name date ______ period
... 23. A _G_ __ __ __ __ _B_ __ __ __ looks like a stack of pancakes and packages molecules for transport out of the cell. 24. _I_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ proteins stick into the cell membrane that can go part way or all the way through to the other side. 25. Space for storing food, water, enzymes, or wa ...
... 23. A _G_ __ __ __ __ _B_ __ __ __ looks like a stack of pancakes and packages molecules for transport out of the cell. 24. _I_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ proteins stick into the cell membrane that can go part way or all the way through to the other side. 25. Space for storing food, water, enzymes, or wa ...
Cell Structure - Boone County Schools
... Cells are filled with a gelatin-like substance called cytoplasm. Constantly flows inside the cell membrane. Region between the nucleus and the cell membrane. Throughout the cytoplasm is a framework called the cytoskeleton. Helps maintain its shape and enable some cells to move. The cytoskeleton is m ...
... Cells are filled with a gelatin-like substance called cytoplasm. Constantly flows inside the cell membrane. Region between the nucleus and the cell membrane. Throughout the cytoplasm is a framework called the cytoskeleton. Helps maintain its shape and enable some cells to move. The cytoskeleton is m ...
Cell in its environment - Somerset Academy North Las Vegas
... Effects of osmosis in animals Animal cells do not have cell walls. In hypotonic solutions, animal cells swell up and explode as they cannot become turgid because there is no cell wall to prevent the cell from bursting. When the cell is in danger of bursting, organelles called contractile vacuol ...
... Effects of osmosis in animals Animal cells do not have cell walls. In hypotonic solutions, animal cells swell up and explode as they cannot become turgid because there is no cell wall to prevent the cell from bursting. When the cell is in danger of bursting, organelles called contractile vacuol ...
Goal Two
... o Chloroplast- photosynthesis, makes food, ONLY IN PLANTS o Ribosomes- protein synthesis, makes protein o Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)- transports material o Gogi Apparatus(complex)- packages materials o Lysosomes- suicide sac- contains digestive enzymes o Cytoskeleton (microtubules, microfilaments)- ...
... o Chloroplast- photosynthesis, makes food, ONLY IN PLANTS o Ribosomes- protein synthesis, makes protein o Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)- transports material o Gogi Apparatus(complex)- packages materials o Lysosomes- suicide sac- contains digestive enzymes o Cytoskeleton (microtubules, microfilaments)- ...
Cell Play Grading Rubric
... structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles. ...
... structure and function of major organelles of plant and animal cells, including cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles. ...
Cell city analogy
... Everyone in the town has something to do with steel widget making and the entire town is designed to build and export widgets. The town hall has the instructions for widget making, widgets come in all shapes and sizes and any citizen of Grant can get the instructions and begin making their own widge ...
... Everyone in the town has something to do with steel widget making and the entire town is designed to build and export widgets. The town hall has the instructions for widget making, widgets come in all shapes and sizes and any citizen of Grant can get the instructions and begin making their own widge ...
The Cell
... 1. All living things are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of function of all living things (they carry on life activities) 3. All cells are produced from other cells! (by the process of cell divison) ...
... 1. All living things are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of function of all living things (they carry on life activities) 3. All cells are produced from other cells! (by the process of cell divison) ...
The Cell Cycle
... The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. Interphase is divided into G1 , S, and G2 phases. Th ...
... The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. Interphase is divided into G1 , S, and G2 phases. Th ...
Eukaryotic Organelles
... (membrane sacs associated with the ER) Sorts, Purifies, and Packages many organic molecules originally made in the ER. Responsible for Producing Plasma Membranes. Resembles a “Stack of Pancakes”. ...
... (membrane sacs associated with the ER) Sorts, Purifies, and Packages many organic molecules originally made in the ER. Responsible for Producing Plasma Membranes. Resembles a “Stack of Pancakes”. ...
Cell structure
... between the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope. It consists of primarily of water. It also contains various organelles as well as salts, dissolved gasses and nutrients. There are 3 groups of organelles in the cytoplasm: Protein producers, Energy Producers and ...
