Development of Animal Cells
... • In deuterostomes this will form the anus. – Cells that are folding inward form a cavity lined with a 2nd layer of cells – Gastrulation - sorts all the cells into distinct cell layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) ...
... • In deuterostomes this will form the anus. – Cells that are folding inward form a cavity lined with a 2nd layer of cells – Gastrulation - sorts all the cells into distinct cell layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) ...
Training Course 2007 “Transdifferentiation to Beta Cells”
... JDRF Center for Beta Cell Therapy in Diabetes supported by the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation and the European Union organizes ...
... JDRF Center for Beta Cell Therapy in Diabetes supported by the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation and the European Union organizes ...
Cells - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Cellular respiration digests glucose while photosynthesis synthesizes it. Cellular respiration uses oxygen and photosynthesis produces oxygen. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and cellular respiration produces ...
... Cellular respiration digests glucose while photosynthesis synthesizes it. Cellular respiration uses oxygen and photosynthesis produces oxygen. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and cellular respiration produces ...
Comparing Bacteria, Archaea and Eucarya
... synthesis. Translate from one cell language to the other. ...
... synthesis. Translate from one cell language to the other. ...
Slide ()
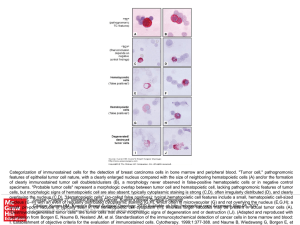
... Education. All rights reserved "Destroyed/degenerated tumor cells" are tumor cells that show morphologic signs of degeneration and or destruction (I,J). (Adapted and reproduced with permission from Borgen E, Naume B, Nesland JM, et al. Standardisation of the immunocytochemical detection of cancer ce ...
... Education. All rights reserved "Destroyed/degenerated tumor cells" are tumor cells that show morphologic signs of degeneration and or destruction (I,J). (Adapted and reproduced with permission from Borgen E, Naume B, Nesland JM, et al. Standardisation of the immunocytochemical detection of cancer ce ...
29 - Alamo Colleges
... Outer membrane is continuous with the rough ER and is studded with ribosomes Inner membrane is the nuclear lamina, which maintains the shape of the nucleus Pore complex regulates transport of large molecules ...
... Outer membrane is continuous with the rough ER and is studded with ribosomes Inner membrane is the nuclear lamina, which maintains the shape of the nucleus Pore complex regulates transport of large molecules ...
Investigation 2 power point
... • What this means is a adult bacteria splits and two and will form an entire new bacteria. ...
... • What this means is a adult bacteria splits and two and will form an entire new bacteria. ...
Cell Project Rubric
... Biology Project due: 10-12/13-09 On Friday 10-9-09, Students are to bring supplies to class to work on project. If project is completed by this date, project may be stored in classroom for presentation and grading on due date listed above. ...
... Biology Project due: 10-12/13-09 On Friday 10-9-09, Students are to bring supplies to class to work on project. If project is completed by this date, project may be stored in classroom for presentation and grading on due date listed above. ...
Notes: Life Cycle of a Cell
... However, after DNA has been replicated and it is needed to transfer into a new nucleus it must be condensed so that it is more easily moved. Chromosomes are visible only during Mitosis or Meiosis (nuclear division). ...
... However, after DNA has been replicated and it is needed to transfer into a new nucleus it must be condensed so that it is more easily moved. Chromosomes are visible only during Mitosis or Meiosis (nuclear division). ...
Chapter 1: Structure of Living Things Test Study Guide
... a. Cell : smallest unit of living things that can carry out basic processes of life b. Cell Membrane: a thin outer layer of a plant or animal cell that lets things pass in and out of the cell (the fence) c. Nucleus :the structure at the center of the cell that controls all of the cells activities by ...
... a. Cell : smallest unit of living things that can carry out basic processes of life b. Cell Membrane: a thin outer layer of a plant or animal cell that lets things pass in and out of the cell (the fence) c. Nucleus :the structure at the center of the cell that controls all of the cells activities by ...
CELLS
... are the building blocks of plants and animals. Cells are the smallest functioning units of life. Cells are produced through the division of preexisting cells. Each cell maintains homeostasis. ...
... are the building blocks of plants and animals. Cells are the smallest functioning units of life. Cells are produced through the division of preexisting cells. Each cell maintains homeostasis. ...
Proliferation
... division when there is a need to maintain or replace tissue, and they stop dividing when the necessary growth is complete. In G1, protein and RNA synthesis are active. If conditions are permissive for subsequent cell division, cells pass through the R (restriction) point and quickly move into the S ...
