H-R Diagram
... Black Dwarf • White dwarfs are some of the hottest objects in the known universe with temperatures ranging from 30,000 K to 200,000 K. • They continue to radiate their immense internal energy into space as they continue on their journey to become black dwarfs. • When they reach 4000 K these bizarre ...
... Black Dwarf • White dwarfs are some of the hottest objects in the known universe with temperatures ranging from 30,000 K to 200,000 K. • They continue to radiate their immense internal energy into space as they continue on their journey to become black dwarfs. • When they reach 4000 K these bizarre ...
N-Body Simulations of Star Clusters with IMBH
... We followed the evolution of MGG-11 by N-body simulations of star clusters containing N= 130.000 stars, and starting from King models with initial concentrations in the range 3.0 < Wo < ...
... We followed the evolution of MGG-11 by N-body simulations of star clusters containing N= 130.000 stars, and starting from King models with initial concentrations in the range 3.0 < Wo < ...
Astronomy and Space articles by Martin George of the Launceston
... Kepler's mission is to carefully observe a large number of stars to try to detect the slight drop in light as planets pass in front of their parent stars as seen from here. This particular observation is of a star system called Kepler 16, which is about 200 light years away. By comparison, the neare ...
... Kepler's mission is to carefully observe a large number of stars to try to detect the slight drop in light as planets pass in front of their parent stars as seen from here. This particular observation is of a star system called Kepler 16, which is about 200 light years away. By comparison, the neare ...
Make one copy for each student on plain paper. Life Cycle of Star
... Our Sun is an average star that formed from a nebula. It produces its own heat and light by nuclear reactions. They live for billions of years before becoming a red giant. ...
... Our Sun is an average star that formed from a nebula. It produces its own heat and light by nuclear reactions. They live for billions of years before becoming a red giant. ...
Apparent brightness
... Color and temperature can classify stars well enough but SPECTROSCOPY gives us spectral-line radiation which is a much more detailed classification theme. The composition of these stars are the same the difference in absorption spectra is temperature. ...
... Color and temperature can classify stars well enough but SPECTROSCOPY gives us spectral-line radiation which is a much more detailed classification theme. The composition of these stars are the same the difference in absorption spectra is temperature. ...
Stellar Evolution and the HR Diagram – Study Guide
... phosphorus, magnesium, iron, and calcium that make up our bodies. So we really are made of atoms that were formed first in the dying explosions of long dead stars. 29. MINI-Essay: How is a supernova both a beginning and an end? Supernovae are the result of the death of a star that can no longer car ...
... phosphorus, magnesium, iron, and calcium that make up our bodies. So we really are made of atoms that were formed first in the dying explosions of long dead stars. 29. MINI-Essay: How is a supernova both a beginning and an end? Supernovae are the result of the death of a star that can no longer car ...
Module 3: Exploring Other Stars Assignment 5: Estimating
... age, astronomers have found it’s much more accurate to represent the spectrum as a plot of intensity versus wavelength. This is what the applet in the last module was doing for a theoretical blackbody. In the document Module3_spectra.pdf you see the digital spectra of six real stars. The actual spec ...
... age, astronomers have found it’s much more accurate to represent the spectrum as a plot of intensity versus wavelength. This is what the applet in the last module was doing for a theoretical blackbody. In the document Module3_spectra.pdf you see the digital spectra of six real stars. The actual spec ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own HertzsprungRussell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own HertzsprungRussell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
The structure and evolution of stars
... Stars are held together by gravitation – attraction exerted on each part of the star by all other parts Collapse is resisted by internal thermal pressure. These two forces play the principal role in determining stellar structure – they must be (at least almost) in balance Thermal properties of stars ...
... Stars are held together by gravitation – attraction exerted on each part of the star by all other parts Collapse is resisted by internal thermal pressure. These two forces play the principal role in determining stellar structure – they must be (at least almost) in balance Thermal properties of stars ...
Slide 1
... spectral type and colour) of a range of stars. An example is shown in Figure 1 (A). Stars at the bottom right are faint, cool and red while stars at the top left are bright, hot and blue. The period of time during which a star is in the process of core hydrogen fusion is called the main sequence. Th ...
... spectral type and colour) of a range of stars. An example is shown in Figure 1 (A). Stars at the bottom right are faint, cool and red while stars at the top left are bright, hot and blue. The period of time during which a star is in the process of core hydrogen fusion is called the main sequence. Th ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... The Universe is believed to have been formed from a very dense fireball _____________ of years ago. As the fireball expanded and cooled stars and galaxies formed. The fireball explosion is often called the ___ ________. The explosion threw all the material outwards; that is why scientists believe th ...
... The Universe is believed to have been formed from a very dense fireball _____________ of years ago. As the fireball expanded and cooled stars and galaxies formed. The fireball explosion is often called the ___ ________. The explosion threw all the material outwards; that is why scientists believe th ...
7a Properties of Stars.pptx
... – Based on distance away – abs. mag. Sun = 5 – less than 5 brighter than Sun – Greater than 5 dimmer than Sun ...
... – Based on distance away – abs. mag. Sun = 5 – less than 5 brighter than Sun – Greater than 5 dimmer than Sun ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
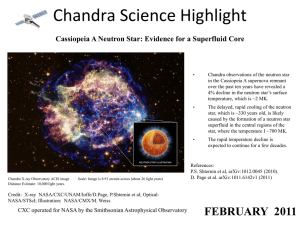
... The delayed, rapid cooling of the neutron star, which is ~330 years old, is likely caused by the formation of a neutron star superfluid in the central regions of the star, where the temperature I ~700 MK. ...
... The delayed, rapid cooling of the neutron star, which is ~330 years old, is likely caused by the formation of a neutron star superfluid in the central regions of the star, where the temperature I ~700 MK. ...
Describe essential ideas about the composition and structure of the
... and the Earth’s place in it. Compare various planets’ characteristics. Describe basic star types and identify the sun as a star type. Describe and differentiate comets, asteroids, and meteors Identify gravity as the force that keeps planets in orbit around the sun and governs the rest of the ...
... and the Earth’s place in it. Compare various planets’ characteristics. Describe basic star types and identify the sun as a star type. Describe and differentiate comets, asteroids, and meteors Identify gravity as the force that keeps planets in orbit around the sun and governs the rest of the ...
Powerpoint for today
... surface temperature. A quantitative measure of “color”, and thus temperature, can be made by observing star through various color filters. See text for how this is done. ...
... surface temperature. A quantitative measure of “color”, and thus temperature, can be made by observing star through various color filters. See text for how this is done. ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.