DoAr21_AAS2005 - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
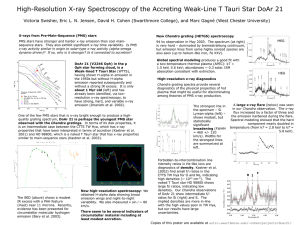
... x-ray activity similar in origin to solar-type x-ray activity (alpha-omega dynamo driven)? If so, why is it stronger? Is it connected to accretion? ...
... x-ray activity similar in origin to solar-type x-ray activity (alpha-omega dynamo driven)? If so, why is it stronger? Is it connected to accretion? ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
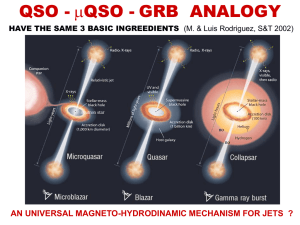
... • Quasars are the brightest active galactic nuclei • Emit immense amounts of radiation • Some are brighter than 1,000 Milky Ways ...
... • Quasars are the brightest active galactic nuclei • Emit immense amounts of radiation • Some are brighter than 1,000 Milky Ways ...
August 29 - Astronomy
... life Without carbon, life could not exist in the early Universe. Planets like the Earth could not form without iron, silicon and oxygen. ...
... life Without carbon, life could not exist in the early Universe. Planets like the Earth could not form without iron, silicon and oxygen. ...
Last time we left off at hydrogen and helium, because that`s all that
... 100 million years old it is possible that no stars had formed yet. However, it appears that by the time the universe was 1 billion years old, stars and galaxies were in full bloom everywhere. From that standpoint, therefore, life in principle had the necessary raw materials no later than 1 billion y ...
... 100 million years old it is possible that no stars had formed yet. However, it appears that by the time the universe was 1 billion years old, stars and galaxies were in full bloom everywhere. From that standpoint, therefore, life in principle had the necessary raw materials no later than 1 billion y ...
A1993KK54100001
... begun. A world of very high density, very high energy concentration had opened up. Here relativity theory was supreme, not a minor correction to Newtonian gravitation. It was a world not only of strong radio pulses, but of X-rays and high energy particles. The knowledge that neutron stars with masse ...
... begun. A world of very high density, very high energy concentration had opened up. Here relativity theory was supreme, not a minor correction to Newtonian gravitation. It was a world not only of strong radio pulses, but of X-rays and high energy particles. The knowledge that neutron stars with masse ...
Why do the stars shine?
... is U(initial)-U(final), but U(initial)=0 since the cloud radius is so much larger than the final star. • Assume the Sun has shown at constant luminosity for t years. Total energy radiated = L0x t=4x1033 ergs/sec x t. • (We know today that main sequence stars do not change luminosity over the life of ...
... is U(initial)-U(final), but U(initial)=0 since the cloud radius is so much larger than the final star. • Assume the Sun has shown at constant luminosity for t years. Total energy radiated = L0x t=4x1033 ergs/sec x t. • (We know today that main sequence stars do not change luminosity over the life of ...
III - National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... cluster, and the controversy over the age and formation stage of these clusters. They explain that in addition to using ccd images, they have taken spectra of hundreds of stars. In OBSERVATIONS AND DATA REDUCTION they present a detailed explanation of every step of their work. The first sentence, “U ...
... cluster, and the controversy over the age and formation stage of these clusters. They explain that in addition to using ccd images, they have taken spectra of hundreds of stars. In OBSERVATIONS AND DATA REDUCTION they present a detailed explanation of every step of their work. The first sentence, “U ...
9.1 Introduction 9.2 Static Models
... So, we have five coupled differential equations describing the run of mass, pressure, luminosity and temperature within a star with r, the distance from the centre of the star , as the independent variable. Note that the first two equations describe the mechanical structure of the star, while the la ...
... So, we have five coupled differential equations describing the run of mass, pressure, luminosity and temperature within a star with r, the distance from the centre of the star , as the independent variable. Note that the first two equations describe the mechanical structure of the star, while the la ...
Relativistic jets in microquasars, AGN and GRBs
... Proper motion with HST + radial velocity from ground RUNAWAY VELOCITY ~120 km/s MOMENTUM = 550 M km/s as in runaway neutron stars ...
