"nrr.r"r----147
... If the mitotic process has been normal, the resulting daughter nuclei will contain the same genetic information. This information is an identical copy of the genetic information found in the parent nucleus. Mitosis is usually followed by the dividing of the cytoplasm into two parts. A plasma membran ...
... If the mitotic process has been normal, the resulting daughter nuclei will contain the same genetic information. This information is an identical copy of the genetic information found in the parent nucleus. Mitosis is usually followed by the dividing of the cytoplasm into two parts. A plasma membran ...
The Cell Cycle
... Cell Growth and Cell Division are carefully controlled Not all cells move through the cell cycle at the same rate ...
... Cell Growth and Cell Division are carefully controlled Not all cells move through the cell cycle at the same rate ...
section_10
... 5. Circle the letter(s) of each sentence that is true about external regulators. (3 pts) a. They direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. b. They prevent the cell from entering anaphase until all its chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle. c. They include growth factors. d. The ...
... 5. Circle the letter(s) of each sentence that is true about external regulators. (3 pts) a. They direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle. b. They prevent the cell from entering anaphase until all its chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle. c. They include growth factors. d. The ...
Active Transport
... AGAINST a concentration ____________ gradient. Active transport requires ____________. ENERGY ...
... AGAINST a concentration ____________ gradient. Active transport requires ____________. ENERGY ...
The Endosymbiotic Theory
... apparently empty (F, arrowhead). Fractions show almost empty vacuoles containing an electrondense material in their periphery (G and H). A membrane is clearly seen enclosing the vacuoles (arrow in E; arrowheads in F, G, andH). Bars, 0.1 μm. Seufferheld M, et al. (2003) JBC, 278, 29971-29978. ...
... apparently empty (F, arrowhead). Fractions show almost empty vacuoles containing an electrondense material in their periphery (G and H). A membrane is clearly seen enclosing the vacuoles (arrow in E; arrowheads in F, G, andH). Bars, 0.1 μm. Seufferheld M, et al. (2003) JBC, 278, 29971-29978. ...
Prokaryote vs. Eukaryotic Cell Notes
... Prokaryote vs. Eukaryotic Cell Notes The many different kinds of cells that exist can be divided into two groups. Cells that have DNA loose inside the cell are called Prokaryotic and cells that have a nucleus to hold the DNA are called Eukaryotic. ...
... Prokaryote vs. Eukaryotic Cell Notes The many different kinds of cells that exist can be divided into two groups. Cells that have DNA loose inside the cell are called Prokaryotic and cells that have a nucleus to hold the DNA are called Eukaryotic. ...
Ribosomes
... Ribosomes are small organelles where protein synthesis occurs , it is composed of two subunits , one large and one small . Ribosomes can be found free in the cytoplasm either singly or in groups called poly ribosomes, also can be found attached to endoplasmic reticulum and can be found stored in nuc ...
... Ribosomes are small organelles where protein synthesis occurs , it is composed of two subunits , one large and one small . Ribosomes can be found free in the cytoplasm either singly or in groups called poly ribosomes, also can be found attached to endoplasmic reticulum and can be found stored in nuc ...
Cell City
... Think of the cell as a microscopic city. Like a real city it requires many services to keep it clean and running smoothly. Think of some of the services a real city needs: traffic control, waste disposal, and authority figure just to name a few. Like our imagined city a cell needs the same services. ...
... Think of the cell as a microscopic city. Like a real city it requires many services to keep it clean and running smoothly. Think of some of the services a real city needs: traffic control, waste disposal, and authority figure just to name a few. Like our imagined city a cell needs the same services. ...
Mitosis Meiosis Study Guide.notebook
... helps in growth, maintenance and repair of regular body cells, ...
... helps in growth, maintenance and repair of regular body cells, ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Genetic material duplicated and readies a cell for division into two cells Occurs toward the end of interphase DNA uncoils and each side serves as a template ...
... Genetic material duplicated and readies a cell for division into two cells Occurs toward the end of interphase DNA uncoils and each side serves as a template ...
Adv Biology
... • In 1838 Schleiden proposed that all plants are composed of cells; together with his friend Theodor Schwann he formulated the cell theory of life. Schleiden observed various cell structures and activities such as protoplasmic streaming. • Schleiden also found that certain fungi live on or within th ...
