The relationship between forest biodiversity, ecosystem
... harvest of ‘best’ trees) and plant several seed stocks • protect primary forests and species at the edges of their ranges • plan to reduce invasive species ...
... harvest of ‘best’ trees) and plant several seed stocks • protect primary forests and species at the edges of their ranges • plan to reduce invasive species ...
Approaches to ecosystem management
... …………………………..; the end result is species extinctions, ecosystem destruction and reduction and possible ecosystem collapse. Philosophies of ecosystem management The philosophies at the extremes of ecosystem management are radical …………………………… and environmental imperialism. With radical environmentalism ...
... …………………………..; the end result is species extinctions, ecosystem destruction and reduction and possible ecosystem collapse. Philosophies of ecosystem management The philosophies at the extremes of ecosystem management are radical …………………………… and environmental imperialism. With radical environmentalism ...
Concepts in contemporary ecological theory Ecology is the study of
... long period necessary to return to stability they continue to persist as systems since their parts do not change. On the other hand, ecosystems may be highly stable, that is they return to equilibrium quickly, but have low resilience because they are likely to collapse. How/why are humans different? ...
... long period necessary to return to stability they continue to persist as systems since their parts do not change. On the other hand, ecosystems may be highly stable, that is they return to equilibrium quickly, but have low resilience because they are likely to collapse. How/why are humans different? ...
REV - kimscience.com
... trophic structure/level consumer level (first order, etc) energy flow producers, autotrophs primary consumers, herbivores omnivores detritivores decomposers detritus food chain food web biological magnification gross primary production net primary production productivity 10% law – ecological efficie ...
... trophic structure/level consumer level (first order, etc) energy flow producers, autotrophs primary consumers, herbivores omnivores detritivores decomposers detritus food chain food web biological magnification gross primary production net primary production productivity 10% law – ecological efficie ...
Predicting
... – Why is species richness important? – Is functional diversity more important than species diversity? – Should we worry about rare species? ...
... – Why is species richness important? – Is functional diversity more important than species diversity? – Should we worry about rare species? ...
1.2 Ecosystems – Student Notes
... Abiotic factors include: • _____________ - produced by green plants & micro-organisms • _____________- necessary for all life • _____________ - for growth • _____________ - required for photosynthesis • _____________ - contains water & nutrients Biotic Interactions in Ecosystems • ________________: ...
... Abiotic factors include: • _____________ - produced by green plants & micro-organisms • _____________- necessary for all life • _____________ - for growth • _____________ - required for photosynthesis • _____________ - contains water & nutrients Biotic Interactions in Ecosystems • ________________: ...
Environmental Challenges
... Cannot always see waste, but may see the harmful effects that it causes (health problems for humans and animals) Amount of pollution has increased with human population (Industrial Revolution) ...
... Cannot always see waste, but may see the harmful effects that it causes (health problems for humans and animals) Amount of pollution has increased with human population (Industrial Revolution) ...
3.2 How Humans Influence Ecosystems
... By the end of section 3.2 you should be able to understand the following: A sustainable ecosystem is not only good for biodiversity and maintaining future healthy ecosystems, but can also be very good economic opportunities. Currently, ecosystem sustainability is often threatened by human activi ...
... By the end of section 3.2 you should be able to understand the following: A sustainable ecosystem is not only good for biodiversity and maintaining future healthy ecosystems, but can also be very good economic opportunities. Currently, ecosystem sustainability is often threatened by human activi ...
Resiliência, Incerteza e Gestão de Sistemas Socioecológicos
... change and industrial development, we have been grappling with the question of whether fundamental change is possible without a major collapse. What has your experience studying system change told you about this question? I think the key is to look for windows of opportunity for change. Such windows ...
... change and industrial development, we have been grappling with the question of whether fundamental change is possible without a major collapse. What has your experience studying system change told you about this question? I think the key is to look for windows of opportunity for change. Such windows ...
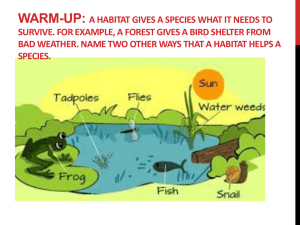
Warm-UP: A habitat gives a species what it needs to survive. For
... The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that supports life. This includes the top of Earths’s crust (lithosphere), the water on Earth’s surface (hydrosphere), and the atmosphere. ...
... The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that supports life. This includes the top of Earths’s crust (lithosphere), the water on Earth’s surface (hydrosphere), and the atmosphere. ...
Sustainable improvements to incomes, food security and the
... More effective water utilisation Preventing and adapting to salinisation Improved access to better varieties and seeds Promoting greater crop diversity Losing less to pests, diseases and invasive weeds ...
... More effective water utilisation Preventing and adapting to salinisation Improved access to better varieties and seeds Promoting greater crop diversity Losing less to pests, diseases and invasive weeds ...
Chapter 1 Key Concept Review
... 3 SOCIAL SCIENCE principles of sustainability: 1. Full cost pricing: including the environmental effects and costs in goods pricing. 2. Win-win solutions: Solutions that benefit both the largest number of people and the environment. 3. A responsibility to future generations: Leave the planet in as g ...
... 3 SOCIAL SCIENCE principles of sustainability: 1. Full cost pricing: including the environmental effects and costs in goods pricing. 2. Win-win solutions: Solutions that benefit both the largest number of people and the environment. 3. A responsibility to future generations: Leave the planet in as g ...
Ecosystem Conservation of the Coastal Douglas-fir Zone
... Re-align for highly altered ecosystems: consider planting more drought tolerant species such as pine, increase harvesting rotation periods, adjust resource use and legislation; change expectations for urban expansion Establish Refugia: identify and manage localized micro climates to provide exis ...
... Re-align for highly altered ecosystems: consider planting more drought tolerant species such as pine, increase harvesting rotation periods, adjust resource use and legislation; change expectations for urban expansion Establish Refugia: identify and manage localized micro climates to provide exis ...
The relationship between biodiversity and forest ecosystem
... overcome and the system moves to a new state that may not be a forest • e.g., if a forest becomes dry, it loses species, is subject to increased frequency of fire fire, and moves to a savannah or grassland state • this new state is stable and will require considerable change to move to another state ...
... overcome and the system moves to a new state that may not be a forest • e.g., if a forest becomes dry, it loses species, is subject to increased frequency of fire fire, and moves to a savannah or grassland state • this new state is stable and will require considerable change to move to another state ...
Ecological resilience

In ecology, resilience is the capacity of an ecosystem to respond to a perturbation or disturbance by resisting damage and recovering quickly. Such perturbations and disturbances can include stochastic events such as fires, flooding, windstorms, insect population explosions, and human activities such as deforestation, fracking of the ground for oil extraction, pesticide sprayed in soil, and the introduction of exotic plant or animal species. Disturbances of sufficient magnitude or duration can profoundly affect an ecosystem and may force an ecosystem to reach a threshold beyond which a different regime of processes and structures predominates. Human activities that adversely affect ecosystem resilience such as reduction of biodiversity, exploitation of natural resources, pollution, land-use, and anthropogenic climate change are increasingly causing regime shifts in ecosystems, often to less desirable and degraded conditions. Interdisciplinary discourse on resilience now includes consideration of the interactions of humans and ecosystems via socio-ecological systems, and the need for shift from the maximum sustainable yield paradigm to environmental resource management which aims to build ecological resilience through ""resilience analysis, adaptive resource management, and adaptive governance"".