
TIMELINE – WW II AUG. 23, 1939 – Nonagression Pact: 10 yr
... Summer of 1940 – Battle of Britain (continued until May 1941); Winston Churchill rallied the Brits Aug. 1940 – US became aware of Japan’s plans to take SE Asian colonies from Europe Sept. 1940 – June 1942 – Allied and Axis powers fight in North Africa; victories go back and forth Early 1941 – Bulgar ...
... Summer of 1940 – Battle of Britain (continued until May 1941); Winston Churchill rallied the Brits Aug. 1940 – US became aware of Japan’s plans to take SE Asian colonies from Europe Sept. 1940 – June 1942 – Allied and Axis powers fight in North Africa; victories go back and forth Early 1941 – Bulgar ...
The Home Front - Fort Bend ISD
... Even before the battle in North Africa was won, Roosevelt, Churchill, and their commanders met in Casablanca. The two leaders also discussed where to strike next. Churchill thought it would be safer to first attack Italy. The Italian campaign got off to a good start with the capture of Sicily in the ...
... Even before the battle in North Africa was won, Roosevelt, Churchill, and their commanders met in Casablanca. The two leaders also discussed where to strike next. Churchill thought it would be safer to first attack Italy. The Italian campaign got off to a good start with the capture of Sicily in the ...
Timeline
... September 2: General Douglas MacArthur, named Supreme Commander of Allied Powers in Japan, accepts the formal surrender of Japan aboard the battleship USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay. November 20: Nuremberg War Crimes Trials begin in Germany. The victorious Allies (the U.S., France, Great Britain and the ...
... September 2: General Douglas MacArthur, named Supreme Commander of Allied Powers in Japan, accepts the formal surrender of Japan aboard the battleship USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay. November 20: Nuremberg War Crimes Trials begin in Germany. The victorious Allies (the U.S., France, Great Britain and the ...
World War I - Toolbox Pro
... An environment in Germany that allowed Hitler to rise to power WW II Hitler’s reasons to rebuild an army and take over lands ...
... An environment in Germany that allowed Hitler to rise to power WW II Hitler’s reasons to rebuild an army and take over lands ...
Conflicting Superpowers WHAP/Napp “In 1946, in a speech at
... Germany’s political division by building the Berlin Wall, a structure designed primarily to prevent its citizens from fleeing to the noncommunist western part of the city. A more explosive crisis erupted in Korea, where the Second World War had left Soviet troops in control north of the thirty-eight ...
... Germany’s political division by building the Berlin Wall, a structure designed primarily to prevent its citizens from fleeing to the noncommunist western part of the city. A more explosive crisis erupted in Korea, where the Second World War had left Soviet troops in control north of the thirty-eight ...
1. The purpose of the Marshall Plan was to do
... D. to attract foreign economic investments 19. What was one outcome of World War II? A. England and France increased their overseas colonial possessions. B. The communists gained control over most of Western Europe. C. Japan and Germany became dominant military powers in their regions. D. The Soviet ...
... D. to attract foreign economic investments 19. What was one outcome of World War II? A. England and France increased their overseas colonial possessions. B. The communists gained control over most of Western Europe. C. Japan and Germany became dominant military powers in their regions. D. The Soviet ...
World War II: The Road to War
... F. Hitler and Mussolini: Rise of the Rome-Berlin Axis, I. Spanish Civil War begins 1936. - Viewed as an ideological struggle between Fascism, led by General Francisco Franco and Republicanism, the loyalists. - Hitler and Mussolini dispatched troops and supplies to back Franco. This close cooperatio ...
... F. Hitler and Mussolini: Rise of the Rome-Berlin Axis, I. Spanish Civil War begins 1936. - Viewed as an ideological struggle between Fascism, led by General Francisco Franco and Republicanism, the loyalists. - Hitler and Mussolini dispatched troops and supplies to back Franco. This close cooperatio ...
US Hisory
... 47. What was the “over-age destroyer” deal with England? 48. What was the Lend-Lease Act? 49. In what area were the U.S. and Germany coming into armed conflict, in spite of American “neutrality”? 50. What nation was attacked by Hitler in June of 1941? 51. What was the Panay incident? 52. What nation ...
... 47. What was the “over-age destroyer” deal with England? 48. What was the Lend-Lease Act? 49. In what area were the U.S. and Germany coming into armed conflict, in spite of American “neutrality”? 50. What nation was attacked by Hitler in June of 1941? 51. What was the Panay incident? 52. What nation ...
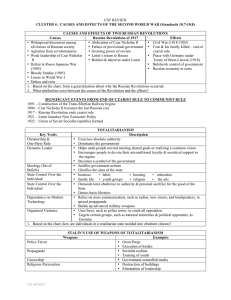
CST REVIEW CLUSTER 4: CAUSES AND EFFECTS
... • Natural resources depleted • Heavy loss of life • Major cities in shambles ...
... • Natural resources depleted • Heavy loss of life • Major cities in shambles ...
Final Exam Review - Spring 2006
... • Hitler, Mussolini, and Tojo did not cause World War II. • The Treaty of Versailles which ended World War I is the chief cause of World War II. – This is the single most important cause of WWII! ...
... • Hitler, Mussolini, and Tojo did not cause World War II. • The Treaty of Versailles which ended World War I is the chief cause of World War II. – This is the single most important cause of WWII! ...
UNIT 1 - StudyGuide.PK
... During the years 1945 –48, all the countries which had been occupied by the Red Army at the end of the war were brought under Soviet control (Poland, Bulgaria, Romania, Hungary – the Baltic States of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania had been absorbed in 1940 and then kept as part of the Soviet Union). ...
