MITOSIS
... a. Individual condensed chromosomes visibleCondensation continues b. Ribosomal RNA synthesis ceases, nucleolus disappears c. Spindle fibers begins to assemble(microtubules) d. In plant cells, spindle apparatus forms e. Nuclear envelope breaks down ...
... a. Individual condensed chromosomes visibleCondensation continues b. Ribosomal RNA synthesis ceases, nucleolus disappears c. Spindle fibers begins to assemble(microtubules) d. In plant cells, spindle apparatus forms e. Nuclear envelope breaks down ...
I`m a real “powerhouse” That`s plain to see. I break down food To
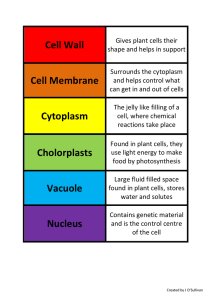
... Found only in plant cells, I’m green as can be. I make food for the plant Using the sun’s energy. CHLOROPLASTS ...
... Found only in plant cells, I’m green as can be. I make food for the plant Using the sun’s energy. CHLOROPLASTS ...
AP Biology - Mitosis and Meiosis Experiments
... 1. Observe prepared slides of onion root tips up to 400x magnification. 2. Observe at least 200 different cells in the apical meristem region. 3. Catagorize each cell as to the cell cycle phase (Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis). 4. Calculate the percentage of cells ...
... 1. Observe prepared slides of onion root tips up to 400x magnification. 2. Observe at least 200 different cells in the apical meristem region. 3. Catagorize each cell as to the cell cycle phase (Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis). 4. Calculate the percentage of cells ...
mitosis
... The cell cycle is the series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. Consists of 4 phases: 1. G1 phase : period of growth. 2. S phase: DNA replicates itself. 3. G2 phase: the cell prepares for mitosis. ...
... The cell cycle is the series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. Consists of 4 phases: 1. G1 phase : period of growth. 2. S phase: DNA replicates itself. 3. G2 phase: the cell prepares for mitosis. ...
Mitosis - KS Blogs
... S phase – chromosome replication (S = synthesis = “to make”) G2 phase – molecules and organelles required for cell division produced ...
... S phase – chromosome replication (S = synthesis = “to make”) G2 phase – molecules and organelles required for cell division produced ...
Unit 5 – Cell Reproduction
... All cells arise from pre-existing cells (except for the first cell(s) ever). The genetic library (genome) of a cell is passed onto divided (sister) cells. Mitosis – this is the process of how one cell makes exact (almost) copies of itself. Mitosis results in two genetically identical (almost) daught ...
... All cells arise from pre-existing cells (except for the first cell(s) ever). The genetic library (genome) of a cell is passed onto divided (sister) cells. Mitosis – this is the process of how one cell makes exact (almost) copies of itself. Mitosis results in two genetically identical (almost) daught ...
Mitosis
... • Produces two new daughter cells with the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent cell. ...
... • Produces two new daughter cells with the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent cell. ...
What are the main events of the cell cycle?
... performs its function; nuclear membrane is in tact; DNA in the form of chromatin; nucleolus is visible; made up of 3 stages ...
... performs its function; nuclear membrane is in tact; DNA in the form of chromatin; nucleolus is visible; made up of 3 stages ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... 2. What happens in interphase? 3. What are the stages of mitosis? 4. How does mitosis differ in plants and ...
... 2. What happens in interphase? 3. What are the stages of mitosis? 4. How does mitosis differ in plants and ...
10-2 Cell Division
... o Cell is ready for Cell Division! Biologists divide the events of mitosis into four phases: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase ...
... o Cell is ready for Cell Division! Biologists divide the events of mitosis into four phases: Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase ...
Adv. Bio. Ch 12 Mitosis
... • Turns out that a protein kinase called CDK and a protein called Cyclin are mainly responsible for the cell cycle • CDK catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP “activating” the protein • Cyclin binds to the protein kinase creating ...
... • Turns out that a protein kinase called CDK and a protein called Cyclin are mainly responsible for the cell cycle • CDK catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP “activating” the protein • Cyclin binds to the protein kinase creating ...
Instructor`s Copy
... 10. Toward what area of the cell are the chromosomes being directed? The poles. 11. Can you see two distinct sets of chromosomes? Yes. 12. Does it look like the number of chromosomes at one side of the cell is equal to the number at the other side? Yes. Telophase 13. How many cells have now formed f ...
... 10. Toward what area of the cell are the chromosomes being directed? The poles. 11. Can you see two distinct sets of chromosomes? Yes. 12. Does it look like the number of chromosomes at one side of the cell is equal to the number at the other side? Yes. Telophase 13. How many cells have now formed f ...
Cell Continuity
... What is the diploid number of the animal in which this cell is found? ………..………………… ...
... What is the diploid number of the animal in which this cell is found? ………..………………… ...
Mitosis Webquest
... 7. List the stages of mitosis (Notice – there’s an extra phase here…”prometaphase” – sometimes that is added as an “in-between” phase between prophase and metaphase. In our class you are only responsible for knowing PMAT) Write the steps of the cell cycle below. Provide one MAJOR thing that occurs i ...
... 7. List the stages of mitosis (Notice – there’s an extra phase here…”prometaphase” – sometimes that is added as an “in-between” phase between prophase and metaphase. In our class you are only responsible for knowing PMAT) Write the steps of the cell cycle below. Provide one MAJOR thing that occurs i ...
reproductionKUD2014 CP
... insure the orderly division of DNA. Mitosis produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Gametes (sex cells) are made during the process of meiosis and produce four daughter cells with half the chromosomes of the parent cell. Sexual reproduction is an advantage over ase ...
... insure the orderly division of DNA. Mitosis produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. Gametes (sex cells) are made during the process of meiosis and produce four daughter cells with half the chromosomes of the parent cell. Sexual reproduction is an advantage over ase ...
Stages of Mitosis & Chromosome structure
... regulating the progress at certain checkpoints. The enzyme responsible for controlling the cell cycle overall is called cyclin. If cells don’t respond to the regulatory proteins, the result can be uncontrolled growth, causing ...
... regulating the progress at certain checkpoints. The enzyme responsible for controlling the cell cycle overall is called cyclin. If cells don’t respond to the regulatory proteins, the result can be uncontrolled growth, causing ...
Bozeman Mitosis Video Notes and
... 6. What are the four phases of mitosis. Give a mnemonic device to remember these stages by. 7. Following mitosis, how many cells should be produced? 8. If you start with 46 chromosomes, how many chromosomes should be in each daughter cell following mitosis? 9. During what phase of mitosis are you fi ...
... 6. What are the four phases of mitosis. Give a mnemonic device to remember these stages by. 7. Following mitosis, how many cells should be produced? 8. If you start with 46 chromosomes, how many chromosomes should be in each daughter cell following mitosis? 9. During what phase of mitosis are you fi ...
Biology 9 - Unit 4b Meiosis Practice Name: 1. (a) Draw a
... Small structures in the cytoplasm of a cell that all have more than one function. ...
... Small structures in the cytoplasm of a cell that all have more than one function. ...
MITOTIC CELL DIVISION
... protein and cell RNA • S – synthesis phase when DNA duplicates • G2 - phase of organelle development and growth in preparation for cell division ...
... protein and cell RNA • S – synthesis phase when DNA duplicates • G2 - phase of organelle development and growth in preparation for cell division ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.