Section 17 Organelle Genetics
... Eukaryotic cell --phagocytosis of alpha-proteobacterium--> cell + symbiont -genes lost or transferred to nucleus--> cell + mitochondria Cell + mitochondrion --phagocytosis of cyanobacterium cell + symbiont--genes lost or transferred to nucleus cell + chloroplast In subsequent evolution, mito and c ...
... Eukaryotic cell --phagocytosis of alpha-proteobacterium--> cell + symbiont -genes lost or transferred to nucleus--> cell + mitochondria Cell + mitochondrion --phagocytosis of cyanobacterium cell + symbiont--genes lost or transferred to nucleus cell + chloroplast In subsequent evolution, mito and c ...
Cigarette Smoking - International Conference on Eye and Vision
... elderly population worldwide. • The prevalence of this disease is expected to increase in the coming years as people live longer. • There are different forms of AMD: • (1) Wet or neovascular form: In wet AMD, choroidal neovascularization (CNV) develops, which causes hemorrhage, swelling, and macular ...
... elderly population worldwide. • The prevalence of this disease is expected to increase in the coming years as people live longer. • There are different forms of AMD: • (1) Wet or neovascular form: In wet AMD, choroidal neovascularization (CNV) develops, which causes hemorrhage, swelling, and macular ...
2106lecture 2a powerpoint
... Metabolism cannot take place without the cell b) The cell -required as a location to house some metabolism and to produce components for metabolism no matter where such metabolism occurs -specific aspects of metabolism occur at specific points in the cell -must know where metabolism occurs to under ...
... Metabolism cannot take place without the cell b) The cell -required as a location to house some metabolism and to produce components for metabolism no matter where such metabolism occurs -specific aspects of metabolism occur at specific points in the cell -must know where metabolism occurs to under ...
Tools and Procedures
... What technique do biologists use to separate one part of a cell from the rest of the cell? ...
... What technique do biologists use to separate one part of a cell from the rest of the cell? ...
“D”ecreasing Rh Type
... Fetomaternal Hemorrhage Is this an OB patient who has experienced a large ...
... Fetomaternal Hemorrhage Is this an OB patient who has experienced a large ...
to get the file - Oxford Brookes University
... putative receptors, proteases, oxidases, extensins, and lipid-transfer-proteins. A ...
... putative receptors, proteases, oxidases, extensins, and lipid-transfer-proteins. A ...
the cell cycle of symbiotic chlorella
... increased. In the first paper of this series it was shown that during prolonged host starvation the percentage of algae with multiple nuclei fell almost to zero (McAuley, 1985a). Thus, algae were able to synthesize DNA but were unable to initiate mitosis. In contrast, an 5 phase/mitosis peak was dis ...
... increased. In the first paper of this series it was shown that during prolonged host starvation the percentage of algae with multiple nuclei fell almost to zero (McAuley, 1985a). Thus, algae were able to synthesize DNA but were unable to initiate mitosis. In contrast, an 5 phase/mitosis peak was dis ...
File - BINZHOU MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
... (Spontaneous Generation does not occur). Cells contains hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition. All energy flow (metabolism & biochemistry) of life occurs within cells. ...
... (Spontaneous Generation does not occur). Cells contains hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition. All energy flow (metabolism & biochemistry) of life occurs within cells. ...
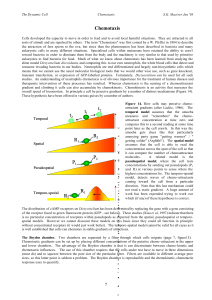
34 Chemotaxis
... Cells developed the capacity to move in order to feed and to avoid local harmful situations. They are attracted to all sorts of stimuli and are repulsed by others. The term "Chemotaxis" was first coined by a W. Pfeffer in 1884 to describe the attraction of fern sperm to the ova, but since then the p ...
... Cells developed the capacity to move in order to feed and to avoid local harmful situations. They are attracted to all sorts of stimuli and are repulsed by others. The term "Chemotaxis" was first coined by a W. Pfeffer in 1884 to describe the attraction of fern sperm to the ova, but since then the p ...
Classification Summary
... Typical Reproduction (asexual, sexual or both) Body system (none, radial, or bilateral) Can cells form tissues? Yes or no? Capable of movement? How? ...
