Global Impact of WWII
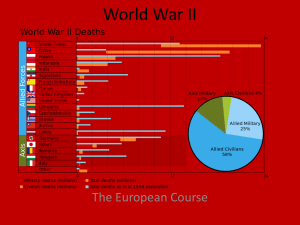
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
world war ii
... the war was to have such a big bomber force yourself that no one would dare attack you. (In the popular 1936 film of H.G. Wells’s Things to Come there is a scene where massive waves of enemy bombers fly over the city and destroy it). b. Part of the initial thinking with the emphasis on bombers is th ...
... the war was to have such a big bomber force yourself that no one would dare attack you. (In the popular 1936 film of H.G. Wells’s Things to Come there is a scene where massive waves of enemy bombers fly over the city and destroy it). b. Part of the initial thinking with the emphasis on bombers is th ...
Global Impact of World War II
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
AP EH CH - Wichita Falls ISD
... sent troops into the demilitarized Rhineland 9. France would not respond to German troops being sent into the Rhineland without British support and the London Times summed up British sentiments when it noted that the Germans were only “going into their own back garden.” 10. as Hitler’s popularity gr ...
... sent troops into the demilitarized Rhineland 9. France would not respond to German troops being sent into the Rhineland without British support and the London Times summed up British sentiments when it noted that the Germans were only “going into their own back garden.” 10. as Hitler’s popularity gr ...
Global Impact of WWII
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
1 - Eldred Central School
... the United States felt obligated to honor its commitments to its allies United States interests were threatened the public had elected Presidents who supported expansion American manufacturers lobbied for sales to belligerents ...
... the United States felt obligated to honor its commitments to its allies United States interests were threatened the public had elected Presidents who supported expansion American manufacturers lobbied for sales to belligerents ...
pptx
... joined the Axis Powers • Mussolini wanted to build another Italian Empire but fell in Greece and Egypt. • Hitler had hoped to take Libya and North Africa in early 1941 but the British stopped Erwin Rommel in October in the Battle of El ...
... joined the Axis Powers • Mussolini wanted to build another Italian Empire but fell in Greece and Egypt. • Hitler had hoped to take Libya and North Africa in early 1941 but the British stopped Erwin Rommel in October in the Battle of El ...
my Fascism/World War Two Study Guide
... Treaty of Versailles -1919 Treaty ending ww1. Punishes Germany with War Guilt Clause Leads to rise of Hitler. Franklyn Delano Roosevelt (FDR) – US President from pre ww2 until death before end of war Neville Chamberlin – English Prime Minister, participated in Munich Conference. “Peace in our Time” ...
... Treaty of Versailles -1919 Treaty ending ww1. Punishes Germany with War Guilt Clause Leads to rise of Hitler. Franklyn Delano Roosevelt (FDR) – US President from pre ww2 until death before end of war Neville Chamberlin – English Prime Minister, participated in Munich Conference. “Peace in our Time” ...
Chapter 25
... who opposed U.S. intervention in the war. This committee became famous when it was endorsed by many large businessmen like Sears executive Robert. E. Wood and many famous celebrities like Henry Ford and Robert Young. Within a year of being founded, America first had recruited over 850,000 members. 1 ...
... who opposed U.S. intervention in the war. This committee became famous when it was endorsed by many large businessmen like Sears executive Robert. E. Wood and many famous celebrities like Henry Ford and Robert Young. Within a year of being founded, America first had recruited over 850,000 members. 1 ...
the timeline in worksheet format
... try (and fail) to defeat those of the British RAF as the first step towards an invasion of Britain. Mission Roosevelt: 1941 (Summer): Hitler invades Russia. His armies fail to get a quick victory and his winter defeat at the Battle of Stalingrad is a turning point. Mission Stalin: 1941 (Dec): Pearl ...
... try (and fail) to defeat those of the British RAF as the first step towards an invasion of Britain. Mission Roosevelt: 1941 (Summer): Hitler invades Russia. His armies fail to get a quick victory and his winter defeat at the Battle of Stalingrad is a turning point. Mission Stalin: 1941 (Dec): Pearl ...
Cabinet memorandum by the Foreign Secretary, E. Bevin
... intensify the struggle. It denounced the “Truman-Marshall Plan as a component part of the general policy of the United States and Great Britain for “strengthening imperialism and stifling democracy”8. It called upon the European Communist parties to head the resistance to these plans, to rally and u ...
... intensify the struggle. It denounced the “Truman-Marshall Plan as a component part of the general policy of the United States and Great Britain for “strengthening imperialism and stifling democracy”8. It called upon the European Communist parties to head the resistance to these plans, to rally and u ...
Japanese Path to War
... World War II had its roots in the beliefs of Adolf Hitler. He believed that Germans belonged to a so-called Aryan race that was superior to all other races and nationalities. He also believed that Germany was capable of building a great civilization and needed more land in order to become a great po ...
... World War II had its roots in the beliefs of Adolf Hitler. He believed that Germans belonged to a so-called Aryan race that was superior to all other races and nationalities. He also believed that Germany was capable of building a great civilization and needed more land in order to become a great po ...
AP 29 TEST BANK
... d. Had relatively little impact because fuel reserves throughout Europe remained adequate e. Brought about an East-West rapprochement as the Eastern Bloc provided much need coal The collapse of Communist rule throughout Eastern Europe occurred peacefully in all of the following countries EXCEPT a. C ...
