
The Endosymbiotic Theory
... A timeline of life on Earth: Scientists have fossil evidence of bacterial life on Earth ~3.8 billion years ago. At this time, the atmosphere of the Earth did not contain oxygen, and all life (bacterial cells) was anaerobic. About ~3.2 billion years ago, fossil evidence of photosynthetic bacteria ...
... A timeline of life on Earth: Scientists have fossil evidence of bacterial life on Earth ~3.8 billion years ago. At this time, the atmosphere of the Earth did not contain oxygen, and all life (bacterial cells) was anaerobic. About ~3.2 billion years ago, fossil evidence of photosynthetic bacteria ...
Why dread a bump on the head? October 2014 Lesson 5: What
... cytoplasm of the cell becomes denser and the organelles begin to break down and become tightly packed. 2. Inside the nucleus, the chromatin DNA begins to condense and aggregate. An enzyme activated by the apoptotic pathway breaks down the DNA by cutting it at very specified places. This results in v ...
... cytoplasm of the cell becomes denser and the organelles begin to break down and become tightly packed. 2. Inside the nucleus, the chromatin DNA begins to condense and aggregate. An enzyme activated by the apoptotic pathway breaks down the DNA by cutting it at very specified places. This results in v ...
Word - New Haven Science
... the number of chromosomes that are typical of that species. For example, cells in human beings contain 23 pairs of chromosomes; 46 in all. 4. Organisms grow by increasing the number of body cells. During mitosis, a body cell first duplicates the chromosomes and then divides into two daughter cells, ...
... the number of chromosomes that are typical of that species. For example, cells in human beings contain 23 pairs of chromosomes; 46 in all. 4. Organisms grow by increasing the number of body cells. During mitosis, a body cell first duplicates the chromosomes and then divides into two daughter cells, ...
Biology for Kids - Mr. Bloch WWMS Room 312
... others are made up of trillions of cells. Human beings are made up of cells, too. Different Types of Cells There are lots of different types of cells. Each type of cell is different and performs a different function. In the human body, we have nerve cells which can be as long as from our feet to our ...
... others are made up of trillions of cells. Human beings are made up of cells, too. Different Types of Cells There are lots of different types of cells. Each type of cell is different and performs a different function. In the human body, we have nerve cells which can be as long as from our feet to our ...
Journal Activity: The Scientist of the Cell Theory
... as their science journal. Making this not only puts their hands to work, but also their minds. Using two pages, the information and illustrations of the inventors and scientists who contributed to the development of the Cell Theory are shown for the student. For each scientist, there is a place for ...
... as their science journal. Making this not only puts their hands to work, but also their minds. Using two pages, the information and illustrations of the inventors and scientists who contributed to the development of the Cell Theory are shown for the student. For each scientist, there is a place for ...
Cell membrane
... – Still perform life functions (use energy, make proteins), but they’re done in cytoplasm – e.g. bacteria, Archaea ...
... – Still perform life functions (use energy, make proteins), but they’re done in cytoplasm – e.g. bacteria, Archaea ...
You Light Up My Life
... • 1) In animal cells, continuous with nuclear membrane • 2) Extends throughout cytoplasm • 3) Two regions - rough and smooth` ...
... • 1) In animal cells, continuous with nuclear membrane • 2) Extends throughout cytoplasm • 3) Two regions - rough and smooth` ...
What is a cell?
... and keep phospholipids from sticking together. _____________ on the surface help cells recognize each other. _____________ in the membrane are used for transporting molecules ...
... and keep phospholipids from sticking together. _____________ on the surface help cells recognize each other. _____________ in the membrane are used for transporting molecules ...
Slide ()
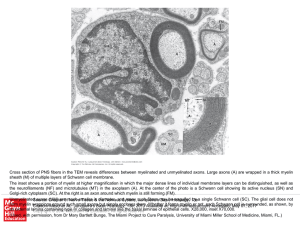
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
Interesting facts: • Many cells in the body use exocytosis to release
... forms them in order to take particles into the cell via the cell membrane and involves a reduction in cell membrane area, as part of the membrane is pinched off to form a vesicle; exocytosis forms them in order to expel things from the cell via the cell membrane and results in an increase in cell me ...
... forms them in order to take particles into the cell via the cell membrane and involves a reduction in cell membrane area, as part of the membrane is pinched off to form a vesicle; exocytosis forms them in order to expel things from the cell via the cell membrane and results in an increase in cell me ...
EUCARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
... This is a reductive division in which one diploid (2N) cell produces two haploid (1N) cells. Prophase I: Similar to prophase of mitosis with one important difference: Crossing Over in which pairs of homologous chromosomes synapse together to form tetrads and exchange genetic information (DNA). Cross ...
... This is a reductive division in which one diploid (2N) cell produces two haploid (1N) cells. Prophase I: Similar to prophase of mitosis with one important difference: Crossing Over in which pairs of homologous chromosomes synapse together to form tetrads and exchange genetic information (DNA). Cross ...
Life From Life - Rocky View Schools
... Robert Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Microscopes and the Cell Theory ...
... Robert Hooke, Leeuwenhoek, Microscopes and the Cell Theory ...
• SWBAT create and label cell diagrams in order to compare and
... 8) What do scientists think mitochondria used to be? ...
... 8) What do scientists think mitochondria used to be? ...
Cell Organelles
... cell Contains DNA Surrounded by a double membrane Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope Usually one per cell ...
... cell Contains DNA Surrounded by a double membrane Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope Usually one per cell ...
ch7iv-Use This 3rd
... 1. Specialized animal cells – eg. Red blood cells equipped to carry oxygen ;cells specialized to produce proteins produced in pancreas(have many ribosomes and rough ER);muscle cells have actin and myosin cytoskeleton elements for contraction 2. Specialized Plant cells ______________________-are tiny ...
... 1. Specialized animal cells – eg. Red blood cells equipped to carry oxygen ;cells specialized to produce proteins produced in pancreas(have many ribosomes and rough ER);muscle cells have actin and myosin cytoskeleton elements for contraction 2. Specialized Plant cells ______________________-are tiny ...
Prokaryotes - AP Biology Overview
... Capsule – covers outer cell wall – sticky protection from host cells Fimbriae – short numerous hairs that attach prokaryotes to one another Pili – longer hair – can be used for conjugation – DNA transfer from one bacteria to another ...
... Capsule – covers outer cell wall – sticky protection from host cells Fimbriae – short numerous hairs that attach prokaryotes to one another Pili – longer hair – can be used for conjugation – DNA transfer from one bacteria to another ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.

















![Cells_Alive_Lab[1] 2](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011540557_1-c3f606b1b33bc1e29b015c6b59251a13-300x300.png)