... Proper motion with HST + radial velocity from ground RUNAWAY VELOCITY ~120 km/s MOMENTUM = 550 M km/s as in runaway neutron stars ...
Study Guide 8th Grade Ocean Motions In the Northern Hemisphere
... Gas Giant: the name often given to the first four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Ring: a thin disk of small ice and rock particles surrounding a planet Asteroid: rocky objects revolving around the sun that are too small and numerous to be considered planets Asteroid belt: the region ...
... Gas Giant: the name often given to the first four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Ring: a thin disk of small ice and rock particles surrounding a planet Asteroid: rocky objects revolving around the sun that are too small and numerous to be considered planets Asteroid belt: the region ...
Study Guide 8th Grade 2nd Semester Test Ocean Motions In the
... Gas Giant: the name often given to the first four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Ring: a thin disk of small ice and rock particles surrounding a planet Asteroid: rocky objects revolving around the sun that are too small and numerous to be considered planets Asteroid belt: the region ...
... Gas Giant: the name often given to the first four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Ring: a thin disk of small ice and rock particles surrounding a planet Asteroid: rocky objects revolving around the sun that are too small and numerous to be considered planets Asteroid belt: the region ...
Skills Worksheet
... Starlight, Star Heat Read the following paragraphs, and complete the exercises below. ...
... Starlight, Star Heat Read the following paragraphs, and complete the exercises below. ...
Stan Woosley (UCSC)
... If in the models the mass cut is taken at the edge of the iron core the average gravitational mass for for stars in the 10 – 21 solar mass range is (12 models; above this black holes start to form by fall back): ...
... If in the models the mass cut is taken at the edge of the iron core the average gravitational mass for for stars in the 10 – 21 solar mass range is (12 models; above this black holes start to form by fall back): ...
SETI: First Considerations (PowerPoint)
... Don’t assume that flife = 0.5 (a 50:50 chance), in the hopes of being “unbiassed.” That’s rather like saying “I have a 50:50 chance of winning the lottery: either I will, or I won’t.” flife is probably very close to zero (with very rare exceptions!) or very close to unity. But we don’t know which it ...
... Don’t assume that flife = 0.5 (a 50:50 chance), in the hopes of being “unbiassed.” That’s rather like saying “I have a 50:50 chance of winning the lottery: either I will, or I won’t.” flife is probably very close to zero (with very rare exceptions!) or very close to unity. But we don’t know which it ...
Astronomy 1020 Exam 1 Review Questions
... 7. Name the 7 regions of the electromagnetic spectrum from shortest to longest wavelength and from highest to lowest energy. 8. A photon has a frequency of 5.00 × 1014 Hz, what is its wavelength? (Hint: c = speed of light = 3.00 × 108 m/s.) 9. What is meant be thermal equilibrium? What type of spect ...
... 7. Name the 7 regions of the electromagnetic spectrum from shortest to longest wavelength and from highest to lowest energy. 8. A photon has a frequency of 5.00 × 1014 Hz, what is its wavelength? (Hint: c = speed of light = 3.00 × 108 m/s.) 9. What is meant be thermal equilibrium? What type of spect ...
4. Sketch and label the life cycle of a star. Give a short phrase
... Mass – A measure of how much matter an object contains. It is a property of the object and not affected by gravity. Your mass is the same, no matter where you are in the universe! Weight – The resulting force of the gravitational pull on an object. You will weigh less on the moon because there is le ...
... Mass – A measure of how much matter an object contains. It is a property of the object and not affected by gravity. Your mass is the same, no matter where you are in the universe! Weight – The resulting force of the gravitational pull on an object. You will weigh less on the moon because there is le ...
The Universe Section 1
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
CHAPTER 30: STARS, GALAXIES AND THE UNIVERSE Analyzing
... A white dwarf may also become a supernova, which is a star that has such a tremendous explosion that it blows itself apart. Supernovas are a thousand times more violent than novas. The explosions of supernovas completely destroy the white dwarf star and may destroy much of the red giant. The Final S ...
... A white dwarf may also become a supernova, which is a star that has such a tremendous explosion that it blows itself apart. Supernovas are a thousand times more violent than novas. The explosions of supernovas completely destroy the white dwarf star and may destroy much of the red giant. The Final S ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.