Cytoskeletal elements in bacteria
... group found that MreB and Mbl form filamentous structures in B. subtilis cells, as revealed by immunofluorescence and GFP (green fluorescent protein) tagging to visualize the proteins [31] (Figure 1c,d). Both filaments formed helical structures underneath the cell membrane, with Mbl filaments extend ...
... group found that MreB and Mbl form filamentous structures in B. subtilis cells, as revealed by immunofluorescence and GFP (green fluorescent protein) tagging to visualize the proteins [31] (Figure 1c,d). Both filaments formed helical structures underneath the cell membrane, with Mbl filaments extend ...
Cell Membrane Cellular Transport
... Examples of Osmosis in Nature ... • Plant cells are supported by turgor pressure within the vacuole when placed in a hypotonic solution. • Plant cells wilt when water leaves the vacuole due to plasmolysis when placed in a hypertonic solution. ...
... Examples of Osmosis in Nature ... • Plant cells are supported by turgor pressure within the vacuole when placed in a hypotonic solution. • Plant cells wilt when water leaves the vacuole due to plasmolysis when placed in a hypertonic solution. ...
Prokaryotic cells
... Rickettsia)) are only 0.1 to 0.2 µm in diameter diameter,, whereas larger bacteria may be many microns in length.. Most species are approximately 1 µm in length diameter and are therefore visible using the light microscope which has a resolution of 0.2 µm. ...
... Rickettsia)) are only 0.1 to 0.2 µm in diameter diameter,, whereas larger bacteria may be many microns in length.. Most species are approximately 1 µm in length diameter and are therefore visible using the light microscope which has a resolution of 0.2 µm. ...
Plasmodesmata 2004. Surfing the Symplasm
... a superhighway for the delivery of systemic informational molecules (Bill Lucas, University of California, Davis) has gained considerable support from the study of movement of viruses and endogenous macromolecules. Recent work establishing that non-cell autonomous macromolecules are able to function ...
... a superhighway for the delivery of systemic informational molecules (Bill Lucas, University of California, Davis) has gained considerable support from the study of movement of viruses and endogenous macromolecules. Recent work establishing that non-cell autonomous macromolecules are able to function ...
Unit 3 Cell Str Func
... All organisms are made of cells Cells are all the same shape and size Cells are the basic unit of life All cells come from preexisting cells ...
... All organisms are made of cells Cells are all the same shape and size Cells are the basic unit of life All cells come from preexisting cells ...
Peer-reviewed Article PDF
... program, the so called programmed cell death (PCD). PCD is a highly regulated and organized cell suicide process that is essential for all living organisms. PCD plays an important role in cell homeostasis maintenance, tissue specialization, removing of damaged or infected cells, and acclamatory resp ...
... program, the so called programmed cell death (PCD). PCD is a highly regulated and organized cell suicide process that is essential for all living organisms. PCD plays an important role in cell homeostasis maintenance, tissue specialization, removing of damaged or infected cells, and acclamatory resp ...
Aria Sample Prep 110210
... provide BD Falcon 12 " 75 mm 35 !m filter-top tubes for this purpose at a charge of $1.00 per tube. The sample injection chamber has a heating/cooling unit that can maintain the sample temperature at 4°, 20°, 37°, or 42° C. The heating/cooling unit is meant only to maintain the sample temperature, n ...
... provide BD Falcon 12 " 75 mm 35 !m filter-top tubes for this purpose at a charge of $1.00 per tube. The sample injection chamber has a heating/cooling unit that can maintain the sample temperature at 4°, 20°, 37°, or 42° C. The heating/cooling unit is meant only to maintain the sample temperature, n ...
Supplementary figure legends
... phosphatases that are essential for cell cycle progression and have redundant function, we generated a dendrogram tree of the kinases and phosphatases. The dendrogram trees were generated with Neighbor-Joining method using ClustalW version 1.81 with full dynamic programming option9 and BLOSUM-62 com ...
... phosphatases that are essential for cell cycle progression and have redundant function, we generated a dendrogram tree of the kinases and phosphatases. The dendrogram trees were generated with Neighbor-Joining method using ClustalW version 1.81 with full dynamic programming option9 and BLOSUM-62 com ...
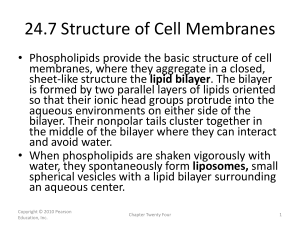
24.7 Structure of Cell Membranes
... membranes, where they aggregate in a closed, sheet-like structure the lipid bilayer. The bilayer is formed by two parallel layers of lipids oriented so that their ionic head groups protrude into the aqueous environments on either side of the bilayer. Their nonpolar tails cluster together in the midd ...
... membranes, where they aggregate in a closed, sheet-like structure the lipid bilayer. The bilayer is formed by two parallel layers of lipids oriented so that their ionic head groups protrude into the aqueous environments on either side of the bilayer. Their nonpolar tails cluster together in the midd ...
§ 58-10-90
... A protected cell company, with respect to any of its protected cells, shall engage in fully funded indemnity triggered insurance securitization to support in full the protected cell exposures attributable to that protected cell. A protected cell company insurance securitization that is nonindemnity ...
