AP Biology - SPS186.org
... partition cell into compartments create different local environments ...
... partition cell into compartments create different local environments ...
Death associated proteins (DAPs)
... Keywords: apoptosis; DAP-kinase; cathepsin D; interferon-g; metastasis; functional gene cloning ...
... Keywords: apoptosis; DAP-kinase; cathepsin D; interferon-g; metastasis; functional gene cloning ...
Laser-Micropipet Combination for Single-Cell Analysis
... prior to sampling. For nonadherent cells, the use of electroosmotic flow (EOF) to move the cell into the capillary inlet may impact the cellular process to be measured. A large body of literature exists on the biological effects of electric fields.16-19 Electric fields as low as 1-15 V/cm can cause ...
... prior to sampling. For nonadherent cells, the use of electroosmotic flow (EOF) to move the cell into the capillary inlet may impact the cellular process to be measured. A large body of literature exists on the biological effects of electric fields.16-19 Electric fields as low as 1-15 V/cm can cause ...
How Neurons Communicate (the Neuron Game)
... a) Dendrites: collects input signals from many neurons using receptors (more a on receptors later). They have many branches and sometimes even spines along each branch so that there is a lot a of area for other neurons to contact its surface. a b) Cell Body: decides whether or not to continue passin ...
... a) Dendrites: collects input signals from many neurons using receptors (more a on receptors later). They have many branches and sometimes even spines along each branch so that there is a lot a of area for other neurons to contact its surface. a b) Cell Body: decides whether or not to continue passin ...
MODEL 1: Movement of Water – a type of diffusion.
... As the plants get surrounded by seawater the concentration outside the cells is stronger than inside, so it causes water to move out of the cells by osmosis, causing the plants to wilt. ...
... As the plants get surrounded by seawater the concentration outside the cells is stronger than inside, so it causes water to move out of the cells by osmosis, causing the plants to wilt. ...
Arabidopsis R-SNARE Proteins VAMP721 and VAMP722 Are
... targeted secretion along the phragmoplast, where homotypic fusion of Golgi-derived vesicles gives rise to the cell plate [3]. After the cell plate eventually fuses with the parental plasma membrane, two individual cells are separated by a new cell wall [4,5]. The maturation of the cell plate to a ri ...
... targeted secretion along the phragmoplast, where homotypic fusion of Golgi-derived vesicles gives rise to the cell plate [3]. After the cell plate eventually fuses with the parental plasma membrane, two individual cells are separated by a new cell wall [4,5]. The maturation of the cell plate to a ri ...
Cell cycle control by ubiquitylation
... are periodic1. This is the result of a constant synthetic rate coupled with a defined window in the cycle of specific proteolysis, which is executed by the ubiquitinproteasome ...
... are periodic1. This is the result of a constant synthetic rate coupled with a defined window in the cycle of specific proteolysis, which is executed by the ubiquitinproteasome ...
Secured cutting: controlling separase at the metaphase to anaphase
... Is cleavage of cohesin sufficient to trigger anaphase? If true, any protease capable of cleaving cohesin should be able to do so. This has been tested in budding yeast. One of the two separase cleavage sites in Scc1 was replaced by the specific recognition sequence of a plant virus protease. Cleavag ...
... Is cleavage of cohesin sufficient to trigger anaphase? If true, any protease capable of cleaving cohesin should be able to do so. This has been tested in budding yeast. One of the two separase cleavage sites in Scc1 was replaced by the specific recognition sequence of a plant virus protease. Cleavag ...
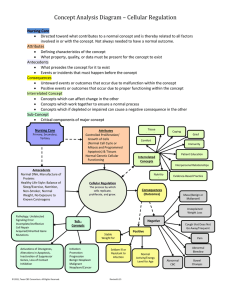
Concept Analysis Diagram * Cellular Regulation
... Concept Analysis Diagram – Cellular Regulation Explanation of Cellular Regulation Diagram Cellular Regulation is the process by which cells replicate, proliferate, and grow. In order for Cellular Regulation to occur the following antecedents should be present: normal DNA, manufacture of proteins, h ...
... Concept Analysis Diagram – Cellular Regulation Explanation of Cellular Regulation Diagram Cellular Regulation is the process by which cells replicate, proliferate, and grow. In order for Cellular Regulation to occur the following antecedents should be present: normal DNA, manufacture of proteins, h ...
A proteomic approach to identify endosomal cargoes controlling
... These were surrounded by basement membranes as evidenced by immunofluorescence staining for the basolateral marker β4 integrin and the basement membrane component laminin-V (Fig. 3B). We quantitatively assessed the shape of these organoids and found that MCF10DCIS.com cells formed structures that we ...
... These were surrounded by basement membranes as evidenced by immunofluorescence staining for the basolateral marker β4 integrin and the basement membrane component laminin-V (Fig. 3B). We quantitatively assessed the shape of these organoids and found that MCF10DCIS.com cells formed structures that we ...
Cell Wall
... peptidoglycan surrounded by a second lipid membrane containing lipopolysaccharides and lipoproteins. Most bacteria have the Gram-negative cell wall and only the Firmicutes and Actinobacteria (previously known as the low G+C and high G+C Gram-positive bacteria, respectively) have the alternative Gram ...
