the magellanic clouds newsletter - Keele University Astrophysics
... have initial substructure. Furthermore, both clusters may be evolving along a very similar dynamical sequence, with the key difference that NGC 1805 is dynamically older than NGC 1818. The F-type binaries in NGC 1818 still show evidence of an initial period of rapid dynamical disruptions (which occu ...
... have initial substructure. Furthermore, both clusters may be evolving along a very similar dynamical sequence, with the key difference that NGC 1805 is dynamically older than NGC 1818. The F-type binaries in NGC 1818 still show evidence of an initial period of rapid dynamical disruptions (which occu ...
A Sense of Scale - Young Scientists Journal
... least dense planet at 0.14g/cm3 [4] (compared to 1.33g/cm3 for Jupiter) and was the first discovered planet with a retrograde orbit – which is in the opposite direction of the rotation of its host star. The physical upper mass limit for a planet is roughly 13 times the mass of Jupiter; [5] this is ...
... least dense planet at 0.14g/cm3 [4] (compared to 1.33g/cm3 for Jupiter) and was the first discovered planet with a retrograde orbit – which is in the opposite direction of the rotation of its host star. The physical upper mass limit for a planet is roughly 13 times the mass of Jupiter; [5] this is ...
ILÍDIO LOPES ()
... In these layers we have an intricate web of different processes occurring and interacting in the same region and in the same time scale: convection, magnetic fields and pulsations. Beneath the stellar surface (a few percent of the star’s radius) this interaction becomes even more complicated due to ...
... In these layers we have an intricate web of different processes occurring and interacting in the same region and in the same time scale: convection, magnetic fields and pulsations. Beneath the stellar surface (a few percent of the star’s radius) this interaction becomes even more complicated due to ...
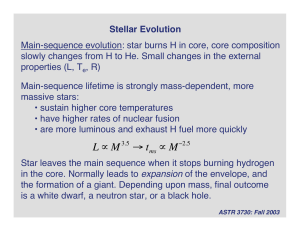
Introduction to Stellar Evolution
... Or surface temperature Our Sun: 5,700 deg Kelvin Or about 10,000 F ...
... Or surface temperature Our Sun: 5,700 deg Kelvin Or about 10,000 F ...
The Milky Way - University of North Texas
... b. Objects below this mass can only form in HI clouds. c. Objects below this mass are not hot enough to fuse normal hydrogen. d. They form too slowly and hot stars nearby clear the gas and dust quickly. e. Our telescopes do not have enough light gathering power to detect dim objects. ...
... b. Objects below this mass can only form in HI clouds. c. Objects below this mass are not hot enough to fuse normal hydrogen. d. They form too slowly and hot stars nearby clear the gas and dust quickly. e. Our telescopes do not have enough light gathering power to detect dim objects. ...
The Size and Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy
... for Contemporary Physics and Astronomy • Stars are a small fraction of the mass of major galaxies • The dark matter problem becomes more pronounced as you go out in the universe • The form of the dark matter is unknown; probably not what you studied in chemistry • Possibly/probably an unknown form o ...
... for Contemporary Physics and Astronomy • Stars are a small fraction of the mass of major galaxies • The dark matter problem becomes more pronounced as you go out in the universe • The form of the dark matter is unknown; probably not what you studied in chemistry • Possibly/probably an unknown form o ...
Concise pioneers of astronomy
... one had any idea what these unusual objects were at the time, so the name little green men (LGM) was used. Soon, Thomas Gold suggested that pulsars were rapidly spinning neutron stars, the remnants of a supernova. ...
... one had any idea what these unusual objects were at the time, so the name little green men (LGM) was used. Soon, Thomas Gold suggested that pulsars were rapidly spinning neutron stars, the remnants of a supernova. ...
Origin of Ocean
... Milky Way Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy is 100 million light in diameter Our galaxy contains roughly 400 billion stars Sun is a very typical star located in one of the arms of the Milky Way Galaxy Other planetary systems have been found in our galaxy ...
... Milky Way Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy is 100 million light in diameter Our galaxy contains roughly 400 billion stars Sun is a very typical star located in one of the arms of the Milky Way Galaxy Other planetary systems have been found in our galaxy ...
Origins of Earth
... Milky Way Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy is 100 million light in diameter Our galaxy contains roughly 400 billion stars Sun is a very typical star located in one of the arms of the Milky Way Galaxy Other planetary systems have been found in our galaxy ...
... Milky Way Galaxy Milky Way Galaxy is 100 million light in diameter Our galaxy contains roughly 400 billion stars Sun is a very typical star located in one of the arms of the Milky Way Galaxy Other planetary systems have been found in our galaxy ...
Star Formation - Leslie Looney
... A Star is Born! •! Density increase, temperature increases until fusion can occur. –! Blows away most of its natal circumstellar material. –! Becomes a star on the main sequence of the HR diagram, –! For low mass stars, this whole process can take a few 106 years. –! Expect to see a large number of ...
