Understanding critical processes and functions
... takes place over longer timescales than those normally represented by observations, and what are the drivers? 2) What are the critical dynamical characteristics that lead to nonlinear changes (eg. resilience, thresholds, irreversible), and how can they be simulated to produce realistic scenarios ove ...
... takes place over longer timescales than those normally represented by observations, and what are the drivers? 2) What are the critical dynamical characteristics that lead to nonlinear changes (eg. resilience, thresholds, irreversible), and how can they be simulated to produce realistic scenarios ove ...
Human impacts on ecosystems
... climate and provide humans with cultural and recreational opportunities. Sustainable use of an ecosystem means using resources in a way that meets our current needs without compromising our future. ...
... climate and provide humans with cultural and recreational opportunities. Sustainable use of an ecosystem means using resources in a way that meets our current needs without compromising our future. ...
Human impacts on ecosystems
... climate and provide humans with cultural and recreational opportunities. Sustainable use of an ecosystem means using resources in a way that meets our current needs without compromising our future. ...
... climate and provide humans with cultural and recreational opportunities. Sustainable use of an ecosystem means using resources in a way that meets our current needs without compromising our future. ...
Ecology - TeacherWeb
... nutrients (if in short demand growth is limited) – thereby becoming a limiting factor When an ecosystem receives a large input of a limiting nutrient (ie fertilized field runoff into streams) can cause and immediate increase in populations (ie – algal blooms, red tides) ...
... nutrients (if in short demand growth is limited) – thereby becoming a limiting factor When an ecosystem receives a large input of a limiting nutrient (ie fertilized field runoff into streams) can cause and immediate increase in populations (ie – algal blooms, red tides) ...
MS Word Document - 2.5 MB - Department of Environment, Land
... susceptible to invasion by exotic species. Across the landscape, there are 29,100 ha of these communities, which are listed as important under State or Commonwealth legislation. These communities are often in small isolated patches, and include Alpine Sphagnum Bogs and associated Fens, Littoral Rain ...
... susceptible to invasion by exotic species. Across the landscape, there are 29,100 ha of these communities, which are listed as important under State or Commonwealth legislation. These communities are often in small isolated patches, and include Alpine Sphagnum Bogs and associated Fens, Littoral Rain ...
Report - IUFRO
... change impacts on forests and forest ecosystem services. In particular, responses to anthropogenic stressors - such as CO2 enrichment, elevated levels of background ozone, enhanced nitrogen deposition, acidic deposition - and scenarios of climate change - such as altered temperature and moisture reg ...
... change impacts on forests and forest ecosystem services. In particular, responses to anthropogenic stressors - such as CO2 enrichment, elevated levels of background ozone, enhanced nitrogen deposition, acidic deposition - and scenarios of climate change - such as altered temperature and moisture reg ...
ECOLOGY VOCAB QUESTIONS
... 10. For Competition, Herbivores, omnivores, carnivores: Are these Autotrophs or Heterotrophs? Explain competition using one kind of organism. 11. For Pioneer organisms, climax community, ecological succession, tundra, taiga, temperate-deciduous forest, tropical rain forest, grasslands, desert: Pick ...
... 10. For Competition, Herbivores, omnivores, carnivores: Are these Autotrophs or Heterotrophs? Explain competition using one kind of organism. 11. For Pioneer organisms, climax community, ecological succession, tundra, taiga, temperate-deciduous forest, tropical rain forest, grasslands, desert: Pick ...
Ecology Vocabulary Ecosystem
... Abiotic Factor – the nonliving parts of an ecosystem. * including soil, temperature, water, and sunlight. Biotic Factor – the living parts of an ecosystem. Population – a group of the same type of organisms living in the same place at the same time. Community – all the populations that live in an ec ...
... Abiotic Factor – the nonliving parts of an ecosystem. * including soil, temperature, water, and sunlight. Biotic Factor – the living parts of an ecosystem. Population – a group of the same type of organisms living in the same place at the same time. Community – all the populations that live in an ec ...
Trophic Modelling for Ecosystem Based
... Reservoirs ecosystems are dynamic, undergoing both natural and anthropogenic change that can impact ecosystem process on a continual basis. These water bodies are complex system that exhibit a range of ecological interactions. A reservoir ecosystem contains detritus, hundreds of kind of organisms in ...
... Reservoirs ecosystems are dynamic, undergoing both natural and anthropogenic change that can impact ecosystem process on a continual basis. These water bodies are complex system that exhibit a range of ecological interactions. A reservoir ecosystem contains detritus, hundreds of kind of organisms in ...
Global Climate Change
... Deforestation = conversion of forest to non-forest. • Especially high in tropical rainforest. • Due to logging, agriculture, urbanization, mining, oil exploitation, etc. ...
