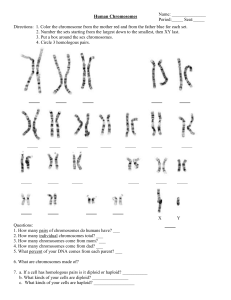
MOCK TEST for mitosi.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 15. Prior to the 8- cell stage, an embryo is said to be ? . 16. A hollow ball of cells that the embryo develops into is called a ? 17. Cells don’t age, but they do only divide a set number of times. Name a human cell type which never divides. 18. Cancer cells that can dislodge and spread to another ...
... 15. Prior to the 8- cell stage, an embryo is said to be ? . 16. A hollow ball of cells that the embryo develops into is called a ? 17. Cells don’t age, but they do only divide a set number of times. Name a human cell type which never divides. 18. Cancer cells that can dislodge and spread to another ...
The Cell Cycle, Mitosis and Meiosis
... The spindle fibers shorten, pulling the sister chromatids apart to opposite ends of the cell. Once apart they are now each called Chromosomes. ...
... The spindle fibers shorten, pulling the sister chromatids apart to opposite ends of the cell. Once apart they are now each called Chromosomes. ...
Meiosis and Mendelian Genetics Digital
... genetic crosses Distinguish between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids Distinguish between the terms haploid and diploid Differentiate between gametogenesis in males and females Explain how crossing-over leads to genetic diversity Explain the relationship between Mendel’s law of independen ...
... genetic crosses Distinguish between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids Distinguish between the terms haploid and diploid Differentiate between gametogenesis in males and females Explain how crossing-over leads to genetic diversity Explain the relationship between Mendel’s law of independen ...
Chapter 10 PowerPoint - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web Pages
... - results in FOUR cells from the parent ...
... - results in FOUR cells from the parent ...
Meiosis Chapeter 11 section #4
... • Full set = 2N=Diploid are the sets of • N= pair •each # pairs • 1 pair from mother • 1 pair from father • Humans= 23 pairs or • 46 total ...
... • Full set = 2N=Diploid are the sets of • N= pair •each # pairs • 1 pair from mother • 1 pair from father • Humans= 23 pairs or • 46 total ...
cell-division-review-no-answers
... ____ 1. Each human somatic cell contains two copies of each chromosome for a total of 23 homologous chromosomes. ____ 2. Gametes are diploid so that when fertilization occurs, the resulting zygote will have the characteristic number of chromosomes for that species. ____ 3. Cells spend most of their ...
... ____ 1. Each human somatic cell contains two copies of each chromosome for a total of 23 homologous chromosomes. ____ 2. Gametes are diploid so that when fertilization occurs, the resulting zygote will have the characteristic number of chromosomes for that species. ____ 3. Cells spend most of their ...
Cellular Reproduction Vocabulary
... 1. DNA—deoxyribonucleic acid; the genetic information passed from parent to offspring 2. chromatin—loose DNA strands (uncoiled) 3. chromosome—the whole X; made of DNA and histone proteins 4. gene—section of a chromosome; each gene codes for a specific protein 5. sister chromatid—half of a chromosome ...
... 1. DNA—deoxyribonucleic acid; the genetic information passed from parent to offspring 2. chromatin—loose DNA strands (uncoiled) 3. chromosome—the whole X; made of DNA and histone proteins 4. gene—section of a chromosome; each gene codes for a specific protein 5. sister chromatid—half of a chromosome ...
Cellular Reproduction
... • “All cells come from previously existing cells.” (Virchow, 1858) • Continuity of life (binary fission in prokaryotes, mitosis and/or meiosis in eukaryotes) from generation to generation. ...
... • “All cells come from previously existing cells.” (Virchow, 1858) • Continuity of life (binary fission in prokaryotes, mitosis and/or meiosis in eukaryotes) from generation to generation. ...
