Immunology
... antigen with very high specificity. Made in response to exposure to the antigen. One virus or microbe may have several antigenic determinant sites, to which different antibodies may bind. Each antibody has at least two identical sites that bind antigen: Antigen binding sites. Belong to a gro ...
... antigen with very high specificity. Made in response to exposure to the antigen. One virus or microbe may have several antigenic determinant sites, to which different antibodies may bind. Each antibody has at least two identical sites that bind antigen: Antigen binding sites. Belong to a gro ...
Unit E Microbiology in Agriscience and Production Agriculture
... Cells o Specialized reproductive cells in eukaryotes that contain ½ the amount of genetic material of normal (diploid) cells o Also called o Haploid cells combine during sexual reproduction to create a fertilized egg o 4 distinct types Male FemaleStem Cells o Produced from the o Special cells tha ...
... Cells o Specialized reproductive cells in eukaryotes that contain ½ the amount of genetic material of normal (diploid) cells o Also called o Haploid cells combine during sexual reproduction to create a fertilized egg o 4 distinct types Male FemaleStem Cells o Produced from the o Special cells tha ...
m5zn_b0eb6573d04d81d
... These cells have the following criteria: a- Always attached to each other by one or more type of cellular junctions. b- The cytoplasm of these cells is stained with ordinary stain as H & E. c- Their cytoplasm contains characteristic tonofilaments. ...
... These cells have the following criteria: a- Always attached to each other by one or more type of cellular junctions. b- The cytoplasm of these cells is stained with ordinary stain as H & E. c- Their cytoplasm contains characteristic tonofilaments. ...
Diffusion and Osmosis
... •A protist like paramecium has contractile vacuoles that collect water flowing in and pump it out to prevent them from over-expanding. •Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized gills so they ...
... •A protist like paramecium has contractile vacuoles that collect water flowing in and pump it out to prevent them from over-expanding. •Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized gills so they ...
3-D Cell Model
... F.) Actual numbers of organelles found in real cells should be represented. Ex: Each cell has one nucleus but animal cells have multiple mitochondria and other organelles. G.) Each organelle type should have its function clearly described and should be provided on a chart or table. H.) Be unique and ...
... F.) Actual numbers of organelles found in real cells should be represented. Ex: Each cell has one nucleus but animal cells have multiple mitochondria and other organelles. G.) Each organelle type should have its function clearly described and should be provided on a chart or table. H.) Be unique and ...
Injuries to the Tissues
... unit of ALL living organisms. • Cells divide to form tissues (specialization) ...
... unit of ALL living organisms. • Cells divide to form tissues (specialization) ...
SCNS480 Cell Biology Laboratory
... Prerequisites: SCNS210 or SCNS310 Instructor(s): Michael Wolfgang Lassalle ...
... Prerequisites: SCNS210 or SCNS310 Instructor(s): Michael Wolfgang Lassalle ...
Methods of Transport Across a Cell Membrane
... – A cell takes in macromolecules or other substances when regions of the plasma membrane surround the substance, pinch off, and form a vesicle within the cell. ...
... – A cell takes in macromolecules or other substances when regions of the plasma membrane surround the substance, pinch off, and form a vesicle within the cell. ...
Nervous System: General Principles
... Parameters necessary to create a resting membrane potential: •A semi-permeable membrane •Distribution of ions across membrane •Presence of large non-diffusible anions in interior ...
... Parameters necessary to create a resting membrane potential: •A semi-permeable membrane •Distribution of ions across membrane •Presence of large non-diffusible anions in interior ...
FALL UNIT PLAN OUTLINE Jessica Najar
... Now that we have made our way through this work and we have created an understanding of what we believe this is about, I would like you to consider the following. Look at your paintings and think about what would happen to the painting if I removed the women in the background from this scene and lef ...
... Now that we have made our way through this work and we have created an understanding of what we believe this is about, I would like you to consider the following. Look at your paintings and think about what would happen to the painting if I removed the women in the background from this scene and lef ...
Cell Membrane
... Carrier proteins in the cell membrane form tunnels across the membrane to move materials Channel proteins may always be open or have gates that open & close to control the movement of materials; called gated channels Gates open & close in response to concentration inside & outside the cell Ion Chann ...
... Carrier proteins in the cell membrane form tunnels across the membrane to move materials Channel proteins may always be open or have gates that open & close to control the movement of materials; called gated channels Gates open & close in response to concentration inside & outside the cell Ion Chann ...
Do you know? - Sakshieducation.com
... Leave the bread in the open air for about an hour, so it is exposed to contaminants in the air. Place the bread in a plastic bag, sprinkle water over it to have dampness then seal the bag, leaving some air inside. Place the bag in a dark, warm place. A kitchen cup board close to the stove may be one ...
... Leave the bread in the open air for about an hour, so it is exposed to contaminants in the air. Place the bread in a plastic bag, sprinkle water over it to have dampness then seal the bag, leaving some air inside. Place the bag in a dark, warm place. A kitchen cup board close to the stove may be one ...
