Ch. 8 Honors PP
... hypotonic environments must have adaptations for OSMOREGULATION, the control of water balance Ex: Paramecium has a contractile vacuole that pumps excess water out of the cell ...
... hypotonic environments must have adaptations for OSMOREGULATION, the control of water balance Ex: Paramecium has a contractile vacuole that pumps excess water out of the cell ...
PHYSIOLOGICAL ROLE OF CELL ORGANELLE
... Vesicle contains proteins destined for extracellular release. After packaging the vesicles bud off and immediately move towards the plasma membrane. Where they fuse and release the contents into the extracellular space in a process known as constitutive secretion. Antibodies release by activ ...
... Vesicle contains proteins destined for extracellular release. After packaging the vesicles bud off and immediately move towards the plasma membrane. Where they fuse and release the contents into the extracellular space in a process known as constitutive secretion. Antibodies release by activ ...
bk1B_ch09_sug ans_e
... They also need to obtain water and minerals from the soil for the production of different substances they need. 1m Carbon dioxide and oxygen: Plants exchange gases with the environment by diffusion. In terrestrial plants, gas exchange takes place through leaves, stems and roots. In leaves, gases fro ...
... They also need to obtain water and minerals from the soil for the production of different substances they need. 1m Carbon dioxide and oxygen: Plants exchange gases with the environment by diffusion. In terrestrial plants, gas exchange takes place through leaves, stems and roots. In leaves, gases fro ...
Chapter 7 Section 2: Cell organelles Quiz: For 3 extra credit points
... b. nucleolus c. chromatin d. DNA 8. Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton? a. helps a cell keep its shape b. contains DNA c. surrounds the cell d. helps make proteins 9. Which organelle makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? a. Golgi apparatus b. mitoc ...
... b. nucleolus c. chromatin d. DNA 8. Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton? a. helps a cell keep its shape b. contains DNA c. surrounds the cell d. helps make proteins 9. Which organelle makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? a. Golgi apparatus b. mitoc ...
Online Activity: Types of Transport
... 1. What is the concentration of salt in animal cells? _________________________ 2. When cells are in isotonic solution, is there movement of water into or out of the cell? If so, describe this movement. ______________________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
... 1. What is the concentration of salt in animal cells? _________________________ 2. When cells are in isotonic solution, is there movement of water into or out of the cell? If so, describe this movement. ______________________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
ultrastructural aspects of programmed cell death in the exocarp oil
... reticulum (ER) greatly develops into many short elements having a dark content (Fig. 1C). Fragmented ER-elements have a normal thickness (66 nm) and do not aggregate at certain areas of the cytoplasm, but they are uniformly scattered all over the cytoplasm. Close associations of the ER-elements with ...
... reticulum (ER) greatly develops into many short elements having a dark content (Fig. 1C). Fragmented ER-elements have a normal thickness (66 nm) and do not aggregate at certain areas of the cytoplasm, but they are uniformly scattered all over the cytoplasm. Close associations of the ER-elements with ...
July 28, 1914
... What is the setting of the story To Kill A Mockingbird (town, state and time period) ...
... What is the setting of the story To Kill A Mockingbird (town, state and time period) ...
Cell Transport Practice Answers
... 2. Water passes quickly through the cell membrane because a. The bilayer is hydrophilic b. Water movement is tied to ATP hydrolysis c. It is a small, polar, charged molecule d. It moves through aquaporins in the membrane 3. Carrots that are immersed in fresh water for several hours become stiff and ...
... 2. Water passes quickly through the cell membrane because a. The bilayer is hydrophilic b. Water movement is tied to ATP hydrolysis c. It is a small, polar, charged molecule d. It moves through aquaporins in the membrane 3. Carrots that are immersed in fresh water for several hours become stiff and ...
Membranes of Living Organisms Outline
... Active transport occurs against a concentration gradient. Active Transport proteins that move molecules = Pumps Transport protein ...
... Active transport occurs against a concentration gradient. Active Transport proteins that move molecules = Pumps Transport protein ...
10-2 Cell Division
... parent using mitosis. •The offspring are therefore genetically identical to each other and to their “parent”- in other words they are clones. •Asexual reproduction is very common in nature, and we humans have ...
... parent using mitosis. •The offspring are therefore genetically identical to each other and to their “parent”- in other words they are clones. •Asexual reproduction is very common in nature, and we humans have ...
cell process study guide answers
... 4. Two substances produced during photosynthesis are glucose and oxygen. 5. The green pigment found in plants is called chlorophyll. 6. Mitosis is the process in which the cell reproduces to make an exact copy of itself. 7. The organelle that performs cellular respiration is the mitochondria. 8. The ...
... 4. Two substances produced during photosynthesis are glucose and oxygen. 5. The green pigment found in plants is called chlorophyll. 6. Mitosis is the process in which the cell reproduces to make an exact copy of itself. 7. The organelle that performs cellular respiration is the mitochondria. 8. The ...
Cell Transport
... This prevents sodium from building up inside the cell, which would cause the cell to burst due to osmosis bringing in too much water ...
... This prevents sodium from building up inside the cell, which would cause the cell to burst due to osmosis bringing in too much water ...
Plant Cell Plasmolysis
... When a cell is in a balanced solution (like blood), it will experience neither a net gain or loss of water. A balanced solution contains an equal concentration of dissolved materials as the cell and therefore an equal concentration of water. Consequently, water will flow equally into and out of the ...
... When a cell is in a balanced solution (like blood), it will experience neither a net gain or loss of water. A balanced solution contains an equal concentration of dissolved materials as the cell and therefore an equal concentration of water. Consequently, water will flow equally into and out of the ...
Root Growth under Drought
... Missouri, Columbia, MO 65211; Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0C6, Canada ...
... Missouri, Columbia, MO 65211; Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0C6, Canada ...
1-· Which of the following sentences best describes the transport
... folding of the polypeptide chain ...
... folding of the polypeptide chain ...
Study Guide for Exam 1: Cell Biology
... Notebook: Topic 4: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles CA Science Biology Standard 1e: Students know the role of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in the secretion of proteins. 1f: Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar f ...
... Notebook: Topic 4: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles CA Science Biology Standard 1e: Students know the role of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus in the secretion of proteins. 1f: Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar f ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell
... What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS ...
... What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS ...
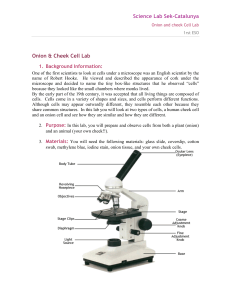
Onion and cheek Cell Lab
... because they looked like the small chambers where monks lived. By the early part of the 19th century, it was accepted that all living things are composed of cells. Cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and cells perform different functions. Although cells may appear outwardly different, they ...
... because they looked like the small chambers where monks lived. By the early part of the 19th century, it was accepted that all living things are composed of cells. Cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and cells perform different functions. Although cells may appear outwardly different, they ...
CELLS - Peoria Public Schools
... What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS ...
... What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS ...
File
... The Cellular Structure of Life: Review • Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists; provides support and protection. • Plasma membrane: serves as boundary between the cell and its environment; allows materials such ...
... The Cellular Structure of Life: Review • Cell wall: firm, fairly rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plants, fungi, most bacteria, and some protists; provides support and protection. • Plasma membrane: serves as boundary between the cell and its environment; allows materials such ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.