origins of the Universe
... begin to contract and close in on itself eventually exploding again and starting the process all over again. ...
... begin to contract and close in on itself eventually exploding again and starting the process all over again. ...
Homework 5 (stellar properties)
... 6. (3 pts.) What two observations/measurements would you make to classify a star according to its luminosity (i.e., luminosity class, e.g., Ia, Ib, II, III, IV, or V)? (Hint: Look at the HR diagram.) Which equation relates these two quantities to the size (radius) of a star (after all, the luminosit ...
... 6. (3 pts.) What two observations/measurements would you make to classify a star according to its luminosity (i.e., luminosity class, e.g., Ia, Ib, II, III, IV, or V)? (Hint: Look at the HR diagram.) Which equation relates these two quantities to the size (radius) of a star (after all, the luminosit ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... white dwarf of about 0.6 its initial mass. These are relatively stable structures, lasting for billions of years. Depending on its initial mass, the star may explode into a supernova or degenerate further into a black dwarf. If the mass of the white dwarf is above 1.4 solar mass for stars made up of ...
... white dwarf of about 0.6 its initial mass. These are relatively stable structures, lasting for billions of years. Depending on its initial mass, the star may explode into a supernova or degenerate further into a black dwarf. If the mass of the white dwarf is above 1.4 solar mass for stars made up of ...
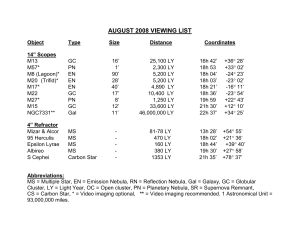
August
... M13 At a distance of 25,100 light years, this globular cluster in the constellation Hercules (HER-cueleez) is about 145 light years in diameter. The age of M13 has been estimated at over 10 billion years. It contains over 300,000 stars. At the center, stars are about 500 times more concentrated than ...
... M13 At a distance of 25,100 light years, this globular cluster in the constellation Hercules (HER-cueleez) is about 145 light years in diameter. The age of M13 has been estimated at over 10 billion years. It contains over 300,000 stars. At the center, stars are about 500 times more concentrated than ...
Solutions
... giant. This is incorrect! The Sun will not be more massive; it doesn’t pull in any extra matter from anywhere. It will be bigger (larger volume), but will have at most the mass that it’s got now. (When it starts out as a red giant, it will only be very slightly less massive than it is now, due to th ...
... giant. This is incorrect! The Sun will not be more massive; it doesn’t pull in any extra matter from anywhere. It will be bigger (larger volume), but will have at most the mass that it’s got now. (When it starts out as a red giant, it will only be very slightly less massive than it is now, due to th ...
hea-www.harvard.edu
... due to curved space-time Want to derive population properties brightness, size, etc - as function of distance (therefore, cosmic time) But - biases in sample ...
... due to curved space-time Want to derive population properties brightness, size, etc - as function of distance (therefore, cosmic time) But - biases in sample ...
Slide 1
... Irregulars: No definite shape. Ex. Large and small Magellanic clouds. Dominate universe by number, although generally smaller. Star formation, but less dust than disks. Peculiar: (Pec) Have a definite form, but with peculiarities. Radio jets or other strangeness. ...
... Irregulars: No definite shape. Ex. Large and small Magellanic clouds. Dominate universe by number, although generally smaller. Star formation, but less dust than disks. Peculiar: (Pec) Have a definite form, but with peculiarities. Radio jets or other strangeness. ...
Earth in space
... knew that when a light source is moving away from an observer it’s wavelength becomes longer… This results in a shift of its spectrum towards the red end conversely, when a light source moves towards an observer, there is a shift towards the blue end of the spectrum ...
... knew that when a light source is moving away from an observer it’s wavelength becomes longer… This results in a shift of its spectrum towards the red end conversely, when a light source moves towards an observer, there is a shift towards the blue end of the spectrum ...
Kepler Mission
... Astrophysical effects such as Doppler boosting, and near-field microlensing are being seen for the first time. First 45 days of data become public on June 15 for 99.5% of targets, the other 0.5% are KOIs to be released February 2011. Cycle 2 of GO program starts ~ June 20th with 36 proposals approve ...