MEIOSIS 19 FEBRUARY 2014 Lesson Description
... ultraviolet light and the other one (B) was left in the dark. The two Petri dishes were examined after 5 days. In A, all but one of the bacterial colonies were red. One bacterial colony was white. In B, all the ...
... ultraviolet light and the other one (B) was left in the dark. The two Petri dishes were examined after 5 days. In A, all but one of the bacterial colonies were red. One bacterial colony was white. In B, all the ...
Thomas Hunt Morgan`s Conclusions
... Thomas Hunt Morgan’s Conclusions - modified Mendel’s work - used the fruit fly (Drosophila) to study inheritance Why use fruit flies? - Reproduce rapidly - Large number of offspring to study - Life cycle is only 10 – 15 days so it is possible to study many generations in a short period of time - Sma ...
... Thomas Hunt Morgan’s Conclusions - modified Mendel’s work - used the fruit fly (Drosophila) to study inheritance Why use fruit flies? - Reproduce rapidly - Large number of offspring to study - Life cycle is only 10 – 15 days so it is possible to study many generations in a short period of time - Sma ...
Male Anatomy
... to reduce the number of chromosomes by half. This must occur prior to sexual reproduction. The cell at the top contains two homologous pairs of chromosomes, for a total of four chromosomes. The final products of meiosis are four daughter cells. Each cell contains one chromatid from each original hom ...
... to reduce the number of chromosomes by half. This must occur prior to sexual reproduction. The cell at the top contains two homologous pairs of chromosomes, for a total of four chromosomes. The final products of meiosis are four daughter cells. Each cell contains one chromatid from each original hom ...
Genes, Alleles, and Meiosis PowerPoint
... • Each of a human’s 46 chromosomes has thousands of genes, so the presence of all chromosomes is essential for normal functioning Humans who are missing a chromosome don’t survive past the embryo stage Humans with more than two copies of a chromosome may survive but will not develop properly (this ...
... • Each of a human’s 46 chromosomes has thousands of genes, so the presence of all chromosomes is essential for normal functioning Humans who are missing a chromosome don’t survive past the embryo stage Humans with more than two copies of a chromosome may survive but will not develop properly (this ...
BIOL 1406 - Meiosis - Chapter 13
... difference between mitosis and meiosis? 1. A single cell is divided into two cells in mitosis and four cells in meiosis. 2. Mitosis produces haploid cells, and meiosis produces diploid cells. 3. Mitosis involves two cellular divisions, and meiosis has only one cellular division. 4. The chromosomes r ...
... difference between mitosis and meiosis? 1. A single cell is divided into two cells in mitosis and four cells in meiosis. 2. Mitosis produces haploid cells, and meiosis produces diploid cells. 3. Mitosis involves two cellular divisions, and meiosis has only one cellular division. 4. The chromosomes r ...
-apsis = juncture (synapsis: the pairing of replicated homologous
... the cell cycle to organize the cell's microtubules) telos- = an end (telophase: the final stage of mitosis in which daughter nuclei are forming and cytokinesis has typically begun) trans- = across; -form = shape (transformation: the process that converts a normal cell into a cancer cell) ...
... the cell cycle to organize the cell's microtubules) telos- = an end (telophase: the final stage of mitosis in which daughter nuclei are forming and cytokinesis has typically begun) trans- = across; -form = shape (transformation: the process that converts a normal cell into a cancer cell) ...
Meiosis
... Meiosis Overview Gametes produced during meiosis are needed for sexual reproduction Cells (diploid) divide twice resulting in 4 daughter cells (haploid) Each cell has half the number of chromosomes as the original cell Each new cell is genetically different ...
... Meiosis Overview Gametes produced during meiosis are needed for sexual reproduction Cells (diploid) divide twice resulting in 4 daughter cells (haploid) Each cell has half the number of chromosomes as the original cell Each new cell is genetically different ...
Mitosis and Meiosis
... –The cell just finished dividing so in Gap 1 the cell is recovering from mitosis ...
... –The cell just finished dividing so in Gap 1 the cell is recovering from mitosis ...
