Constellations
... How stars would appear if they were all the same distance from earth. All stars place 32.6 LY from the sun Our sun abs. Mag = 4.8 Negative is brighter ...
... How stars would appear if they were all the same distance from earth. All stars place 32.6 LY from the sun Our sun abs. Mag = 4.8 Negative is brighter ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... As astronomers study stars, there are a number of characteristics that can be investigated: temperature, composition, luminosity, mass, motion, and more. Some characteristics are directly observable (such as temperature and some motions), while others (such as mass) require inference from other data ...
... As astronomers study stars, there are a number of characteristics that can be investigated: temperature, composition, luminosity, mass, motion, and more. Some characteristics are directly observable (such as temperature and some motions), while others (such as mass) require inference from other data ...
1_Introduction
... The Galaxy has an entourage of star clusters that (on average) are at rest with respect to the Galaxy’s center. ...
... The Galaxy has an entourage of star clusters that (on average) are at rest with respect to the Galaxy’s center. ...
Astronomy HOMEWORK Chapter 15 1. Where in the Galaxy is the
... 3. Which statement about the Milky Way Galaxy is correct? a. Our Galaxy is but one of many galaxies. b. Our Galaxy contains all stars in the universe. c. All stars in our Galaxy take the same time to complete one orbit. d. Most stars in our Galaxy are in the central bulge. e. None of the stars in ou ...
... 3. Which statement about the Milky Way Galaxy is correct? a. Our Galaxy is but one of many galaxies. b. Our Galaxy contains all stars in the universe. c. All stars in our Galaxy take the same time to complete one orbit. d. Most stars in our Galaxy are in the central bulge. e. None of the stars in ou ...
Misc-ReviewForAstroTest
... 2. A graduate student named Jocelyn Bell Burnell discovered a strong night time source of “twinkling”. 3. Its location was fixed with respect to the stars. From Jay Pasachoff’s “Contemporary Astronomy” ...
... 2. A graduate student named Jocelyn Bell Burnell discovered a strong night time source of “twinkling”. 3. Its location was fixed with respect to the stars. From Jay Pasachoff’s “Contemporary Astronomy” ...
1705 Star Charts
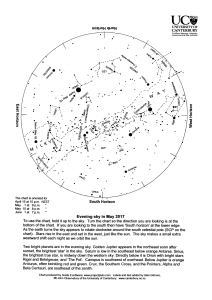
... brightest of all the stars, appears midway down the northwest sky. Canopus, second brightest, is southwest of overhead. Midway up the southeast sky are 'The Pointers', Beta and Alpha Centauri. Well below them is the hook-shaped pattern of Scorpius with orange Antares marking the Scorpion's body. Bel ...
... brightest of all the stars, appears midway down the northwest sky. Canopus, second brightest, is southwest of overhead. Midway up the southeast sky are 'The Pointers', Beta and Alpha Centauri. Well below them is the hook-shaped pattern of Scorpius with orange Antares marking the Scorpion's body. Bel ...
Core-collapse supernovae and their massive progenitors
... Observations of the luminosity and the kinetic energy of core-collapse supernovae are vital to constrain the explosion models and determine if there is any link between the explosion mechanism and mass of the star. There are peculiar Type II-P SNe that have distinctly lower luminosities and kinetic ...
... Observations of the luminosity and the kinetic energy of core-collapse supernovae are vital to constrain the explosion models and determine if there is any link between the explosion mechanism and mass of the star. There are peculiar Type II-P SNe that have distinctly lower luminosities and kinetic ...
Introduction
... How can a large, more-or-less spherical cloud of interstellar gas and dust slowly evolve into a solar system, with a central star and several orbiting planets? Explain in at most 1 page, including reference to the roles played by gravity, rotation and "clumping" (10 marks, graded for writing as well ...
... How can a large, more-or-less spherical cloud of interstellar gas and dust slowly evolve into a solar system, with a central star and several orbiting planets? Explain in at most 1 page, including reference to the roles played by gravity, rotation and "clumping" (10 marks, graded for writing as well ...
d 2
... Earth = a grain of sand The Earth orbits the Sun at a distance of one meter Proxima Centauri lies 270 kilometers (170 miles) away Barnard’s Star lies 370 kilometers (230 miles) away Less than 100 stars lie within 1000 kilometers (600 miles) ...
... Earth = a grain of sand The Earth orbits the Sun at a distance of one meter Proxima Centauri lies 270 kilometers (170 miles) away Barnard’s Star lies 370 kilometers (230 miles) away Less than 100 stars lie within 1000 kilometers (600 miles) ...