... Deforestation = conversion of forest to non-forest. • Especially high in tropical rainforest. • Due to logging, agriculture, urbanization, mining, oil exploitation, etc. ...
Instructor`s Copy Transparency master – You Can`t Catch Me
... Instructor’s Copy Transparency master – You Can’t Catch Me ...
... Instructor’s Copy Transparency master – You Can’t Catch Me ...
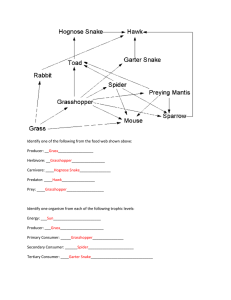
Identify one of the following from the food web shown above
... Explain how the development of agriculture can be harmful to the environment even though it is beneficial to society. A. Deforestation for farming destroys natural habitats and can cause habitat fragmentation B. Deforestation can cause desertification if the soil is allowed to erode C. Chemical pest ...
... Explain how the development of agriculture can be harmful to the environment even though it is beneficial to society. A. Deforestation for farming destroys natural habitats and can cause habitat fragmentation B. Deforestation can cause desertification if the soil is allowed to erode C. Chemical pest ...
REVIEW FOR ENV. SCIENCE FINAL 2015 *Environment
... REVIEW FOR ENV. SCIENCE FINAL 2015 *Environment, ecosystem, ecology, 5 levels of ecology (organism, population, community, ecosystem, biosphere), biomes (large geographic areas with similar climate), indicator species (trout in a stream) *Population, endangered, threatened, reasons for extinction, h ...
... REVIEW FOR ENV. SCIENCE FINAL 2015 *Environment, ecosystem, ecology, 5 levels of ecology (organism, population, community, ecosystem, biosphere), biomes (large geographic areas with similar climate), indicator species (trout in a stream) *Population, endangered, threatened, reasons for extinction, h ...
An ecosystem is a group of plants, animals, and other living things
... An ecosystem's health depends on a delicate balance among all its members and the environment. If something disturbs the balance, the ecosystem and all its members may suffer. Natural things that can disturb ecosystems include a changing climate and natural disasters. Human activities that can distu ...
... An ecosystem's health depends on a delicate balance among all its members and the environment. If something disturbs the balance, the ecosystem and all its members may suffer. Natural things that can disturb ecosystems include a changing climate and natural disasters. Human activities that can distu ...
Disruption to Ecosystems
... • The sea otter is the predator responsible for keeping the urchin at bay • BUT the sea otter was hunted by humans during the 19th and early 20th Century • The whole ecosystem collapsed • The sea otter is known as a keystone species ...
... • The sea otter is the predator responsible for keeping the urchin at bay • BUT the sea otter was hunted by humans during the 19th and early 20th Century • The whole ecosystem collapsed • The sea otter is known as a keystone species ...
Ffridd / Coedcae
... movement of numerous species. Ffridd is a vital component of the landscape, allowing species to adapt to changing conditions by making altitudinal and longitudinal movements, as they seek suitable areas to fulfil their various life-cycles. The importance of this should not be underestimated. This in ...
... movement of numerous species. Ffridd is a vital component of the landscape, allowing species to adapt to changing conditions by making altitudinal and longitudinal movements, as they seek suitable areas to fulfil their various life-cycles. The importance of this should not be underestimated. This in ...
ASSESSMENT of the IMPACT of HUMAN ACTIVITIES on MARINE ENVIRONMENT
... • Need for businesses to increase their awareness of sustainability issues and to integrate these into their practices, especially when operating close to conservation areas. • Local authorities and policy makers should encourage SMEs’ sustainable development by recognizing their economic value and ...
... • Need for businesses to increase their awareness of sustainability issues and to integrate these into their practices, especially when operating close to conservation areas. • Local authorities and policy makers should encourage SMEs’ sustainable development by recognizing their economic value and ...
Ecological resilience

In ecology, resilience is the capacity of an ecosystem to respond to a perturbation or disturbance by resisting damage and recovering quickly. Such perturbations and disturbances can include stochastic events such as fires, flooding, windstorms, insect population explosions, and human activities such as deforestation, fracking of the ground for oil extraction, pesticide sprayed in soil, and the introduction of exotic plant or animal species. Disturbances of sufficient magnitude or duration can profoundly affect an ecosystem and may force an ecosystem to reach a threshold beyond which a different regime of processes and structures predominates. Human activities that adversely affect ecosystem resilience such as reduction of biodiversity, exploitation of natural resources, pollution, land-use, and anthropogenic climate change are increasingly causing regime shifts in ecosystems, often to less desirable and degraded conditions. Interdisciplinary discourse on resilience now includes consideration of the interactions of humans and ecosystems via socio-ecological systems, and the need for shift from the maximum sustainable yield paradigm to environmental resource management which aims to build ecological resilience through ""resilience analysis, adaptive resource management, and adaptive governance"".