9-10 Review Questions and Essay Exams
... 3. Are gametes haploid or diploid? Be able to figure out the diploid number of an organism when given the haploid number (or vice versa). 4. What is a fertilized egg called? 5. What is another name for a tetrad? What is the synaptonemal complex? To what does chiasma refer? When does crossing over oc ...
... 3. Are gametes haploid or diploid? Be able to figure out the diploid number of an organism when given the haploid number (or vice versa). 4. What is a fertilized egg called? 5. What is another name for a tetrad? What is the synaptonemal complex? To what does chiasma refer? When does crossing over oc ...
Endocrinology 3
... Protooncogenes = Normal gene precursors of oncogenes I V Mutational Agents I V Oncogenes = Gene associated with abnormal cell growth ...
... Protooncogenes = Normal gene precursors of oncogenes I V Mutational Agents I V Oncogenes = Gene associated with abnormal cell growth ...
AP Chapter 13 Study Guide: The Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
... ARE YOU AWAKE AND ALERT??? WHAT FOLLOWS IS CRITIAL!!! 23. What does it mean to segregate? _____________________ Write Mendel’s Law of Segregation _________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... ARE YOU AWAKE AND ALERT??? WHAT FOLLOWS IS CRITIAL!!! 23. What does it mean to segregate? _____________________ Write Mendel’s Law of Segregation _________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
Meiosis and Variation
... Contraction of the _________ fibres results in separation of whole chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. This contrasts with mitosis ______________________________ __________________. Note: the orientation of one bivalent at metaphase is independent of the orientation of other bivalents. Thus, ...
... Contraction of the _________ fibres results in separation of whole chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell. This contrasts with mitosis ______________________________ __________________. Note: the orientation of one bivalent at metaphase is independent of the orientation of other bivalents. Thus, ...
Section 6.1 Reinforcement
... that will undergo meiosis and form gametes. Gametes are sex cells. They include eggs and sperm cells. Each species has a characteristic number of chromosomes per cell. Body cells are diploid, which means that each cell has two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent. Gametes are haploid, whi ...
... that will undergo meiosis and form gametes. Gametes are sex cells. They include eggs and sperm cells. Each species has a characteristic number of chromosomes per cell. Body cells are diploid, which means that each cell has two copies of each chromosome, one from each parent. Gametes are haploid, whi ...
1. Define the terms chromosome, chromatid, centromere, chromatin
... JUST A SAMPLE OF GENETICS QUESTIONS ...
... JUST A SAMPLE OF GENETICS QUESTIONS ...
Meiosis
Meiosis /maɪˈoʊsɨs/ is a specialized type of cell division which reduces the chromosome number by half. This process occurs in all sexually reproducing single-celled and multi-celled eukaryotes, including animals, plants, and fungi. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The two meiotic divisions are known as meiosis I and meiosis II. Before meiosis begins, during S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA of each chromosome is replicated so that it consists of two identical sister chromatids. In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair with each other and can exchange genetic material in a process called chromosomal crossover. The homologous chromosomes are then segregated into two new daughter cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end of meiosis I, sister chromatids remain attached and may differ from one another if crossing-over occurred. In meiosis II, the two cells produced during meiosis I divide again. Sister chromatids segregate from one another to produce four total daughter cells. These cells can mature into various types of gametes such as ova, sperm, spores, or pollen.Because the number of chromosomes is halved during meiosis, gametes can fuse (i.e. fertilization) to form a zygote with a complete chromosome count containing a combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes. Thus, meiosis and fertilization facilitate sexual reproduction with successive generations maintaining the same number of chromosomes. For example, a typical diploid human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total, half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin). Meiosis produces haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with the mother and father each contributing 23 chromosomes. This same pattern, but not the same number of chromosomes, occurs in all organisms that utilize meiosis. Thus, if a species has 30 chromosomes in its somatic cells, it will produce gametes with 15 chromosomes.