Extended version
... Present tense 3rd person singular and plural: e.g. Plant cells have…, An animal cell has…, Respiration happens… Reactions happen… …made up of…, …full of…, …made from… ...
... Present tense 3rd person singular and plural: e.g. Plant cells have…, An animal cell has…, Respiration happens… Reactions happen… …made up of…, …full of…, …made from… ...
Test 3
... easily in the plane of the bildayer, but cannot flip-flop from one side to the other. In fact the lipid composition of the inside of membrane is often different than the lipid composition of the outside of the bilayer. Protein are thought to float freely in this surface and can also mover laterally ...
... easily in the plane of the bildayer, but cannot flip-flop from one side to the other. In fact the lipid composition of the inside of membrane is often different than the lipid composition of the outside of the bilayer. Protein are thought to float freely in this surface and can also mover laterally ...
Cell Reading Packet
... important activities of cells. Other than using energy from your food to keep you warm, the most important use of energy in your body is to help pump substances across the membranes of your cells by active transport—a process that goes on all the time. Cells get the energy for active transport from ...
... important activities of cells. Other than using energy from your food to keep you warm, the most important use of energy in your body is to help pump substances across the membranes of your cells by active transport—a process that goes on all the time. Cells get the energy for active transport from ...
File - Science at St. Dominics
... • the water inside the cell would move out by osmosis • the cell wall stays intact but the membrane shrivels up away from it ...
... • the water inside the cell would move out by osmosis • the cell wall stays intact but the membrane shrivels up away from it ...
Notes Unit 5 Part 4
... Modern taxonomy now classifies organisms based on their _______________ characteristics as well as their ______________________ relationships phylogeny = the _________________ history for a group of __________________ cladogram = a diagram that shows the common ________________ and derived _____ ...
... Modern taxonomy now classifies organisms based on their _______________ characteristics as well as their ______________________ relationships phylogeny = the _________________ history for a group of __________________ cladogram = a diagram that shows the common ________________ and derived _____ ...
Osmosis Experimental Design Lab
... Vanilla Balloon Analysis 7. After the twenty minutes, did it smell inside the bag? 8. How did the smell get into the bag? 9. After the bag was open for two minutes, was the smell more or less concentrated compared to when you first opened it? Why? Conclusion Questions 10. Were your predictions corre ...
... Vanilla Balloon Analysis 7. After the twenty minutes, did it smell inside the bag? 8. How did the smell get into the bag? 9. After the bag was open for two minutes, was the smell more or less concentrated compared to when you first opened it? Why? Conclusion Questions 10. Were your predictions corre ...
Slide ()
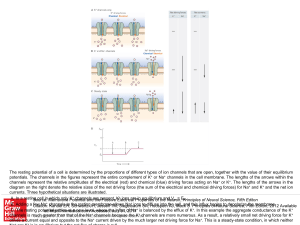
... Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available C. The resting potential settles at a new level, where the influx Na+ is balanced by the efflux of K+. In this example the aggregate conductance of the K+ at: http://mhm ...
... Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available C. The resting potential settles at a new level, where the influx Na+ is balanced by the efflux of K+. In this example the aggregate conductance of the K+ at: http://mhm ...
fde6f5e7fc46f32
... Types of Active Transport • 2. Endocytosis: taking bulky material into a cell • Uses energy • Cell membrane in-folds around food particle • “cell eating” • forms food vacuole & digests food • This is how white blood cells eat bacteria! ...
... Types of Active Transport • 2. Endocytosis: taking bulky material into a cell • Uses energy • Cell membrane in-folds around food particle • “cell eating” • forms food vacuole & digests food • This is how white blood cells eat bacteria! ...
Clear cell follicular adenoma of the thyroid: A case report
... follicular growth. The cells were large with a clear cytoplasm (Fig. 3). There was no evidence of vascular or capsular invasion. The tumor cells stained positive for intracytoplasmic thyroglobulin (Fig. 4) (APAAP method with a fast red substrate). Ultrastructurally, the cells were dominated by close ...
... follicular growth. The cells were large with a clear cytoplasm (Fig. 3). There was no evidence of vascular or capsular invasion. The tumor cells stained positive for intracytoplasmic thyroglobulin (Fig. 4) (APAAP method with a fast red substrate). Ultrastructurally, the cells were dominated by close ...
Read this article
... proportion of actively dividing cells and are more responsive to a callus initiation programme. The exact conditions required to initiate and sustain plant cells in culture, or to regenerate intact plants from cultured cells, are different for each plant species. Each variety of a species will often ...
... proportion of actively dividing cells and are more responsive to a callus initiation programme. The exact conditions required to initiate and sustain plant cells in culture, or to regenerate intact plants from cultured cells, are different for each plant species. Each variety of a species will often ...
Isabel Hoyt Membrane
... Extracellular matrix – Connects the cell, surrounds it. Carbohydrate – Short, branched chains that are covalently bonded to lipids, forming molecules called glycolipids. Glycoplipids- Cell-cell recognition Glycoprotein – Glycolipids are covalently bonded to proteins, which are thereby glycoprotein. ...
