350-Cell Cycle-DF - Department Of Biological Sciences Hunter
... Blocking cells in S-phase with aphidicolin sensitizes cells to rapamycin In the presence of serum/TGF- - if cells are allowed to enter S-phase, then the lack of mTORC1 signals to 4E-BP1 tells the cell that nutrients are in short supply and that replicating the genome is probably a bad career move! ...
... Blocking cells in S-phase with aphidicolin sensitizes cells to rapamycin In the presence of serum/TGF- - if cells are allowed to enter S-phase, then the lack of mTORC1 signals to 4E-BP1 tells the cell that nutrients are in short supply and that replicating the genome is probably a bad career move! ...
Macromolecule?
... What are the three concepts that make up the cell theory? a. All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living ...
... What are the three concepts that make up the cell theory? a. All living things are composed of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living ...
Chapter 7- Microbial Nutrition, Ecology, and
... Osmotic pressure is defined as the minimum amount of pressure that must be applied to a solution to prevent the flow of water across a membrane within a solution. Most bacteria live in hypotonic environments. Osmotic pressure increases as more and more water is taken up by the cell. The cell wall ke ...
... Osmotic pressure is defined as the minimum amount of pressure that must be applied to a solution to prevent the flow of water across a membrane within a solution. Most bacteria live in hypotonic environments. Osmotic pressure increases as more and more water is taken up by the cell. The cell wall ke ...
A novel checkpoint mechanism regulating the G1/S transition
... occurs in G1 and not in S phase, which is further supported by the following: The Cdc2 inhibitor Rum1, which is only expressed in G1 (Benito et al. 1998), was strongly expressed during the delay period (Fig. 1D). Moreover, the activity of the S-phase-specific checkpoint kinase Cds1 was not activated ...
... occurs in G1 and not in S phase, which is further supported by the following: The Cdc2 inhibitor Rum1, which is only expressed in G1 (Benito et al. 1998), was strongly expressed during the delay period (Fig. 1D). Moreover, the activity of the S-phase-specific checkpoint kinase Cds1 was not activated ...
CELL WALL ACTIVE ANTIBIOTICS I {ST1}
... C=O portion of D-ala/D-ala. Transpeptidase recognizes this analogue structure on penicillin and acylates it covalently. So penicillin is a suicide substrate. This inhibits cross-linking of peptidoglycan by transpeptidase. ...
... C=O portion of D-ala/D-ala. Transpeptidase recognizes this analogue structure on penicillin and acylates it covalently. So penicillin is a suicide substrate. This inhibits cross-linking of peptidoglycan by transpeptidase. ...
File - The Stem Cell Controversy
... 5. Look at the pictures on the right of the page. Explain the visual difference between a stem cells DNA and the DNA in a differentiated cell. Read the caption under the picture to help you out. ...
... 5. Look at the pictures on the right of the page. Explain the visual difference between a stem cells DNA and the DNA in a differentiated cell. Read the caption under the picture to help you out. ...
The Endocrine System
... new enzymes or proteins. In the latter, the hormone receptor complex binds to the DNA itself and triggers transcription of mRNA, the first step in protein synthesis. A gland is an organ that produces and releases a substance, or secretion. Exocrine glands release their secretions, through tube-like ...
... new enzymes or proteins. In the latter, the hormone receptor complex binds to the DNA itself and triggers transcription of mRNA, the first step in protein synthesis. A gland is an organ that produces and releases a substance, or secretion. Exocrine glands release their secretions, through tube-like ...
Osmosis Experimental Design Lab
... Vanilla Balloon Analysis 7. After the twenty minutes, did it smell inside the bag? 8. How did the smell get into the bag? 9. After the bag was open for two minutes, was the smell more or less concentrated compared to when you first opened it? Why? Conclusion Questions 10. Were your predictions corre ...
... Vanilla Balloon Analysis 7. After the twenty minutes, did it smell inside the bag? 8. How did the smell get into the bag? 9. After the bag was open for two minutes, was the smell more or less concentrated compared to when you first opened it? Why? Conclusion Questions 10. Were your predictions corre ...
Organelle Poetry Honoree: Nikky Finney Grade Level: 9
... 2. Once the students have completed the Know and Wonder section of the KWL chart, the teacher will guide students through Cell Organelle PPT Lesson (attached). 3. Teacher introduces Honoree Nikki Finney and samples of her work. 4. Students will make a poetry book using the cell organelles that we ...
... 2. Once the students have completed the Know and Wonder section of the KWL chart, the teacher will guide students through Cell Organelle PPT Lesson (attached). 3. Teacher introduces Honoree Nikki Finney and samples of her work. 4. Students will make a poetry book using the cell organelles that we ...
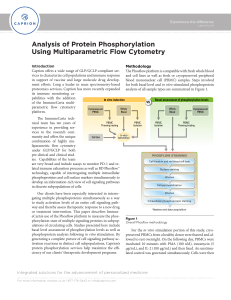
Analysis of Protein Phosphorylation Using Multiparametric Flow
... flow cytometry data can be analyzed using a Boolean gating approach when the phosphorylated forms of proteins studied are well-separated from their non-phosphorylated counterparts, which generates a protein phosphorylation “signature” that can facilitate subsequent data-mining and biomarker discover ...