... between the cell membrane and the nuclear envelope. It consists of primarily of water. It also contains various organelles as well as salts, dissolved gasses and nutrients. There are 3 groups of organelles in the cytoplasm: Protein producers, Energy Producers and ...
coloring packet cells and organelles
... place in the chloroplasts. Only plant cells, not animal cells, can make their own food. Color and label the chloroplasts dark green. Cells also contain fluid-filled sacs called vacuoles. The vacuole fills with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell. In plant cells, ...
... place in the chloroplasts. Only plant cells, not animal cells, can make their own food. Color and label the chloroplasts dark green. Cells also contain fluid-filled sacs called vacuoles. The vacuole fills with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell. In plant cells, ...
Topic 1: Cell Biology
... • Most reactions ATP • Cells with high energy requirements have more mitochondria • Mitochondria are inherited from your mother only ...
... • Most reactions ATP • Cells with high energy requirements have more mitochondria • Mitochondria are inherited from your mother only ...
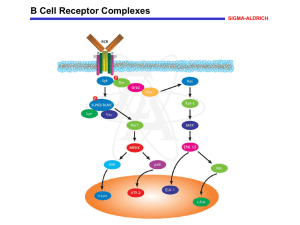
B Cell Receptor Complexes - Sigma
... Additionally, the Tec family member Btk is recruited to the plasma membrane where it is involved in activation of PLC . The SLP-65/BLNK adapter protein has recently been shown to play a role in BCR-induced recruitment and activation of key signal transducing effector proteins. Downstream intermedia ...
... Additionally, the Tec family member Btk is recruited to the plasma membrane where it is involved in activation of PLC . The SLP-65/BLNK adapter protein has recently been shown to play a role in BCR-induced recruitment and activation of key signal transducing effector proteins. Downstream intermedia ...
XPO1 is selinexor`s prime target: validation by mutating cysteine 528
... It exports a broad range of different cargo proteins out of the cell’s nucleus to the cytoplasm. These cargo proteins include tumour suppressor and growth regulatory related proteins; therefore correct XPO1 function is key to normal cell homeostasis. In recent years, overexpression or dysfunction of ...
... It exports a broad range of different cargo proteins out of the cell’s nucleus to the cytoplasm. These cargo proteins include tumour suppressor and growth regulatory related proteins; therefore correct XPO1 function is key to normal cell homeostasis. In recent years, overexpression or dysfunction of ...
Grade: 5 Description: This lesson set covers cells. It goes along with
... material the student’s need to learn. There are optional worksheets and a fun assessment at the end! ...
... material the student’s need to learn. There are optional worksheets and a fun assessment at the end! ...
Pre – AP Biology
... ONLY found in Eukaryotes ONLY because they have the organelle.) – These make proteins that will leave the cell to be used elsewhere. (Most are for communication between cells, such as antibodies for fighting infection.) ...
... ONLY found in Eukaryotes ONLY because they have the organelle.) – These make proteins that will leave the cell to be used elsewhere. (Most are for communication between cells, such as antibodies for fighting infection.) ...
Structure and Function of the Mitochondria - Room N
... • The energy released is not directly usable by the cell. • It is used to convert ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) to ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) ...
... • The energy released is not directly usable by the cell. • It is used to convert ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) to ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) ...
Onion Root Tip Lab
... How Long is Each Phase of Mitosis? Name ___________________________________ Date _______________________ Per. ___________ ...
... How Long is Each Phase of Mitosis? Name ___________________________________ Date _______________________ Per. ___________ ...
Introduction:
... The following is a list of organelles required for the models: Both cells must include: Cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, nucleus, nucleolus, DNA, Golgi complex, vacuole, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough) Plant cells must also contain: cell wall and chloroplasts Animal cell ...
... The following is a list of organelles required for the models: Both cells must include: Cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, nucleus, nucleolus, DNA, Golgi complex, vacuole, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough) Plant cells must also contain: cell wall and chloroplasts Animal cell ...
LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #9 (100 points total) all questions
... cells, radioactive cells will activate the film and show up as black dots when looked at under a microscope). a) During what phase of the cell cycle will the radioactive thymidine be incorporated? Why? (2 point) Radioactive thymidine will be incorporated during S phase, since this is the phase of th ...
... cells, radioactive cells will activate the film and show up as black dots when looked at under a microscope). a) During what phase of the cell cycle will the radioactive thymidine be incorporated? Why? (2 point) Radioactive thymidine will be incorporated during S phase, since this is the phase of th ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.