... • In 1838 Schleiden proposed that all plants are composed of cells; together with his friend Theodor Schwann he formulated the cell theory of life. Schleiden observed various cell structures and activities such as protoplasmic streaming. • Schleiden also found that certain fungi live on or within th ...
lecture notes-microbiology-3-Eucaryotes
... - Chloroplasts are relatively large, chlorophyllcontaining, green organelles that are responsible for photosynthesis in algae or plant cells. ...
... - Chloroplasts are relatively large, chlorophyllcontaining, green organelles that are responsible for photosynthesis in algae or plant cells. ...
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function in the Bacteria and Archaea
... Chapter Summary and Essay Questions Chapter 4 deals with the diversity of the two prokaryotic domains, the Bacteria and the Archaea. This is followed by a discussion of the diversity of their cell shape and arrangement. The remaining parts of the chapter deal primarily with cell structures found ext ...
... Chapter Summary and Essay Questions Chapter 4 deals with the diversity of the two prokaryotic domains, the Bacteria and the Archaea. This is followed by a discussion of the diversity of their cell shape and arrangement. The remaining parts of the chapter deal primarily with cell structures found ext ...
Topic III - Parkway C-2
... Define selectively permeable. Distinguish between passive and active transport. Understand why endocytosis and exocytosis are types of active transport. Recognize the sodium-potassium pump as a type of active transport. Day 9 Review Day 10 Test Application Questions: 1. If you were adrift at sea in ...
... Define selectively permeable. Distinguish between passive and active transport. Understand why endocytosis and exocytosis are types of active transport. Recognize the sodium-potassium pump as a type of active transport. Day 9 Review Day 10 Test Application Questions: 1. If you were adrift at sea in ...
Study Guide for Chapter 4 - Cells: Basic Unit of Life
... Study Guide for Chapter 4 - Cells: Basic Unit of Life Below you will find general questions covering the material we discussed from Chapter 4. You are not required to answer these questions. But can you answer them? If not, make sure you find the answer before the day of the test. NOTE: Please under ...
... Study Guide for Chapter 4 - Cells: Basic Unit of Life Below you will find general questions covering the material we discussed from Chapter 4. You are not required to answer these questions. But can you answer them? If not, make sure you find the answer before the day of the test. NOTE: Please under ...
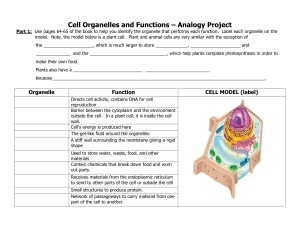
Cell Organelles and Functions – Analogy Project
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
CB - Cell Reproduction presentation.pps
... A. Why is cell division important? 1. cell division - makes new cells 2. this is how unicellular organisms reproduce 3. this is how multicellular organisms grow B. Cell Cycle 1. Length of Cycle a. cell cycle - steps that takes a cell from one cell division to the next b. one complete cell cy ...
... A. Why is cell division important? 1. cell division - makes new cells 2. this is how unicellular organisms reproduce 3. this is how multicellular organisms grow B. Cell Cycle 1. Length of Cycle a. cell cycle - steps that takes a cell from one cell division to the next b. one complete cell cy ...
Cell and Homeostasis
... 1 - Cell division occurs in unicellular organisms and in multicellular organisms. However, the results of cell division are different depending on how many cells an organism has. Unicellular organisms use cell division to reproduce. In multicellular organisms, most cell division occurs in order to r ...
... 1 - Cell division occurs in unicellular organisms and in multicellular organisms. However, the results of cell division are different depending on how many cells an organism has. Unicellular organisms use cell division to reproduce. In multicellular organisms, most cell division occurs in order to r ...
File
... Line up at the equitorial plate (equator) *The mitotic spindle (made of tubes) is complete and extend from each pole (centrioles) to the middle of the cell. ...
... Line up at the equitorial plate (equator) *The mitotic spindle (made of tubes) is complete and extend from each pole (centrioles) to the middle of the cell. ...
HB Unit 3 Homeostasis and Cell Transport
... How Cells Deal with Osmosis • Contractile vacuoles pump excess water from unicellular, freshwater organisms. • Cell walls in plants resist turgor pressure in hypotonic conditions. • Plasmolysis (wilting) occurs in plant cells in hypertonic conditions. • Cytolysis (bursting) occurs in animal cells ...
... How Cells Deal with Osmosis • Contractile vacuoles pump excess water from unicellular, freshwater organisms. • Cell walls in plants resist turgor pressure in hypotonic conditions. • Plasmolysis (wilting) occurs in plant cells in hypertonic conditions. • Cytolysis (bursting) occurs in animal cells ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.