... flow cytometry data can be analyzed using a Boolean gating approach when the phosphorylated forms of proteins studied are well-separated from their non-phosphorylated counterparts, which generates a protein phosphorylation “signature” that can facilitate subsequent data-mining and biomarker discover ...
FREE Sample Here
... 1. A student is observing a cell under the microscope. It is observed to have supercoiled DNA with histones. Which of the following would also be observed by the student? a. A single circular chromosome b. A nucleus c. Free-floating nuclear material d. No organelles ANS: B The cell described is a eu ...
... 1. A student is observing a cell under the microscope. It is observed to have supercoiled DNA with histones. Which of the following would also be observed by the student? a. A single circular chromosome b. A nucleus c. Free-floating nuclear material d. No organelles ANS: B The cell described is a eu ...
Formatting Instructions
... [email protected] Abstract Zeolites due to their low toxicity and high compatibility are considered new biomaterials for medical applications and they can be used in different conformation as pure and hybrid membranes. Their growing applicability is connected with the presence of cavities and ch ...
... [email protected] Abstract Zeolites due to their low toxicity and high compatibility are considered new biomaterials for medical applications and they can be used in different conformation as pure and hybrid membranes. Their growing applicability is connected with the presence of cavities and ch ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... trigger on mast cell. • Cromolyn is to inhibit the release of mediators of mast cell probably because it can stabilize the mast cell membrane. • Antihistamine is the competitor of histamine on tissue. • Pharmacological drug to decrease the effect of allergy. ...
... trigger on mast cell. • Cromolyn is to inhibit the release of mediators of mast cell probably because it can stabilize the mast cell membrane. • Antihistamine is the competitor of histamine on tissue. • Pharmacological drug to decrease the effect of allergy. ...
fluid mosaic model
... converts a mechanical/chemical stimulus to a cell into a specific cellular response. ...
... converts a mechanical/chemical stimulus to a cell into a specific cellular response. ...
Χρήστος Ν. Μπακογιάννης
... Bound smooth muscle cell receptors activate various intracellular smooth muscle cell6proteins. One such protein, mTOR, plays a central regulatory role in the cell cycle. ...
... Bound smooth muscle cell receptors activate various intracellular smooth muscle cell6proteins. One such protein, mTOR, plays a central regulatory role in the cell cycle. ...
Is CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy a Good Strategy for T
... effector : target ratio of 1:1 or 5:1 respectively. The killing efficacy was monitored by xCELLigence RTCA DP (ACEA Biosciences) in real time manner, and the curve represented the target cell growth pattern. ...
... effector : target ratio of 1:1 or 5:1 respectively. The killing efficacy was monitored by xCELLigence RTCA DP (ACEA Biosciences) in real time manner, and the curve represented the target cell growth pattern. ...
Slide 1
... Bound smooth muscle cell receptors activate various intracellular smooth muscle cell6proteins. One such protein, mTOR, plays a central regulatory role in the cell cycle. ...
... Bound smooth muscle cell receptors activate various intracellular smooth muscle cell6proteins. One such protein, mTOR, plays a central regulatory role in the cell cycle. ...
Study Guide A
... Cells use energy to transport materials that cannot diffuse across a membrane. ...
... Cells use energy to transport materials that cannot diffuse across a membrane. ...
Cell membrane
... Along with the model, you must complete the following chart that explains the structure and function of each organelle and what could be used to portray it, and WHY!! In other words, what you use for each organelle must make sense considering the structure and function of that organelle. Please note ...
... Along with the model, you must complete the following chart that explains the structure and function of each organelle and what could be used to portray it, and WHY!! In other words, what you use for each organelle must make sense considering the structure and function of that organelle. Please note ...
A rapid image cytometric analysis method for phagocytosis using
... Phagocytosis is an essential process of the immune system to eliminate cellular debris and pathogens. It is a specific form of endocytosis involving vesicular internalization. Phagocytic cells such as macrophages can be attracted to pathogens or cellular debris and engulf the material to be trapped ...
... Phagocytosis is an essential process of the immune system to eliminate cellular debris and pathogens. It is a specific form of endocytosis involving vesicular internalization. Phagocytic cells such as macrophages can be attracted to pathogens or cellular debris and engulf the material to be trapped ...
DIRECTORATE OF SCHOOL EDUCATION, GOVERNMENT OF
... Electron Microscope (TEM &SEM) 2.5. Ultra Structure of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 2.6. Cell Wall 2.7. Cell Membrance (Fluid Mosaic Model) Membrane Transport Model 2.8. Cell Organelles : Nucleus, Mitochondria, Plastids, Ribosomes 2.9. Cell Divisions : Amitosis, Mitosis and Meiosis and their sig ...
... Electron Microscope (TEM &SEM) 2.5. Ultra Structure of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 2.6. Cell Wall 2.7. Cell Membrance (Fluid Mosaic Model) Membrane Transport Model 2.8. Cell Organelles : Nucleus, Mitochondria, Plastids, Ribosomes 2.9. Cell Divisions : Amitosis, Mitosis and Meiosis and their sig ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.