... division when there is a need to maintain or replace tissue, and they stop dividing when the necessary growth is complete. In G1, protein and RNA synthesis are active. If conditions are permissive for subsequent cell division, cells pass through the R (restriction) point and quickly move into the S ...
Cells and Tissues - Mrs. Hille`s FunZone
... Begins when mitosis is near completion Results in the formation of two daughter cells ...
... Begins when mitosis is near completion Results in the formation of two daughter cells ...
Cells
... located near the center of the cell. The nucleus is a home to the cell’s chromosomes. What are chromosomes you ask? Chromosomes: They are genetic structures that contain information to make new cells. Basically, the instructions for how to make new cells. ...
... located near the center of the cell. The nucleus is a home to the cell’s chromosomes. What are chromosomes you ask? Chromosomes: They are genetic structures that contain information to make new cells. Basically, the instructions for how to make new cells. ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... Here's a simple visual comparison between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell: ...
... Here's a simple visual comparison between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell: ...
THE PLANT CELL 26 FEBRUARY 2014 Lesson
... The diagram on the right shows molecules represented by X both outside and inside of a cell. A process that would result in the movement of these molecules out of the cell requires the use of A ...
... The diagram on the right shows molecules represented by X both outside and inside of a cell. A process that would result in the movement of these molecules out of the cell requires the use of A ...
Anatomy Memorization: Chapter 1
... MESSAGE to make a protein. tRNA = (transfer RNA) RNA that transfers mRNA to an anti-codon to produce a protein. Cell cycle – 1. Interphase – most somatic cells are in this phase during most of their lives…normal metabolism occurs here….DNA replication occurs here 2. M-phase – Mitosis and Cytokenesi ...
... MESSAGE to make a protein. tRNA = (transfer RNA) RNA that transfers mRNA to an anti-codon to produce a protein. Cell cycle – 1. Interphase – most somatic cells are in this phase during most of their lives…normal metabolism occurs here….DNA replication occurs here 2. M-phase – Mitosis and Cytokenesi ...
Student Objectives
... For example: The digestive system is made out of several organs: teeth, tongue, esophagus, stomach, intestine, colon etc. The stomach, is an organ made out of several kinds of tissues. One of those is smooth muscle tissue. Smooth muscle is made out of special smooth muscle cells. 5. Interphase: norm ...
... For example: The digestive system is made out of several organs: teeth, tongue, esophagus, stomach, intestine, colon etc. The stomach, is an organ made out of several kinds of tissues. One of those is smooth muscle tissue. Smooth muscle is made out of special smooth muscle cells. 5. Interphase: norm ...
Cells & Microscope PowerPoint
... carried out by the cells of all living things. Whether an organism is only one cell or made up of many cells, all living things: produce organisms of the same kind, obtain energy from the environment (the chemical activities involved in this are called metabolism and include processes such as respir ...
... carried out by the cells of all living things. Whether an organism is only one cell or made up of many cells, all living things: produce organisms of the same kind, obtain energy from the environment (the chemical activities involved in this are called metabolism and include processes such as respir ...
Candidates should be able to: (a) state the resolution and
... (c) explain the need for staining samples for use in light microscopy and electron microscopy; (d) calculate the linear magnification of an image (HSW3); (e) describe and interpret drawings and photographs of eukaryotic cells as seen under an electron ...
... (c) explain the need for staining samples for use in light microscopy and electron microscopy; (d) calculate the linear magnification of an image (HSW3); (e) describe and interpret drawings and photographs of eukaryotic cells as seen under an electron ...
A Tour of the Cell
... Cells • Eukaryotic cells, including plant and animal cells, contain a nucleus and organelles • Plant cells contain a cell wall, chloroplasts and other organelles • Animal cells contain mitochondria and other organelles ...
... Cells • Eukaryotic cells, including plant and animal cells, contain a nucleus and organelles • Plant cells contain a cell wall, chloroplasts and other organelles • Animal cells contain mitochondria and other organelles ...
chapter_3_powerpoint_im
... Prophase: Chromosomes condense and form visible structures. Metaphase: Chromosomes align on equator of cell. Anaphase: Sister Chromatids separate. Telophase: Chromosomes separated and cleavage furrow appears. – During Telophase cytoplasm and cell organelles divide into both cells. ...
... Prophase: Chromosomes condense and form visible structures. Metaphase: Chromosomes align on equator of cell. Anaphase: Sister Chromatids separate. Telophase: Chromosomes separated and cleavage furrow appears. – During Telophase cytoplasm and cell organelles divide into both cells. ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.