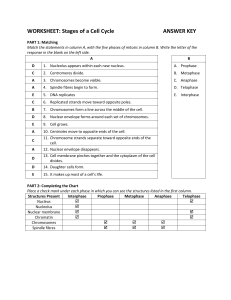
WORKSHEET: Stages of a Cell Cycle ANSWER KEY
... Part of the cytoskeleton. 5. By what structures are chromatids attached to each other during prophase, metaphase, and anaphase? Chromatids are attached to spindle fibres. 6. Suppose the cell shown in interphase has 24 chromosomes before DNA replication. How many chromosomes does each of the two cell ...
... Part of the cytoskeleton. 5. By what structures are chromatids attached to each other during prophase, metaphase, and anaphase? Chromatids are attached to spindle fibres. 6. Suppose the cell shown in interphase has 24 chromosomes before DNA replication. How many chromosomes does each of the two cell ...
My Cell Division Notes [PDF Document]
... same as the parent nucleus. its stages include: 1. Prophase: chromatin-chromosomes, chromosomes attach at centromeres, nuclear membrane begins to dissolve and centrioles produce spindle fibres. 2. Metaphase: chromosomes line up along equator and spindle fibres attach to centromeres. 3. Anaphase: spi ...
... same as the parent nucleus. its stages include: 1. Prophase: chromatin-chromosomes, chromosomes attach at centromeres, nuclear membrane begins to dissolve and centrioles produce spindle fibres. 2. Metaphase: chromosomes line up along equator and spindle fibres attach to centromeres. 3. Anaphase: spi ...
Cell Growth and Division
... • Cell Division – cell divides into two new IDENTICAL “daughter cells” • Mitosis – division of nucleus during eukaryotic cell division • Cytokinesis – division of cytoplasm during eukaryotic cell division ...
... • Cell Division – cell divides into two new IDENTICAL “daughter cells” • Mitosis – division of nucleus during eukaryotic cell division • Cytokinesis – division of cytoplasm during eukaryotic cell division ...
File - biologywithsteiner
... Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which the cell spends the majority of its time and performs the majority of its purposes including preparation for cell division. In preparation for cell division, it increases its size and makes a copy of its DNA. Interphase is also considered to be the ...
... Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which the cell spends the majority of its time and performs the majority of its purposes including preparation for cell division. In preparation for cell division, it increases its size and makes a copy of its DNA. Interphase is also considered to be the ...
How are new cells made? - Social Circle City Schools
... 2. The cell makes a copy of its DNA called replication. 3. The cell prepares to divide into two cells. Page 96 ...
... 2. The cell makes a copy of its DNA called replication. 3. The cell prepares to divide into two cells. Page 96 ...
Mitosis - muhlsdk12.org
... Separation of chromatids In anaphase, proteins holding together sister chromatids are inactivated ...
... Separation of chromatids In anaphase, proteins holding together sister chromatids are inactivated ...
Mitosis Worksheet
... The diagram below shows six cells in various phases of the cell cycle. Note the cells are not arranged in the order in which mitosis occurs and one of the phases of mitosis occurs twice. Use the diagram to answer questions 1-7. ...
... The diagram below shows six cells in various phases of the cell cycle. Note the cells are not arranged in the order in which mitosis occurs and one of the phases of mitosis occurs twice. Use the diagram to answer questions 1-7. ...
Biology Play Dough Mitosis Use your notes to answer the following
... Biology Play Dough Mitosis Use your notes to answer the following questions about cell division. Use complete sentences. ...
... Biology Play Dough Mitosis Use your notes to answer the following questions about cell division. Use complete sentences. ...
MITOSIS
... Mitosis - Telophase The chromosomes have finished their migration to the poles. The spindle has broken down and disappeared. The cell membrane pinches in (forms a cleavage furrow) along the center creating two separate cells . At this time, the chromosomes uncoil and become less visible (as they ar ...
... Mitosis - Telophase The chromosomes have finished their migration to the poles. The spindle has broken down and disappeared. The cell membrane pinches in (forms a cleavage furrow) along the center creating two separate cells . At this time, the chromosomes uncoil and become less visible (as they ar ...
Mitosis
... 3. Spindle apparatus is fully formed Spindle apparatus Centrioles Metaphase plate Centrioles ...
... 3. Spindle apparatus is fully formed Spindle apparatus Centrioles Metaphase plate Centrioles ...
cell division
... Chromosomes begin to separate. Now the centromere splits and the sister chromatids separate from each other. Each chromatid from each pair of sister chromatids move to opposite ends along the spindle. Now the chromatids are again called chromosomes. ...
... Chromosomes begin to separate. Now the centromere splits and the sister chromatids separate from each other. Each chromatid from each pair of sister chromatids move to opposite ends along the spindle. Now the chromatids are again called chromosomes. ...
10.2 The Process of Cell Division Chromosomes
... 9. In eukaryotic cells, what happens in the G1 phase that differs from the G2 phase? 10. In eukaryotic cells, what are the two main stages of cell division? ...
... 9. In eukaryotic cells, what happens in the G1 phase that differs from the G2 phase? 10. In eukaryotic cells, what are the two main stages of cell division? ...