... Extracellular matrix – Connects the cell, surrounds it. Carbohydrate – Short, branched chains that are covalently bonded to lipids, forming molecules called glycolipids. Glycoplipids- Cell-cell recognition Glycoprotein – Glycolipids are covalently bonded to proteins, which are thereby glycoprotein. ...
The Three Major Parts of the Cell
... processes of the cell. These proteins can attach to various cell membranes ...
... processes of the cell. These proteins can attach to various cell membranes ...
Part 1 - Jobworks Biology
... available to the cell. This is why mitochondria are sometimes referred to as the power plants of the cell. They use energy from organic compounds such as glucose to make molecules of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), an energycarrying molecule that is used almost universally inside cells for energy. Sc ...
... available to the cell. This is why mitochondria are sometimes referred to as the power plants of the cell. They use energy from organic compounds such as glucose to make molecules of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), an energycarrying molecule that is used almost universally inside cells for energy. Sc ...
Primary cell wall
... Division of the plant cell The presence of the cell wall differentiate significantly the division of the plant cell with respect to that of animal cell. Interphase of the plant cell is characterized by 2 events: 1. (G1) Nucleus moves to the center of cell through cytoplasmatic bridles; the latter f ...
... Division of the plant cell The presence of the cell wall differentiate significantly the division of the plant cell with respect to that of animal cell. Interphase of the plant cell is characterized by 2 events: 1. (G1) Nucleus moves to the center of cell through cytoplasmatic bridles; the latter f ...
Publications de l`équipe - Centre de recherche de l`Institut Curie
... the inner plasma membrane. They are involved in essential functions requiring cell membrane remodeling and compartmentalization, such as cell division and dendrite morphogenesis, and have been implicated in numerous diseases. Depending on the organisms and on the type of tissue, a specific set of sep ...
... the inner plasma membrane. They are involved in essential functions requiring cell membrane remodeling and compartmentalization, such as cell division and dendrite morphogenesis, and have been implicated in numerous diseases. Depending on the organisms and on the type of tissue, a specific set of sep ...
Pancreatic Stem Cells: A Glimmer of Hope for Diabetes?
... self-renew and differentiate into multiple cell lineages, either embryo-derived or fetal/adult tissue-derived, in treating diabetic patients is ...
... self-renew and differentiate into multiple cell lineages, either embryo-derived or fetal/adult tissue-derived, in treating diabetic patients is ...
... • In the last century biomaterials were used for the fabrication of permanent implants to replace tissue function (e.g., total joint replacement prostheses). • In this century the principal role of biomaterials will likely be to serve as scaffolds/matrices for tissue engineering and cell and gene th ...
Dr. Ken Teter`s and Carly Bader`s Presentation
... Creativity in the Arts & Sciences Event The University of Florida HHMI Science For Life Program invites you to participate in the 3rd Annual Creativity in the Arts and Sciences Event (CASE) sponsored by HHMI. This follows successful events in 2009 and 2010, each of which drew over 150 art and scien ...
... Creativity in the Arts & Sciences Event The University of Florida HHMI Science For Life Program invites you to participate in the 3rd Annual Creativity in the Arts and Sciences Event (CASE) sponsored by HHMI. This follows successful events in 2009 and 2010, each of which drew over 150 art and scien ...
7.391 Concept-Centered Teaching Semester I
... organism? • How efficient is ligation? • How efficient is transformation? • Do antibiotics affect the plasmid or the organism? How does this assist cloning? 7.012 Specific Organismal Cloning • Why is it not necessary to fertilize an egg to make an oocyte divide? • Would you want a nucleus from a mei ...
... organism? • How efficient is ligation? • How efficient is transformation? • Do antibiotics affect the plasmid or the organism? How does this assist cloning? 7.012 Specific Organismal Cloning • Why is it not necessary to fertilize an egg to make an oocyte divide? • Would you want a nucleus from a mei ...
Data/hora: 08/03/2017 04:59:34 Provedor de dados: 56 País: Brazil
... 1024-UV confocal system attached to a Zeiss Axiovert 100 microscope. Since PtK2 cells possess only one nucleolus organizer region, micronucleated cells presented only one or two micronuclei containing nucleolus. By confocal microscopy we showed that in most micronuclei lacking a typical nucleolus a ...
... 1024-UV confocal system attached to a Zeiss Axiovert 100 microscope. Since PtK2 cells possess only one nucleolus organizer region, micronucleated cells presented only one or two micronuclei containing nucleolus. By confocal microscopy we showed that in most micronuclei lacking a typical nucleolus a ...
transport in plants - Seattle Central College
... Figure 36.8 Mycorrhizae, symbiotic associations of fungi and roots roots ...
... Figure 36.8 Mycorrhizae, symbiotic associations of fungi and roots roots ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.