... A Star is Born! •! Density increase, temperature increases until fusion can occur. –! Blows away most of its natal circumstellar material. –! Becomes a star on the main sequence of the HR diagram, –! For low mass stars, this whole process can take a few 106 years. –! Expect to see a large number of ...
1000
... We are not in the center of our solar system, which is not in the center of the Milky Way and we are just one of a billion galaxies in the universe. Earth is made of common elements found throughtout the universe. ...
... We are not in the center of our solar system, which is not in the center of the Milky Way and we are just one of a billion galaxies in the universe. Earth is made of common elements found throughtout the universe. ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... We now believe that all galaxies harbor a SMBH at their center. When the SMBH actively accretes gas it liberates an enormous. amount of energy (AGN, Quasars). Life would probably not be possible if our SMBH wakes up and becomes a Quasar. Astronomers discovered that the larger the mass in stars aroun ...
... We now believe that all galaxies harbor a SMBH at their center. When the SMBH actively accretes gas it liberates an enormous. amount of energy (AGN, Quasars). Life would probably not be possible if our SMBH wakes up and becomes a Quasar. Astronomers discovered that the larger the mass in stars aroun ...
Groups of Stars
... Galaxies Irregular Galaxies A small fraction of all galaxies are known as irregular galaxies. Irregular galaxies have a disorganized appearance. They have many young stars and large amounts of gas and ...
... Galaxies Irregular Galaxies A small fraction of all galaxies are known as irregular galaxies. Irregular galaxies have a disorganized appearance. They have many young stars and large amounts of gas and ...
the universe
... small, gravity eventually leads to the star contracting to form a white dwarf. It fades and changes colour as it cools. The matter in a white dwarf is millions of times denser than the matter on Earth. Stars that are much heavier than our Sun have a different fate. A heavy-weight star will still bec ...
... small, gravity eventually leads to the star contracting to form a white dwarf. It fades and changes colour as it cools. The matter in a white dwarf is millions of times denser than the matter on Earth. Stars that are much heavier than our Sun have a different fate. A heavy-weight star will still bec ...
the universe
... small, gravity eventually leads to the star contracting to form a white dwarf. It fades and changes colour as it cools. The matter in a white dwarf is millions of times denser than the matter on Earth. Stars that are much heavier than our Sun have a different fate. A heavy-weight star will still bec ...
... small, gravity eventually leads to the star contracting to form a white dwarf. It fades and changes colour as it cools. The matter in a white dwarf is millions of times denser than the matter on Earth. Stars that are much heavier than our Sun have a different fate. A heavy-weight star will still bec ...
Essay - CLC Charter School
... Supernovae A supernova is a stellar explosion that happends in result of the death of a massive star. It involves the expulsion of the stars outer layers. A supernova is a relatively rare event in our galaxy, it happens about every 50 years. When a supernova explodes, briefly it can outshine an enti ...
... Supernovae A supernova is a stellar explosion that happends in result of the death of a massive star. It involves the expulsion of the stars outer layers. A supernova is a relatively rare event in our galaxy, it happens about every 50 years. When a supernova explodes, briefly it can outshine an enti ...
Lecture 10: The Hertzsprung
... See also Figure 19-21 in your book There is a mass-luminosity relation on the main sequence. We can use that + a sample of stars where we get all the stars within a certain distance of the Sun to figure out how many stars of what masses are out there. Answer: Lots of low-mass stars! Very few high-m ...
... See also Figure 19-21 in your book There is a mass-luminosity relation on the main sequence. We can use that + a sample of stars where we get all the stars within a certain distance of the Sun to figure out how many stars of what masses are out there. Answer: Lots of low-mass stars! Very few high-m ...
Lecture 30
... Energy generation rate per unit mass: q µ r T …where b - the temperature sensitivity of the nuclear reaction rate, is at least +4 and sometimes +20 or more. Suppose temperature in the core momentarily drops, reducing ...
... Energy generation rate per unit mass: q µ r T …where b - the temperature sensitivity of the nuclear reaction rate, is at least +4 and sometimes +20 or more. Suppose temperature in the core momentarily drops, reducing ...
Galaxies and the Universe
... • What holds clusters of galaxies together? • Conclusion: There must be a lot of invisible mass in the Universe ...
... • What holds clusters of galaxies together? • Conclusion: There must be a lot of invisible mass in the Universe ...
Quiz 1: Answers Physics 55: Introduction to
... Circle the letter that best answers each of the following questions. 1. The typical number of stars in a galaxy, the approximate number of galaxies in the observable universe, and the approximate number of neurons in the human brain all have similar values equal to about (a) 106 . (b) 1010 . (c) 102 ...
... Circle the letter that best answers each of the following questions. 1. The typical number of stars in a galaxy, the approximate number of galaxies in the observable universe, and the approximate number of neurons in the human brain all have similar values equal to about (a) 106 . (b) 1010 . (c) 102 ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.