Answers to Review Questions
... 2. What are the stages of the cell cycle? During which stage does DNA replicate? The cell cycle is composed of interphase (G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phases) and the M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). The genetic material is duplicated during interphase (the S phase, specifically). 3. What are sister ...
... 2. What are the stages of the cell cycle? During which stage does DNA replicate? The cell cycle is composed of interphase (G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phases) and the M phase (mitosis and cytokinesis). The genetic material is duplicated during interphase (the S phase, specifically). 3. What are sister ...
File
... In anaphase, the replicated sister chromatids which make up the chromosome are Sister separated form each other as chromatids the centromere splits. The are pulled spindle fibres shorten, pulling towards opposite poles the sister chromatids further of the cell away from each other towards the poles. ...
... In anaphase, the replicated sister chromatids which make up the chromosome are Sister separated form each other as chromatids the centromere splits. The are pulled spindle fibres shorten, pulling towards opposite poles the sister chromatids further of the cell away from each other towards the poles. ...
Bio07_TR_U03_CH10.QXD
... 2. What happens when the cell copies its chromosomes? 3. What happens during cytokinesis? Classifying On the line provided, label each event with one of the four phases of mitosis in which it occurs. A phase may be used more than once. 4. The chromosomes line up across the middle of the cell. 5. Chr ...
... 2. What happens when the cell copies its chromosomes? 3. What happens during cytokinesis? Classifying On the line provided, label each event with one of the four phases of mitosis in which it occurs. A phase may be used more than once. 4. The chromosomes line up across the middle of the cell. 5. Chr ...
WORKSHEET: Stages of a Cell Cycle ANSWER KEY
... Part of the cytoskeleton. 5. By what structures are chromatids attached to each other during prophase, metaphase, and anaphase? Chromatids are attached to spindle fibres. 6. Suppose the cell shown in interphase has 24 chromosomes before DNA replication. How many chromosomes does each of the two cell ...
... Part of the cytoskeleton. 5. By what structures are chromatids attached to each other during prophase, metaphase, and anaphase? Chromatids are attached to spindle fibres. 6. Suppose the cell shown in interphase has 24 chromosomes before DNA replication. How many chromosomes does each of the two cell ...
Mitosis Notes
... -- the chromosomes exist as chromatin chromatin: chromosomes are NOT distinguishable under the light microscope -- often not classified as a mitotic stage 3 parts of interphase (takes up about 90% of cell cycle) G1 -- growth one phase (organelles grow) S -- synthesis phase (replication of chromosome ...
... -- the chromosomes exist as chromatin chromatin: chromosomes are NOT distinguishable under the light microscope -- often not classified as a mitotic stage 3 parts of interphase (takes up about 90% of cell cycle) G1 -- growth one phase (organelles grow) S -- synthesis phase (replication of chromosome ...
Mitosis Cell Division
... Interphase- the phase a cell stays in longest. Time of growth, DNA replication and preparation for division Mitosis- Actual time of cell division. Nuclear division and separation of chromosomes. Cytokinesis-final phase of division where cytoplasm is divided and cell splits in two. ...
... Interphase- the phase a cell stays in longest. Time of growth, DNA replication and preparation for division Mitosis- Actual time of cell division. Nuclear division and separation of chromosomes. Cytokinesis-final phase of division where cytoplasm is divided and cell splits in two. ...
Cell division
... The stage of cell division during which the nucleus divides into two identical nuclei. The phases of mitosis are: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Cells spend most of their lives in interphase. It’s a time of growing, developing, and carrying on all life activities. At the end of interp ...
... The stage of cell division during which the nucleus divides into two identical nuclei. The phases of mitosis are: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Cells spend most of their lives in interphase. It’s a time of growing, developing, and carrying on all life activities. At the end of interp ...
The Cell Cycle
... Mitosis is the division of cells producing two cells with the same number of chromosomes ...
... Mitosis is the division of cells producing two cells with the same number of chromosomes ...
Learning Target
... 6. Recognize the type of daughter cells formed through mitosis and their chromosome number as compared to the parent cell. ...
... 6. Recognize the type of daughter cells formed through mitosis and their chromosome number as compared to the parent cell. ...
Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction
... •Chromosomes reach poles of cell. •Nuclear envelope re-forms. •Nucleolus reappears. •Chromosomes decondense. ...
... •Chromosomes reach poles of cell. •Nuclear envelope re-forms. •Nucleolus reappears. •Chromosomes decondense. ...
SW Science 10 Unit 1 Mitosis Worksheet
... 5. The drawing below has been made from a photograph showing a cell undergoing mitosis. Based on the drawing, in what stage of mitosis must the cell have been in? ______________________ ...
... 5. The drawing below has been made from a photograph showing a cell undergoing mitosis. Based on the drawing, in what stage of mitosis must the cell have been in? ______________________ ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.
![My Cell Division Notes [PDF Document]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015866407_1-8ba2d4650ee384ad6bb840fcb84f7caa-300x300.png)






