... Astrophysical effects such as Doppler boosting, and near-field microlensing are being seen for the first time. First 45 days of data become public on June 15 for 99.5% of targets, the other 0.5% are KOIs to be released February 2011. Cycle 2 of GO program starts ~ June 20th with 36 proposals approve ...
Northern Circumpolar Constellations
... Dipper) • Ursa Minor, the Little Bear • Cassiopeia, the Queen of Ethiopia • Cepheus, the King of Ethiopia • Draco the Dragon ...
... Dipper) • Ursa Minor, the Little Bear • Cassiopeia, the Queen of Ethiopia • Cepheus, the King of Ethiopia • Draco the Dragon ...
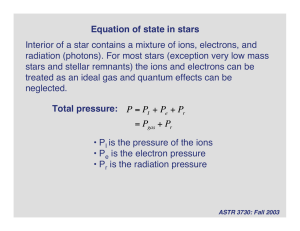
Equation of state in stars Interior of a star contains a mixture of ions
... radiation (photons). For most stars (exception very low mass stars and stellar remnants) the ions and electrons can be treated as an ideal gas and quantum effects can be ...
... radiation (photons). For most stars (exception very low mass stars and stellar remnants) the ions and electrons can be treated as an ideal gas and quantum effects can be ...
Exam 3 Study Guide
... This guide is meant to assist with studying for Exam 3 on March 27, 2017. However, it is not comprehensive. This guide includes topic which might not be on this exam (but which might be on the final). It is also possible that something not specifically mentioned on the guide may be on the exam. Howe ...
... This guide is meant to assist with studying for Exam 3 on March 27, 2017. However, it is not comprehensive. This guide includes topic which might not be on this exam (but which might be on the final). It is also possible that something not specifically mentioned on the guide may be on the exam. Howe ...
The structure and formation of the Solar System
... • These eventually become the foundation for our planets • Some theories show this process to take almost the age of the solar system itself (see the Origin and Evolution of the Solar Sytem – Woolfson) for planets to form, and that the sun should be ...
... • These eventually become the foundation for our planets • Some theories show this process to take almost the age of the solar system itself (see the Origin and Evolution of the Solar Sytem – Woolfson) for planets to form, and that the sun should be ...
The Galaxy–Dark Matter Connection
... Many environmental processes have been proposed. Perhaps the most natural one is starvation (or strangulation): Infalling gas is mainly accreted by the central galaxy. Satellites galaxies (slowly) starve. This is the only environmental process currently included in semi-analytical models. Is this go ...
... Many environmental processes have been proposed. Perhaps the most natural one is starvation (or strangulation): Infalling gas is mainly accreted by the central galaxy. Satellites galaxies (slowly) starve. This is the only environmental process currently included in semi-analytical models. Is this go ...
EXAM II REVIEW - University of Maryland: Department of
... What does Einstein’s famous equation mean? How can we apply it to the Sun? ...
... What does Einstein’s famous equation mean? How can we apply it to the Sun? ...
NEUTRON STAR?
... • We will be holding an optional observing night this coming Tuesday, Nov. 8th from 7-9 p.m. on the Science Center roof. We'll be looking at Mars, stellar clusters, binary stars, and more... • Because we live in lovely cloudy Boston, we have to prepare for inclement weather. We will make an announce ...
... • We will be holding an optional observing night this coming Tuesday, Nov. 8th from 7-9 p.m. on the Science Center roof. We'll be looking at Mars, stellar clusters, binary stars, and more... • Because we live in lovely cloudy Boston, we have to prepare for inclement weather. We will make an announce ...
Binary Star Systems
... hundreds of years to pass through one orbit. For example, astronomers hypothesize that our Sun may have a “stellar companion” of low mass beyond Pluto. Cool huh! ...
... hundreds of years to pass through one orbit. For example, astronomers hypothesize that our Sun may have a “stellar companion” of low mass beyond Pluto. Cool huh! ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.