Anti-CCR4 antibody ab83250 Product datasheet 1 Image
... Predominantly expressed in the thymus, in peripheral blood leukocytes, including T-cells, mostly CD4+ cells, and basophils, and in platelets; at lower levels, in the spleen and in monocytes. Detected also in macrophages, IL-2-activated natural killer cells and skin-homing memory Tcells, mostly the o ...
... Predominantly expressed in the thymus, in peripheral blood leukocytes, including T-cells, mostly CD4+ cells, and basophils, and in platelets; at lower levels, in the spleen and in monocytes. Detected also in macrophages, IL-2-activated natural killer cells and skin-homing memory Tcells, mostly the o ...
Chapter Objectives
... b. Reinforce cell shape c. Fix organelle positions d. Compose nuclear lamina G. Cell Surfaces and Junctions 1. Plant cells are encased by cell walls 2. The extracellular matrix (ECM) of animal cells functions in support, adhesion, movement, and development 3. Intercellular junctions help integrate c ...
... b. Reinforce cell shape c. Fix organelle positions d. Compose nuclear lamina G. Cell Surfaces and Junctions 1. Plant cells are encased by cell walls 2. The extracellular matrix (ECM) of animal cells functions in support, adhesion, movement, and development 3. Intercellular junctions help integrate c ...
Mitosis in the Mouse: A Study of Living and
... tissue culture by W. H. Lewis (1940). This author, however, does not distinguish between the Feulgen-positive chromocentres and the Feulgennegative nucleoli and applies the latter term to all intranuclear granules. It seems clear, however, that the 'small nucleoli' of Lewis which were seen to be in ...
... tissue culture by W. H. Lewis (1940). This author, however, does not distinguish between the Feulgen-positive chromocentres and the Feulgennegative nucleoli and applies the latter term to all intranuclear granules. It seems clear, however, that the 'small nucleoli' of Lewis which were seen to be in ...
The Cell Cycle
... Letters represent cell cycle processes. The pathway shown as red symbols indicates an intrinsic checkpoint mechanism that operates to ensure that event C is completed before event E. After event B is completed, an inhibitory signal is activated that blocks completion of event E. After event C is com ...
... Letters represent cell cycle processes. The pathway shown as red symbols indicates an intrinsic checkpoint mechanism that operates to ensure that event C is completed before event E. After event B is completed, an inhibitory signal is activated that blocks completion of event E. After event C is com ...
Anatomy and Physiology Summer Assignment
... 57) How do the daughter cells at the end of mitosis and cytokinesis compare with their parent cell when it was in G1 of the cell cycle? ...
... 57) How do the daughter cells at the end of mitosis and cytokinesis compare with their parent cell when it was in G1 of the cell cycle? ...
Cell Nutrients
... - present in nucleic acids and in the cell wall of some gram-positive bacteria. - a key element in the regulation of cell metabolism. - sources: Inorganic phosphates. ...
... - present in nucleic acids and in the cell wall of some gram-positive bacteria. - a key element in the regulation of cell metabolism. - sources: Inorganic phosphates. ...
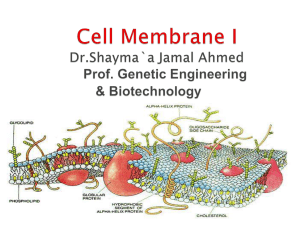
Plasma membrane Dr.Shayma`a Jamal Ahmed
... At the end of this lecture the student will be able to: Define the cell membrane. Describe the structure of cell membrane. Determine the functions of cell membrane. Recognize to the mechanisms of transport. Compare between the Exocytosis & Endocytosis ...
... At the end of this lecture the student will be able to: Define the cell membrane. Describe the structure of cell membrane. Determine the functions of cell membrane. Recognize to the mechanisms of transport. Compare between the Exocytosis & Endocytosis ...
Dichotomous Keys - Blue Valley Schools
... • Each number has an “a” and ‘b” associated with it • Each “a” and “b” statement for one number are opposing statements about some observable characteristic of the organisms (usually not behavioral) • “Go to” directions or the identified “species name” to the rignt • There are always one fewer numbe ...
... • Each number has an “a” and ‘b” associated with it • Each “a” and “b” statement for one number are opposing statements about some observable characteristic of the organisms (usually not behavioral) • “Go to” directions or the identified “species name” to the rignt • There are always one fewer numbe ...
Lecture 2 - UniMAP Portal
... High Pressure Cell Homogenizers - Influence of Pressure Cell disruption follows first-order kinetics as first described by Hetrington et. al. by the equation: ...
... High Pressure Cell Homogenizers - Influence of Pressure Cell disruption follows first-order kinetics as first described by Hetrington et. al. by the equation: ...
Biochemistry and the Organization of Cells
... reactions are located on plasma membrane • Endoplasmic reticulum is absent • Ribosomes are found freely floating in cytosol • Chloroplasts are absent. Photosynthesis takes place in chromatophores which are extensions of plasma membranes ...
... reactions are located on plasma membrane • Endoplasmic reticulum is absent • Ribosomes are found freely floating in cytosol • Chloroplasts are absent. Photosynthesis takes place in chromatophores which are extensions of plasma membranes ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.