Interpreting the HR diagram of stellar clusters
... In fact, it seems that stars are usually born in big groups, as members of a cluster of stars. All the stars in the cluster form at about the same time. So, if we look at a cluster, we see a bunch of stars which are all roughly the same age. However, the stars do not all have the same mass: most ten ...
... In fact, it seems that stars are usually born in big groups, as members of a cluster of stars. All the stars in the cluster form at about the same time. So, if we look at a cluster, we see a bunch of stars which are all roughly the same age. However, the stars do not all have the same mass: most ten ...
Northern Circumpolar Constellations
... Dipper) • Ursa Minor, the Little Bear • Cassiopeia, the Queen of Ethiopia • Cepheus, the King of Ethiopia • Draco the Dragon ...
... Dipper) • Ursa Minor, the Little Bear • Cassiopeia, the Queen of Ethiopia • Cepheus, the King of Ethiopia • Draco the Dragon ...
December 2015
... ionized by high energy photons emitted from stars that have often been formed within the nebula. These star forming nebula are officially called H II (H two) regions. The color red orange is due to their large amounts of hydrogen. Of course the term nebula means “fuzzy cloud” and came about when ear ...
... ionized by high energy photons emitted from stars that have often been formed within the nebula. These star forming nebula are officially called H II (H two) regions. The color red orange is due to their large amounts of hydrogen. Of course the term nebula means “fuzzy cloud” and came about when ear ...
29.2 - Stars - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Based on temperature and pattern of spectra lines – Sun = G2, temperature = ~5800 K ...
... • Based on temperature and pattern of spectra lines – Sun = G2, temperature = ~5800 K ...
$doc.title
... supernovae are powered by nuclear reacBons. While the main energy source of core collapse supernovae and long gamma-‐ray bursts is gravity, nuclear physics triggers the explosion. Neutron stars are giant nuc ...
... supernovae are powered by nuclear reacBons. While the main energy source of core collapse supernovae and long gamma-‐ray bursts is gravity, nuclear physics triggers the explosion. Neutron stars are giant nuc ...
IL CIELO COME LABORATORIO – 2010/2011 STAR FORMATION
... down slowly, the gases condense in the centre forming the bulge’s stars and then distribute themselves on a plane due to the galaxy rotation, continually creating new stars; while in elliptical galaxies stars form roughly at the same time. II. OBSERVATIONAL DATA In the night of 23rd February 2011, t ...
... down slowly, the gases condense in the centre forming the bulge’s stars and then distribute themselves on a plane due to the galaxy rotation, continually creating new stars; while in elliptical galaxies stars form roughly at the same time. II. OBSERVATIONAL DATA In the night of 23rd February 2011, t ...
Perimeter Dark Matter Online Game Worksheet #1 1. Match the
... 8. The mass difference between theory and observation can’t be stars or other luminous objects because: a. If the mass difference was stars, the mass would be too great. b. If the mass difference was stars, the mass would be too small. c. If the mass difference was stars, the brightness would be too ...
... 8. The mass difference between theory and observation can’t be stars or other luminous objects because: a. If the mass difference was stars, the mass would be too great. b. If the mass difference was stars, the mass would be too small. c. If the mass difference was stars, the brightness would be too ...
Which object is a meteor?
... • Option B is the breaking apart of atoms (the opposite of what happens in stars) • Option C is not even a real thing • Option D is not a real thing either • CORRECT ANSWER: Option A nuclear fusion is the process of atoms fusing together and releasing HUGE amounts of energy. ...
... • Option B is the breaking apart of atoms (the opposite of what happens in stars) • Option C is not even a real thing • Option D is not a real thing either • CORRECT ANSWER: Option A nuclear fusion is the process of atoms fusing together and releasing HUGE amounts of energy. ...
Question C:
... Zeilik, Fig. 13-10 is an HR (color-magnitude) diagram for the globular cluster M3. At B-V=0.4, where there are some obvious main sequence stars, we read 18.5 ≤ mV ≤ 19.5 We can find the absolute magnitude MV at B-4=0.4 from a couple of places: • Table A4-3 says that MV≈3.5 • The HR diagram used with ...
... Zeilik, Fig. 13-10 is an HR (color-magnitude) diagram for the globular cluster M3. At B-V=0.4, where there are some obvious main sequence stars, we read 18.5 ≤ mV ≤ 19.5 We can find the absolute magnitude MV at B-4=0.4 from a couple of places: • Table A4-3 says that MV≈3.5 • The HR diagram used with ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.