Test Review: Unit II Cells and microscopes What is a prokaryote? A
... Where are the instructions found that build these cells (#14)? Why aren’t they all the same? In our genetic information (DNA) is where the instructions are found. The cells are not the same because the DNA code that builds the cells is not the same. ...
... Where are the instructions found that build these cells (#14)? Why aren’t they all the same? In our genetic information (DNA) is where the instructions are found. The cells are not the same because the DNA code that builds the cells is not the same. ...
Bio221_Microbiology_Exam_3_2007
... of this group have ever been cultivated in the laboratory. Explain how we know these organisms exist. What procedures were used to find them and what evidence supports placing them in their own “kingdom”? ...
... of this group have ever been cultivated in the laboratory. Explain how we know these organisms exist. What procedures were used to find them and what evidence supports placing them in their own “kingdom”? ...
What Battery is Better? Hess 1 Batteries come in many shapes and
... Batteries come in many shapes and sizes. Some are no larger than a pill while others are too heavy to lift, but most batteries have one thing in common-they store chemical energy and change it into electrical energy. The cell is the basic unit that produces electricity. A battery has 2 or more cells ...
... Batteries come in many shapes and sizes. Some are no larger than a pill while others are too heavy to lift, but most batteries have one thing in common-they store chemical energy and change it into electrical energy. The cell is the basic unit that produces electricity. A battery has 2 or more cells ...
Previous work on CVD
... yield increased optical absorption and photocurrent generation in the photoactive layer over a broad range of visible wavelengths by inducing surface plasmons through careful control of metallic nanoparticle’s properties. With incident light, the surface charges of metallic nanoparticles interact wi ...
... yield increased optical absorption and photocurrent generation in the photoactive layer over a broad range of visible wavelengths by inducing surface plasmons through careful control of metallic nanoparticle’s properties. With incident light, the surface charges of metallic nanoparticles interact wi ...
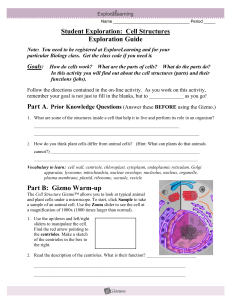
HW Cell Structures Gizmo Gizmo Cell Structures final
... Follow the directions contained in the on-line activity. As you work on this activity, remember your goal is not just to fill in the blanks, but to _____________ as you go! ...
... Follow the directions contained in the on-line activity. As you work on this activity, remember your goal is not just to fill in the blanks, but to _____________ as you go! ...
Student Workbook
... All sides are of equal lengths (X) with surface area equal to (X squared) x 6 and volume equal to X cubed. (3 marks) ...
... All sides are of equal lengths (X) with surface area equal to (X squared) x 6 and volume equal to X cubed. (3 marks) ...
Apoptosis , necrosis, and death
... • Bacteria are haploid - has just one copy of it genome per cell - one bacteria copies its chromosome into two and then divides • Humans are diploid, as are many plants and animals – we have two copies of each chromosome – one set from our dads and the others from our mums. ...
... • Bacteria are haploid - has just one copy of it genome per cell - one bacteria copies its chromosome into two and then divides • Humans are diploid, as are many plants and animals – we have two copies of each chromosome – one set from our dads and the others from our mums. ...
Name: Date: Period: BIOLOGY H EU#1: THE CELL Venn Diagram
... Is the structure of the DNA linear or circular? How is the DNA organized within the cell? (Ex. Chromosomes? Histones?) ...
... Is the structure of the DNA linear or circular? How is the DNA organized within the cell? (Ex. Chromosomes? Histones?) ...
Cell Organelles - Mayfield City Schools
... • A complete copy of DNA, so that when the cell divides, the next cell has a full set of instructions. (full set of genes) ...
... • A complete copy of DNA, so that when the cell divides, the next cell has a full set of instructions. (full set of genes) ...
Cell Theory - stephen fleenor
... Which of the following questions about a flower can be most readily answered by scientific methods? A. Would this kind of flower make a good gift? B. What kind of flower is the most beautiful? C. How pretty is the flower? D. What kinds of pollinators are attracted to this flower? By what process is ...
... Which of the following questions about a flower can be most readily answered by scientific methods? A. Would this kind of flower make a good gift? B. What kind of flower is the most beautiful? C. How pretty is the flower? D. What kinds of pollinators are attracted to this flower? By what process is ...
12_Lecture_Presentation
... • The mitotic spindle is a structure made of microtubules that controls chromosome movement during mitosis • In animal cells, assembly of spindle microtubules begins in the centrosome, the microtubule organizing center • The centrosome replicates during interphase, forming two centrosomes that migra ...