... A protected cell company, with respect to any of its protected cells, shall engage in fully funded indemnity triggered insurance securitization to support in full the protected cell exposures attributable to that protected cell. A protected cell company insurance securitization that is nonindemnity ...
passive-and-active-transport
... Basically molecules tend to move from where they are more crowded to where they are less crowded. They do this because of their own kinetic energy and random movement. ...
... Basically molecules tend to move from where they are more crowded to where they are less crowded. They do this because of their own kinetic energy and random movement. ...
Stem Cell Activation for Smoother, More Even Skin
... culture technique was used to produce the plant raw material in an ecological and sustainable way. The technique is based on ...
... culture technique was used to produce the plant raw material in an ecological and sustainable way. The technique is based on ...
tolerance to cadmium and phytochelatins synthesis in agrostis
... effect on cell growth from the suspension-cultured cells realized by root callus of the Agrostis tenuis ecotype. In the liquid Murashige-Skoog medium culture were added, immediately after the cell inoculation, different Cd ion concentrations. The concentrations of CdSO 4 between 10 and 20 µM (which ...
... effect on cell growth from the suspension-cultured cells realized by root callus of the Agrostis tenuis ecotype. In the liquid Murashige-Skoog medium culture were added, immediately after the cell inoculation, different Cd ion concentrations. The concentrations of CdSO 4 between 10 and 20 µM (which ...
Ch 13 Notes
... • Same basic replication pathway as bacteriophages-perform the process differently • Differences result from • Presence of envelope around some viruses viral genome must be separated from its protein coat • Eukaryotic nature of animal cells • Lack of cell wall in animal cells attach to plasma membra ...
... • Same basic replication pathway as bacteriophages-perform the process differently • Differences result from • Presence of envelope around some viruses viral genome must be separated from its protein coat • Eukaryotic nature of animal cells • Lack of cell wall in animal cells attach to plasma membra ...
Kinds of Cells copy
... To carry our their function — move substances in and out of the cell • To grow • To carry out ...
... To carry our their function — move substances in and out of the cell • To grow • To carry out ...
chapter 2: understanding cancer
... reason a kidney cell cannot behave as a muscle cell, and a lung cell cannot function as a brain cell. Abnormal cell proliferation can begin at any point during a cell’s differentiation process. When a single cell divides, it results in two daughter cells. The daughter cells typically have the same c ...
... reason a kidney cell cannot behave as a muscle cell, and a lung cell cannot function as a brain cell. Abnormal cell proliferation can begin at any point during a cell’s differentiation process. When a single cell divides, it results in two daughter cells. The daughter cells typically have the same c ...
AP Bio membranes
... • Two lipid bilayers may vary in composition. • Membrane synthesis and modification by the ER and Golgi determines the distribution of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. ...
... • Two lipid bilayers may vary in composition. • Membrane synthesis and modification by the ER and Golgi determines the distribution of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. ...
Comparative Analysis of Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotic
... 2.2 Analysis of orthologous relationships between cell cycle regulated genes We observed orthologous relationships between the cell cycle regulated genes in each species using KEGG/OC(OrthologCluster) [5,6], which assigns an orthologous identifier to each gene with sequence similarities stored in KE ...
... 2.2 Analysis of orthologous relationships between cell cycle regulated genes We observed orthologous relationships between the cell cycle regulated genes in each species using KEGG/OC(OrthologCluster) [5,6], which assigns an orthologous identifier to each gene with sequence similarities stored in KE ...
Cellular Imaging and Analysis FAQs
... its benzyl guanine substrates and to remove its affinity for DNA. In mammalian cells, SNAP-tag localizes to the cytoplasm and the nucleus. 2. How does it work? The SNAP-tag is a protein tag that forms a highly stable, covalent thioether bond with fluorophores or other substituted groups when appende ...
... its benzyl guanine substrates and to remove its affinity for DNA. In mammalian cells, SNAP-tag localizes to the cytoplasm and the nucleus. 2. How does it work? The SNAP-tag is a protein tag that forms a highly stable, covalent thioether bond with fluorophores or other substituted groups when appende ...
Transport - Our eclass community
... tubular pathways through which fluids flow. They form the circulatory system of plants Xylem and phloem vessels are found in the roots, stems and leaves of plants are referred to as vascular tissue Vascular tissue is found extensively throughout the plant, from the root tips to the ends of leaves ...
... tubular pathways through which fluids flow. They form the circulatory system of plants Xylem and phloem vessels are found in the roots, stems and leaves of plants are referred to as vascular tissue Vascular tissue is found extensively throughout the plant, from the root tips to the ends of leaves ...
Chapter 16: Cells and plants
... Research one of the following groups of cells to find out about the cells’ shape and function: • sensory cells • smooth, skeletal and cardiac muscle cells • blood cells. ...
... Research one of the following groups of cells to find out about the cells’ shape and function: • sensory cells • smooth, skeletal and cardiac muscle cells • blood cells. ...
21. Potential of modified vaccinia Ankara (MOA) as a vaccine delivery vector for foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV)
... movement of infected products or by means of emergency vaccination in free countries or mass vaccination in endemic countries. However, vaccination is not always implemented, especially in disease-free countries, due the costs associated with the ban on exports from these countries until the disease ...
... movement of infected products or by means of emergency vaccination in free countries or mass vaccination in endemic countries. However, vaccination is not always implemented, especially in disease-free countries, due the costs associated with the ban on exports from these countries until the disease ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.