* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dark matter wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic dust wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Andromeda Galaxy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Globular cluster wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Hubble's law wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Open cluster wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
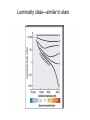
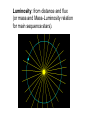
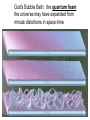
NOTES: Characteristics of Galaxies Classification: The Hubble Tuning Fork Elliptical: E0--E7 Spheroids, E0 is spherical, E7 least spherical. Population II stars, little dust, almost no star formation. Normal Spirals: Sa, Sb, Sc Sa is most tightly wound, Sc least. Population I stars in disk, Pop. II in nucleus. Dust and star formation in disk. Barred Spirals: Sba, Sbb, Sbc Have bars across nucleus, Same winding rules as normal spirals. Same content as normal. Irregulars: No definite shape. Ex. Large and small Magellanic clouds. Dominate universe by number, although generally smaller. Star formation, but less dust than disks. Peculiar: (Pec) Have a definite form, but with peculiarities. Radio jets or other strangeness. The Hubble Tuning Fork—Classification of Galaxies Regular and dwarf ellipticals have no dust and are made up of old Pop. II stars No dust—no aliens! Supergiant Ellipticals as in Coma rich cluster (rich in dust), formed from galactic mergers? S0 Galaxy in Sextans (the sextant) no spirals. M64—the ‘black eye’ galaxy Sa classification Irregular galaxies (Irr): about ½ of galaxies are Irr. Near the Milky Way Peculiar Galaxies (Pec) have a shape, but a ding. NGC4631 Pec class spiral galaxy with a ding. Luminosity class—similar to stars Fritz Zwicky discovered dark matter in galactic clusters in 1930s. Galactic mass for large spirals can be Determined from galactic rotation curves. Which implies the existence of dark matter (not seen). About half is ordinary (baryonic), but other half is exotic. WIMPS, etc.? We can also find mass from movement in a binary galaxy system or cluster. Distance: Standard candles--Cepheids, Supernova type Ia, standard galaxies like brightest spiral or Supergiant ellipticals in Cluster cores. If all else fails, Hubble's Law. Hubble's Law: v = Ho d. Velocity from redshift is proportional to distance. Hubble’s constant = Ho = 70 km/s/Mpc (Friedmann in early ‘1990’s). Observations of redshift first done by Milton Humason, a janitor at Mt. Wilson Observatory (working for Edwin Hubble. Diameter: from distance and angular diameter. Diameter = distance times angle (in radians) How do we get luminosity? Luminosity: from distance and flux (or mass and Mass-Luminosity relation for main sequence stars). NOTES: Where are you? You are here--> Earth, Solar System, Milky Way Galaxy... The Local Group: a galaxy 'poor' cluster of 27 galaxies: three large spirals, 12 dwarf ellipticals, 4 ellipticals, and 8 Irr. Dust in the plane of the Milky Way may obscure more. The Local (Virgo) Supercluster: Pancake-shaped. Composed of the Virgo Cluster (a 'rich' cluster) and about 100 other clusters including Local Grp. We are falling toward Virgo Cluster, which has three supergiant ellipticals (M87 contains accretion disk indicating BH or WH in center--a quadrillion solar masses!) The Pisces-Cetus Complex: may include 400 rich (and lots of poor) clusters. Brent Tully. Is the Universe homogeneous? God's Bubble Bath: Galaxy superclusters seem to from in bubble structures and filaments with Voids 100-500 million LY across. Some call this the Cellular Universe. The Great Wall and The Stick Man--supercluster structures. The Great Attractor--hidden by Milky Way Dust in Centaurus. 1017 Mo! May be dense giant supercluster with lots of dark matter. Tens of thousands of galaxies are falling into it, ignoring the Hubble Flow. What is your cosmic address? Earth, Solar System, Milky Way, then… The local group—our galaxy cluster--a 'poor' cluster of 27 galaxies: three large spirals, 12 dwarf ellipticals, 4 ellipticals, and 8 Irr. Dust in the plane of the Milky Way may obscure more. Then the Local (or Virgo) Supercluster The Local (Virgo) Supercluster: Pancake-shaped. Composed of the Virgo Cluster (a 'rich' cluster) and about 100 other clusters including Local Grp. We are falling toward Virgo Cluster, which has three supergiant ellipticals. M87 in Virgo contains accretion disk indicating BH or WH in center--a quadrillion solar masses! BH is 2 billion solar masses. Accretion disk is shown on the right. In core: An X-ray image of the rich galaxy cluster Abell 2142, taken with the Chandra Observatory. This cluster is clearly elongated, and is believed to be the result of a recent merger between two clusters which have fallen together along the long axis. A larger view! Galaxy superclusters seem to form in bubble structures and filaments with Voids 100-500 million LY across. Some call this the Cellular Universe. God's Bubble Bath: the quantum foam the universe may have expanded from minute distortions in space-time. The Great Attractor —a big lump in the Universe? Great Attractor: hidden by Milky Way Dust in Centaurus. 1017 Msun! May be dense giant supercluster with lots of dark matter. Tens of thousands of galaxies are falling into it, ignoring the Hubble Flow. Alan Dressler, Sandy Faber, and The Seven Samurai from Harvard discovered it. At largest scale? Homogeneous? Yes. Confirmed by observations.