PHOTOSYNTHESIS -
... Chlorophyll is the magic compound that can grab that sunlight and start the whole process. Chlorophyll is actually quite a varied compound. There are four (4) types: a, b, c, and d. Chlorophyll can also be found in many microorganisms and even some prokaryotic cells. However, as far as plants are ...
... Chlorophyll is the magic compound that can grab that sunlight and start the whole process. Chlorophyll is actually quite a varied compound. There are four (4) types: a, b, c, and d. Chlorophyll can also be found in many microorganisms and even some prokaryotic cells. However, as far as plants are ...
Mutations showing specificity for normal growth or Mn
... other. These results also suggest that in TS1 the temperature-sensitive mutation(s) might be in a gene coding a specific component needed for DNA synthesis and expressed in exponential-phase cells. This specific component is essential for the N-CD process, whereas it is not involved in, nor essentia ...
... other. These results also suggest that in TS1 the temperature-sensitive mutation(s) might be in a gene coding a specific component needed for DNA synthesis and expressed in exponential-phase cells. This specific component is essential for the N-CD process, whereas it is not involved in, nor essentia ...
Microscopy and Cell Structure
... – Smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes • 40S, 60S, 80S • Difference often used as target for antimicrobials ...
... – Smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes • 40S, 60S, 80S • Difference often used as target for antimicrobials ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 11. Illustrate and explain the difference between an allosteric and a competitive enzyme regulator An allosteric regulator will bind to an enzyme at a place other than the active site and increase or decrease the protein’s activity by this binding. A competitive inhibitor will bind to the active sit ...
... 11. Illustrate and explain the difference between an allosteric and a competitive enzyme regulator An allosteric regulator will bind to an enzyme at a place other than the active site and increase or decrease the protein’s activity by this binding. A competitive inhibitor will bind to the active sit ...
Adaptation of microorganisms to extreme environments
... life on earth have to be enlarged. Not only are these organisms found in places often considered empty in the biological sense, it also is clear that these microbes have developed numerous special adaptations to survive in extreme habitats. Among these adaptations are: new mechanisms for energy tran ...
... life on earth have to be enlarged. Not only are these organisms found in places often considered empty in the biological sense, it also is clear that these microbes have developed numerous special adaptations to survive in extreme habitats. Among these adaptations are: new mechanisms for energy tran ...
Supplemental Figure Legends
... A, Cells treated with 72h 3μM vemurafenib showed less than 2-fold decrease in HKII mRNA levels. B, PRE vs. EDT patient biopsies showed minimal changes in HKII staining intensity. IHC data represents averaged scores for 100 cells per region with 5 regions scored per biopsy slide. Supplemental Figure ...
... A, Cells treated with 72h 3μM vemurafenib showed less than 2-fold decrease in HKII mRNA levels. B, PRE vs. EDT patient biopsies showed minimal changes in HKII staining intensity. IHC data represents averaged scores for 100 cells per region with 5 regions scored per biopsy slide. Supplemental Figure ...
Supplementary materials and methods
... Isolation and culture of murine hepatocytes Murine hepatocyte were isolated by the two-step collagenase perfusion technique. 350 ml of a warm (37°C) calcium-free buffer (Gibco Liver Perfusion Medium; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) was perfused through the liver in order to remove calcium ions from epithe ...
... Isolation and culture of murine hepatocytes Murine hepatocyte were isolated by the two-step collagenase perfusion technique. 350 ml of a warm (37°C) calcium-free buffer (Gibco Liver Perfusion Medium; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) was perfused through the liver in order to remove calcium ions from epithe ...
Cyclodextrins - Sigma
... Structural representations of β-cyclodextrin, α-cyclodextrin, and γ-cyclodextrin. The cyclodextrins are cyclic oligosaccharides consisting of 7, 6, or 8 (respectively) glucopyranose units. The solubility of natural cyclodextrins is very poor and initially this prevented cyclodextrins from becoming e ...
... Structural representations of β-cyclodextrin, α-cyclodextrin, and γ-cyclodextrin. The cyclodextrins are cyclic oligosaccharides consisting of 7, 6, or 8 (respectively) glucopyranose units. The solubility of natural cyclodextrins is very poor and initially this prevented cyclodextrins from becoming e ...