... peptidoglycan surrounded by a second lipid membrane containing lipopolysaccharides and lipoproteins. Most bacteria have the Gram-negative cell wall and only the Firmicutes and Actinobacteria (previously known as the low G+C and high G+C Gram-positive bacteria, respectively) have the alternative Gram ...
Magic Lysis Buffer Improves the Efficiency of
... bait-prey binding partners. In addition, caution must be taken about the stringency of lysis buffer since it can strip the bait protein of true binding partners. These problems are especially true for IPs using antibodies against endogenous proteins. However, IPs using endogenous antibodies are nece ...
... bait-prey binding partners. In addition, caution must be taken about the stringency of lysis buffer since it can strip the bait protein of true binding partners. These problems are especially true for IPs using antibodies against endogenous proteins. However, IPs using endogenous antibodies are nece ...
Control of Mitotic Events by Nap1 and the Gin4 Kinase
... proteins interact specifically with mitotic cyclins in organisms as evolutionarily divergent as budding yeast and Xenopus. Further experiments in budding yeast demonstrated that one member of this family, a protein called Nap1, is required for the ability of the mitotic cyclin Clb2 to execute a subs ...
... proteins interact specifically with mitotic cyclins in organisms as evolutionarily divergent as budding yeast and Xenopus. Further experiments in budding yeast demonstrated that one member of this family, a protein called Nap1, is required for the ability of the mitotic cyclin Clb2 to execute a subs ...
Spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy of biomass
... results with the spectrum of pure cellulose. Based on previous work by Wadsworth and Kataoka [32,33], we labeled the spectrum associated with our sample of fresh Populus (Fig. 6) and indicated the peaks relative to the carbohydrates in blue and the peaks relative to aromatic compounds (lignin) in gr ...
... results with the spectrum of pure cellulose. Based on previous work by Wadsworth and Kataoka [32,33], we labeled the spectrum associated with our sample of fresh Populus (Fig. 6) and indicated the peaks relative to the carbohydrates in blue and the peaks relative to aromatic compounds (lignin) in gr ...
PATHOGENIC EFFECTS OF VIRUSES
... • Few largest ones are just visible by light microscopy. • Each true virus contains only a single nucleic acid as its genome, that is DNA or RNA contained in a protein shell. The type of nucleic acid forms one of the bases for viral classification. ...
... • Few largest ones are just visible by light microscopy. • Each true virus contains only a single nucleic acid as its genome, that is DNA or RNA contained in a protein shell. The type of nucleic acid forms one of the bases for viral classification. ...
Topics for Discussion The Extracellular Matrix
... mixture, containing a number of different types of molecules – glycoproteins, collagens, proteoglycans. It’s well known that these molecules come together to form the structural framework that stabilizes tissues and provides mechanical support for cell attachment. Importantly, this material plays a ...
... mixture, containing a number of different types of molecules – glycoproteins, collagens, proteoglycans. It’s well known that these molecules come together to form the structural framework that stabilizes tissues and provides mechanical support for cell attachment. Importantly, this material plays a ...
Science Summer Project - Rising 7th Grade
... Summer Assignment Focus: Recap of Cells Your Task: Draw and label a diagram of two cells: one plant and one animal. Understand and include a brief description of the function of each organelle that you label. Your Diagrams: ● You must draw each diagram yourself ● One labelled diagram of a plant ...
... Summer Assignment Focus: Recap of Cells Your Task: Draw and label a diagram of two cells: one plant and one animal. Understand and include a brief description of the function of each organelle that you label. Your Diagrams: ● You must draw each diagram yourself ● One labelled diagram of a plant ...
to get the file - Chair of Computational Biology
... Indeed, the DNA methyltransferases DNMT1 or DNMT3a/3b double-knockout mice exhibit severe defects in embryogenesis and die before midgestation, supporting an essential role for DNA methylation in embryonic development ...
... Indeed, the DNA methyltransferases DNMT1 or DNMT3a/3b double-knockout mice exhibit severe defects in embryogenesis and die before midgestation, supporting an essential role for DNA methylation in embryonic development ...
Written by: Allison Wilson Allison Wilson is a senior Biomedical
... potential to self-replicate for an incredibly prolonged amount of time, which can lead to the creation of cell lines that have become a pivotal component of research and medical practices. The ES cells differentiate into the three embryonic germ layers, the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm, and can ...
... potential to self-replicate for an incredibly prolonged amount of time, which can lead to the creation of cell lines that have become a pivotal component of research and medical practices. The ES cells differentiate into the three embryonic germ layers, the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm, and can ...
fermentation - PharmaStreet
... •Bacteria, Actinomycetes, viruses & fungi can be used •Industrial Biotechnology: the process by which large quantities of cells are grown under aerobic or anaerobic conditions. •The industrial microorganisms are grown under controlled conditions with an aim of optimizing the growth of the organism ...
... •Bacteria, Actinomycetes, viruses & fungi can be used •Industrial Biotechnology: the process by which large quantities of cells are grown under aerobic or anaerobic conditions. •The industrial microorganisms are grown under controlled conditions with an aim of optimizing the growth of the organism ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.