars at the top making up Scorpios head and claws through it's bright red heart, the s ...
... Around mid July just after sunset in Northam if you look due east and about 25 degrees above the horizon you'll see an S shaped collection of stars know as the constellation of Scorpio the scorpion. From the five stars at the top making up Scorpios head and claws through it's bright red heart, the s ...
Star formation PowerPoint
... The differences between the H-R diagrams of open and globular clusters are that the globular clusters are very old, whereas the open clusters are much younger. The absence of massive main sequence stars in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age—those stars have already used up their fuel and ...
... The differences between the H-R diagrams of open and globular clusters are that the globular clusters are very old, whereas the open clusters are much younger. The absence of massive main sequence stars in the globular cluster is due to its extreme age—those stars have already used up their fuel and ...
The Sun and the Origin of the Solar System
... • Region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU) to approximately 55 AU from the Sun ...
... • Region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune (at 30 AU) to approximately 55 AU from the Sun ...
EXERCISES: Set 4 of 4 Q1: (You will need a ruler and a calculator
... Q8(b): Write an expression for the rms mass fluctuation σM within a sphere of radius R using the power spectrum P (k). Assuming a top-hat filtering of density fluctuations, recover the expression for the window function in Fourier space W (kR). [N.B. you should use the expansion in spherical harmoni ...
... Q8(b): Write an expression for the rms mass fluctuation σM within a sphere of radius R using the power spectrum P (k). Assuming a top-hat filtering of density fluctuations, recover the expression for the window function in Fourier space W (kR). [N.B. you should use the expansion in spherical harmoni ...
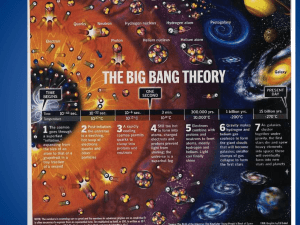
The Big Bang Theory - Red Hook Central Schools
... 5. Stellar formation and evolution • We observe the life cycles of stars across the universe using tools such as satellites and telescopes • we view stars form, burn and explode ...
... 5. Stellar formation and evolution • We observe the life cycles of stars across the universe using tools such as satellites and telescopes • we view stars form, burn and explode ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.