... Typical Reproduction (asexual, sexual or both) Body system (none, radial, or bilateral) Can cells form tissues? Yes or no? Capable of movement? How? ...
Cell division in magnetotactic bacteria splits magnetosome chain in
... with the protein MamJ [10, 11] and this ordinates and aligns the magnetosomes forming a cytoskeletal chain structure down the cell [9 – 11]. Although magnetotactic bacteria are the subject of increased research activity, there are still several basic questions that have not yet been fully answered. ...
... with the protein MamJ [10, 11] and this ordinates and aligns the magnetosomes forming a cytoskeletal chain structure down the cell [9 – 11]. Although magnetotactic bacteria are the subject of increased research activity, there are still several basic questions that have not yet been fully answered. ...
DIRECTIONS 1. TEAMS are chosen to answer the questions. 2. If
... Vacuoles act as water storage for the cell. They also store waste products from the cell before they are removed. ...
... Vacuoles act as water storage for the cell. They also store waste products from the cell before they are removed. ...
Intro Neurology
... them makes it sound like either one or the other is functioning, depending on whether there's an emergency or not. Really, both are typically influencing different parts of the body to varying extents at any given time. ...
... them makes it sound like either one or the other is functioning, depending on whether there's an emergency or not. Really, both are typically influencing different parts of the body to varying extents at any given time. ...
Cell Analogy
... A system is a set of connected things or parts that form a whole. In order for a system to function properly, the individual parts must work together. Sometimes, the parts create a product; other times, they make something happen. A cell is a system that creates a product, protein. I will use the a ...
... A system is a set of connected things or parts that form a whole. In order for a system to function properly, the individual parts must work together. Sometimes, the parts create a product; other times, they make something happen. A cell is a system that creates a product, protein. I will use the a ...
Top of Form Name: AHSGE Biology Standard 2 Multiple Choice
... is placed in salt water in beaker 2. Which statement correctly explains the movement of water across cell membranes in one of the potato slices? a. Water will move out of the potato cells in beaker 2 because the solution is more concentrated. b. Water will move into the potato cells in beaker 1 beca ...
... is placed in salt water in beaker 2. Which statement correctly explains the movement of water across cell membranes in one of the potato slices? a. Water will move out of the potato cells in beaker 2 because the solution is more concentrated. b. Water will move into the potato cells in beaker 1 beca ...
The Role of MET in the Proliferation of Papillary Renal...
... proliferation Figure 2: A real-time measurement (Xcelligence) of cell proliferation in malignant Caki2 cells. Condition A) removes the genomic expression of MET from the DNA of the cell so that it can no longer produce any active MET . Condition B) uses the drug inhibitor INCB028060 to stop the acti ...
... proliferation Figure 2: A real-time measurement (Xcelligence) of cell proliferation in malignant Caki2 cells. Condition A) removes the genomic expression of MET from the DNA of the cell so that it can no longer produce any active MET . Condition B) uses the drug inhibitor INCB028060 to stop the acti ...
ELMS Curriculum Map for: 7th grade Science Semester 1 Unit 1 Unit
... Know: The relationship between the structures and functions of cell organelles; how cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems relate to the complexity of living organisms ...
... Know: The relationship between the structures and functions of cell organelles; how cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems relate to the complexity of living organisms ...
Phase-Contrast Light Microscopy of Living Cells Cultured in
... It is a powerful tool for taking high-resolution images of living cells. It is so common that most scientists don’t even mention phase-contrast microscopy in their materials and methods. The technique is an indispensable tool to examine cell morphology [1] and to distinguish or identify different ki ...
... It is a powerful tool for taking high-resolution images of living cells. It is so common that most scientists don’t even mention phase-contrast microscopy in their materials and methods. The technique is an indispensable tool to examine cell morphology [1] and to distinguish or identify different ki ...
Cell Signaling III: Death comes for the Cell Joe W. Ramos
... morphological changes associated with programmed cell death. • The term was originally used by Wyllie and his colleagues and is from the Greek meaning “dropping away” as the leaves from a tree. ...
... morphological changes associated with programmed cell death. • The term was originally used by Wyllie and his colleagues and is from the Greek meaning “dropping away” as the leaves from a tree. ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.