... • The mitotic spindle is a structure made of microtubules that controls chromosome movement during mitosis • In animal cells, assembly of spindle microtubules begins in the centrosome, the microtubule organizing center • The centrosome replicates during interphase, forming two centrosomes that migra ...
Key Concepts - Wando High School
... a. The lowest level of structure capable of performing all the activities of life is the cell. b. A unicellular organism is composed of one cell and all of life’s activities occur within that single cell. c. In a multicellular organism, each cell carries on most of the major functions of life. 3. Al ...
... a. The lowest level of structure capable of performing all the activities of life is the cell. b. A unicellular organism is composed of one cell and all of life’s activities occur within that single cell. c. In a multicellular organism, each cell carries on most of the major functions of life. 3. Al ...
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
... Anaphase – The two sister chromatids break their attachment to each other. As separate chromosomes, they are pulled to opposite spindle poles by the microtubules. Telophase – The cell now has two clusters of chromosomes at opposite poles. A new nuclear membrane begins to form around each of these cl ...
... Anaphase – The two sister chromatids break their attachment to each other. As separate chromosomes, they are pulled to opposite spindle poles by the microtubules. Telophase – The cell now has two clusters of chromosomes at opposite poles. A new nuclear membrane begins to form around each of these cl ...
Stem Cells - California Science Teacher
... Protestant evangelical and Catholic communities • Embryos are human • Morally wrong to destroy a human • Fertilization is the starting point in life ...
... Protestant evangelical and Catholic communities • Embryos are human • Morally wrong to destroy a human • Fertilization is the starting point in life ...
Onion & Blood Cells Lab
... don’t always have all the structures you would see in other cells. • Red blood cells lack an important organelle that contains the genetic material needed for reproduction – if you can figure this out, you’ll get the answer! ...
... don’t always have all the structures you would see in other cells. • Red blood cells lack an important organelle that contains the genetic material needed for reproduction – if you can figure this out, you’ll get the answer! ...
preview chapter 7
... Thur. Nov 6-Friday Nov 7 Day 1: Life is Cellular OBJECTIVES: 1.Explain what the cell theory is. 2. Describe how researchers explore the living cell. 3. Distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 4. Distinguish between the light microscopes and electron microscopes and the image they produce. VO ...
... Thur. Nov 6-Friday Nov 7 Day 1: Life is Cellular OBJECTIVES: 1.Explain what the cell theory is. 2. Describe how researchers explore the living cell. 3. Distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 4. Distinguish between the light microscopes and electron microscopes and the image they produce. VO ...
11. The two types of lipids are saturated and unsaturated
... Interphase—nucleus (and often nucleolus) is visible; DNA is thin, threadlike chromatin Prophase—nulear membrane disappears, chromosomes become visible, spindle forms Metaphase—chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell Anaphase—chromatids pull apart at the centromere, and move away from the cente ...
... Interphase—nucleus (and often nucleolus) is visible; DNA is thin, threadlike chromatin Prophase—nulear membrane disappears, chromosomes become visible, spindle forms Metaphase—chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell Anaphase—chromatids pull apart at the centromere, and move away from the cente ...
Unit 1 Lesson 3 - Epiphany Catholic School
... • Use scissors to cut out each strip • Use a pen or pencil to write the entire alphabet on each strip • Make the first loop in the chain and tape it together • Now make a chain by threading the loops ...
... • Use scissors to cut out each strip • Use a pen or pencil to write the entire alphabet on each strip • Make the first loop in the chain and tape it together • Now make a chain by threading the loops ...
Notes: Chapter 7
... 1. Larger & more complex than prokaryotes 2. Genetic material contained inside a nucleus 3. Example: plants, animals, fungi, & protists ...
... 1. Larger & more complex than prokaryotes 2. Genetic material contained inside a nucleus 3. Example: plants, animals, fungi, & protists ...
Tissue Repair, Fibrosis, and Healing
... formation of complexes that directly associate with nuclear DNA and activate transcription • For cell surface receptors, ligands bind to a variety of receptor types that ultimately lead to activation of nuclear transcription factors ...
... formation of complexes that directly associate with nuclear DNA and activate transcription • For cell surface receptors, ligands bind to a variety of receptor types that ultimately lead to activation of nuclear transcription factors ...
The Eukaryotic Cell (plant and animal cells) Eukaryotes: Organisms
... -‐ membrane bound sacs of digestive _______________ Functions: * breaks down old ________________ * breaks down ________ items * induces cell death if needed -‐ it’s technically a specialized vesicl ...
... -‐ membrane bound sacs of digestive _______________ Functions: * breaks down old ________________ * breaks down ________ items * induces cell death if needed -‐ it’s technically a specialized vesicl ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.