... During the years 1945 –48, all the countries which had been occupied by the Red Army at the end of the war were brought under Soviet control (Poland, Bulgaria, Romania, Hungary – the Baltic States of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania had been absorbed in 1940 and then kept as part of the Soviet Union). ...
-The Cold War was the continuing state of conflict, tension and
... - After the United States and the countries of western Europe established the North Atlantic Treaty Organization military alliance in 1949, Soviet leaders felt surrounded by hostile forces just when they were trying to recover from the terrible losses sustained in the war against Axis. (Bulliet, 822 ...
... - After the United States and the countries of western Europe established the North Atlantic Treaty Organization military alliance in 1949, Soviet leaders felt surrounded by hostile forces just when they were trying to recover from the terrible losses sustained in the war against Axis. (Bulliet, 822 ...
World War II
... Conclusion of WWII • Most devastating war in history • Over 50 million killed in 6 years (20 million plus in Soviet Union) • Underlying cause of WWII? • WWII ends - Cold War begins ...
... Conclusion of WWII • Most devastating war in history • Over 50 million killed in 6 years (20 million plus in Soviet Union) • Underlying cause of WWII? • WWII ends - Cold War begins ...
World War II PowerPoint
... ‘Noose’ closed around Berlin and Hitler’s Germany British/American forces from the West; Soviets from the East Hitler and his wife, Eva Braun, committed suicide Germany surrendered unconditionally on May 7th & signed the surrender ...
... ‘Noose’ closed around Berlin and Hitler’s Germany British/American forces from the West; Soviets from the East Hitler and his wife, Eva Braun, committed suicide Germany surrendered unconditionally on May 7th & signed the surrender ...
Global Struggles
... – Great Britain’s Royal Air Force and the United States’ Eighth Army Air Force had been bombing Germany every month – This bombing campaign did not destroy Germany’s economy or undermine their morale but. . . – It did cause a severe oil shortage and wrecked the railroad system and destroyed many air ...
... – Great Britain’s Royal Air Force and the United States’ Eighth Army Air Force had been bombing Germany every month – This bombing campaign did not destroy Germany’s economy or undermine their morale but. . . – It did cause a severe oil shortage and wrecked the railroad system and destroyed many air ...
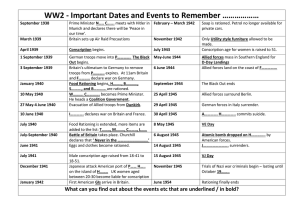
Important Dates and Events to Remember ………………
... Prime Minister N….. C……. meets with Hitler in February – March 1942 Munich and declares there will be ‘Peace in our time’. Britain sets up Air Raid Precautions November 1942 ...
... Prime Minister N….. C……. meets with Hitler in February – March 1942 Munich and declares there will be ‘Peace in our time’. Britain sets up Air Raid Precautions November 1942 ...
Global_Impact_of_WWII[1]
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
2nd SEMESTER FINAL STUDY GUIDE
... 51. Briefly describe the Vietnam War. What was the outcome? US fought to keep communism from taking hold, we were not successful. ...
... 51. Briefly describe the Vietnam War. What was the outcome? US fought to keep communism from taking hold, we were not successful. ...
Document
... – Hitler seizes Leningrad, tries to starve the people outdoesn’t work – Moves on to Moscow: mistake- winter is comingcosts 500,000 German lives! ...
... – Hitler seizes Leningrad, tries to starve the people outdoesn’t work – Moves on to Moscow: mistake- winter is comingcosts 500,000 German lives! ...
20 WWII
... In 1936, Hitler again violated the Versailles Treaty and sent his army into the Rhineland, which was adjacent to France and supposed to remain demilitarized. Again, France and Great Britain protested, but took no action; and again Hitler remained convinced that Great Britain and France would not fi ...
... In 1936, Hitler again violated the Versailles Treaty and sent his army into the Rhineland, which was adjacent to France and supposed to remain demilitarized. Again, France and Great Britain protested, but took no action; and again Hitler remained convinced that Great Britain and France would not fi ...
Global Impact of WWII.ppt
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
Global Impact of WWII
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
... ■ The United States and the Soviet Union split sharply after the war. The USA, the world’s richest and most powerful country, suffered 400,000 deaths, but its cities and factories remained intact. The USSR had at least 50 times as many fatalities and many Soviet cities were demolished. Despite the d ...
Western betrayal

The concept of Western betrayal refers to the view that the United Kingdom and France failed to meet their legal, diplomatic, military and moral obligations with respect to the Czech and Polish nations of Central and Eastern Europe in the prelude to and aftermath of the Second World War.In particular, it refers to Czechoslovakia's treatment during the Munich Agreement and subsequent occupation and partition by Nazi Germany, Hungary (The First Vienna Award) and Poland (Invasion of Zaolzie), as well as the failure of the Western allies to aid Poland upon its invasion by Germany and the USSR in 1939. The same concept also refers to the concessions made by the United States and the United Kingdom to the USSR during the Tehran, Yalta and Potsdam conferences, to their stance during the Warsaw Uprising, and some other events, which allocated the region to the Soviet sphere of influence and created the Eastern Bloc.Historically, such views were intertwined with some of the most significant geopolitical events of the 20th century, including the rise and empowerment of the Third Reich (Nazi Germany), the rise of the Soviet Union (USSR) as a dominant superpower with control of large parts of Europe, and various treaties, alliances, and positions taken during and after World War II, and so on into the Cold War.















![Global_Impact_of_WWII[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011856457_1-a3d52b9686ba52a9e03ef7bd964653ae-300x300.png)