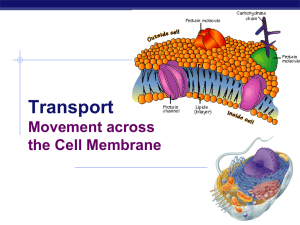
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane
... membrane needs to be semi-permeable specific channels allow ...
... membrane needs to be semi-permeable specific channels allow ...
Chapter 3 Review Packet
... Diffirsion is a result of the natural energy of molecules. V/hen molecules are in solution, they collide and scatter. Over time, these molecules will become evenly spread throughout the solution, which means that the molecules have reached dynamic equilibrium. The molecules continue to move, but the ...
... Diffirsion is a result of the natural energy of molecules. V/hen molecules are in solution, they collide and scatter. Over time, these molecules will become evenly spread throughout the solution, which means that the molecules have reached dynamic equilibrium. The molecules continue to move, but the ...
HiMesoXL Mesenchymal Stem Cell Expansion Medium
... User must ensure suitability of the product(s) in their application prior to use. Products conform solely to the information contained in this and other related HiMedia™ Publications. The information contained in this publication is based on our research and development work and is to the best of ou ...
... User must ensure suitability of the product(s) in their application prior to use. Products conform solely to the information contained in this and other related HiMedia™ Publications. The information contained in this publication is based on our research and development work and is to the best of ou ...
Plant Cells
... unit in plants these eukaryotic cells are similar to yet different from animal cells in many ways, the plant cell official site - the plant cell publishes novel research of special significance in plant biology especially in the areas of cellular biology molecular biology, molecular expressions cell ...
... unit in plants these eukaryotic cells are similar to yet different from animal cells in many ways, the plant cell official site - the plant cell publishes novel research of special significance in plant biology especially in the areas of cellular biology molecular biology, molecular expressions cell ...
Cell-Doc
... 13. The Lipid Tails are HYDROPHOBIC meaning "WATER-FEARING", the Hydrophobic tails will tend to orient themselves away from water. 14. When dropped in WATER, PHOSPHOLIPIDS line up on the surface with their Phosphate Heads Sticking into the Water and Lipid Tails pointing up from the surface. 15. Cell ...
... 13. The Lipid Tails are HYDROPHOBIC meaning "WATER-FEARING", the Hydrophobic tails will tend to orient themselves away from water. 14. When dropped in WATER, PHOSPHOLIPIDS line up on the surface with their Phosphate Heads Sticking into the Water and Lipid Tails pointing up from the surface. 15. Cell ...
Centennial Retrovirus Meeting
... Finally, the proviral DNA step in the retrovirus cell cycle was explained by the discovery of reverse transcriptase made by Baltimore and Temin, and by successful transfection experiments using DNA isolated from virogenic cells. Now, I would like to return to Peyton Rous and recall his far-sighted t ...
... Finally, the proviral DNA step in the retrovirus cell cycle was explained by the discovery of reverse transcriptase made by Baltimore and Temin, and by successful transfection experiments using DNA isolated from virogenic cells. Now, I would like to return to Peyton Rous and recall his far-sighted t ...
Prokaryotic
... seen 5. Prokaryotic—small, simple, no organelles are seen 6. Eukaryotic—unicellular, organelles present ...
... seen 5. Prokaryotic—small, simple, no organelles are seen 6. Eukaryotic—unicellular, organelles present ...
Cell-A-Bration
... outside the cell; act like antennae for the cell, collecting info about extracellular conditions – Enzymes: proteins that assist in reactions inside the cell – Transport proteins: move substances in & out of cell ...
... outside the cell; act like antennae for the cell, collecting info about extracellular conditions – Enzymes: proteins that assist in reactions inside the cell – Transport proteins: move substances in & out of cell ...
Ch. 7 Cell Structure and Function
... a. Chromatin- short condensed strands of DNA wrapped around histone proteins ...
... a. Chromatin- short condensed strands of DNA wrapped around histone proteins ...
Practice Exam for Semester 2, Part II Final Exam - mvhs
... f) Describe another method (or structure) by which an animal will maximize the amount of oxygen that their respiratory systems can take up? _____________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 16) Insulin released from the pan ...
... f) Describe another method (or structure) by which an animal will maximize the amount of oxygen that their respiratory systems can take up? _____________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 16) Insulin released from the pan ...
File
... Theory - a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world that is acquired through the scientific method and repeatedly tested and confirmed through observation and experimentation. ...
... Theory - a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world that is acquired through the scientific method and repeatedly tested and confirmed through observation and experimentation. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.