... d. Had relatively little impact because fuel reserves throughout Europe remained adequate e. Brought about an East-West rapprochement as the Eastern Bloc provided much need coal The collapse of Communist rule throughout Eastern Europe occurred peacefully in all of the following countries EXCEPT a. C ...
World War II Chapter 17 Section 1 Where did we leave off?
... ► The United States sends huge amounts of money and supplies to Europe to help the rebuilding process. ► Stalin would not allow any Eastern European countries to accept aid from the United States. ► This was a plan to get Europe back on its feet. ...
... ► The United States sends huge amounts of money and supplies to Europe to help the rebuilding process. ► Stalin would not allow any Eastern European countries to accept aid from the United States. ► This was a plan to get Europe back on its feet. ...
World War II Notes - Doral Academy Preparatory
... less important than the nation. • Glorifies violence, believes it is needed to “prove” strength of a people. • Uses nationalism and racism. • Dictatorships. • Italy and then Germany became fascist. ...
... less important than the nation. • Glorifies violence, believes it is needed to “prove” strength of a people. • Uses nationalism and racism. • Dictatorships. • Italy and then Germany became fascist. ...
Paths to War: The Drives for Empire
... European countries. Prime Minister of Great Britain, Neville Chamberlain, boasted that the agreement meant “peace for our time.” Instead, Hitler just became more bold, believing that other countries would not interfere with his plans. ...
... European countries. Prime Minister of Great Britain, Neville Chamberlain, boasted that the agreement meant “peace for our time.” Instead, Hitler just became more bold, believing that other countries would not interfere with his plans. ...
Denazification
... Process instituted by the Allies after World War II to remove all traces of Nazism from Germany. Even before the war ended, the Allied leaders met at the Yalta Conference where they agreed to wipe out the Nazi Party and its influence. This view was restated in the Potsdam Agreement of August 1945. B ...
... Process instituted by the Allies after World War II to remove all traces of Nazism from Germany. Even before the war ended, the Allied leaders met at the Yalta Conference where they agreed to wipe out the Nazi Party and its influence. This view was restated in the Potsdam Agreement of August 1945. B ...
World War II * The Battlefronts
... Africa and Europe 1942 & 1943 • Operation Torch – taking of North Africa. What was important about North Africa? • 2nd Front – Stalin was calling for a 2nd front. In Feb., 1943, the Soviets stopped the German advance at the Battle of Stalingrad. Began slow push back. • U.S./British would invade Sic ...
... Africa and Europe 1942 & 1943 • Operation Torch – taking of North Africa. What was important about North Africa? • 2nd Front – Stalin was calling for a 2nd front. In Feb., 1943, the Soviets stopped the German advance at the Battle of Stalingrad. Began slow push back. • U.S./British would invade Sic ...
World War II Studyguide
... Of the more than 16 million people who served in the military, what different groups were represented? What sacrifices did GIs make for their country? ...
... Of the more than 16 million people who served in the military, what different groups were represented? What sacrifices did GIs make for their country? ...
WWII - PHS-Test-Bank
... Which of the following was NOT a reason France and England followed this policy ? A) to avoid war; B) didn’t know about it; C) thought Stalin in Russia was a greater threat; D) many French & English people thought Hitler’s actions were okay. At the Munich Conference, what did Hitler Promise Chamberl ...
... Which of the following was NOT a reason France and England followed this policy ? A) to avoid war; B) didn’t know about it; C) thought Stalin in Russia was a greater threat; D) many French & English people thought Hitler’s actions were okay. At the Munich Conference, what did Hitler Promise Chamberl ...
The Allies Turn the Tide
... Germans Defeated at Stalingrad A major turning point occurred in the Soviet Union. After their lightning advance in 1941, the Germans were stalled outside Moscow and Leningrad. In 1942, Hitler launched a new offensive. This time, he aimed for the rich oil fields of the south. His troops, however, go ...
... Germans Defeated at Stalingrad A major turning point occurred in the Soviet Union. After their lightning advance in 1941, the Germans were stalled outside Moscow and Leningrad. In 1942, Hitler launched a new offensive. This time, he aimed for the rich oil fields of the south. His troops, however, go ...
Western betrayal

The concept of Western betrayal refers to the view that the United Kingdom and France failed to meet their legal, diplomatic, military and moral obligations with respect to the Czech and Polish nations of Central and Eastern Europe in the prelude to and aftermath of the Second World War.In particular, it refers to Czechoslovakia's treatment during the Munich Agreement and subsequent occupation and partition by Nazi Germany, Hungary (The First Vienna Award) and Poland (Invasion of Zaolzie), as well as the failure of the Western allies to aid Poland upon its invasion by Germany and the USSR in 1939. The same concept also refers to the concessions made by the United States and the United Kingdom to the USSR during the Tehran, Yalta and Potsdam conferences, to their stance during the Warsaw Uprising, and some other events, which allocated the region to the Soviet sphere of influence and created the Eastern Bloc.Historically, such views were intertwined with some of the most significant geopolitical events of the 20th century, including the rise and empowerment of the Third Reich (Nazi Germany), the rise of the Soviet Union (USSR) as a dominant superpower with control of large parts of Europe, and various treaties, alliances, and positions taken during and after World War II, and so on into the Cold War.