Name Date Ch 4 reading guide – Biology in Focus
... Concept 4.1 Biologists Use Microscopes and the Tools of Biochemistry to Study Cells 1. The development of electron microscopes has further opened our window on the cell and its organelles. What is considered a major disadvantage of the electron microscopes? ...
... Concept 4.1 Biologists Use Microscopes and the Tools of Biochemistry to Study Cells 1. The development of electron microscopes has further opened our window on the cell and its organelles. What is considered a major disadvantage of the electron microscopes? ...
Diffusion/Osmosis
... Know cells are enclosed within semipermeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. ...
... Know cells are enclosed within semipermeable membranes that regulate their interaction with their surroundings. ...
cell wall - Madeira City Schools
... 2. What limits cell size a. minimum it must house DNA, proteins, and organelles to ...
... 2. What limits cell size a. minimum it must house DNA, proteins, and organelles to ...
29 - Alamo Colleges
... Tough, insoluble protein fibers with high tensile strength Resist pulling forces on the cell and help form desmosomes ...
... Tough, insoluble protein fibers with high tensile strength Resist pulling forces on the cell and help form desmosomes ...
Job - Cloudfront.net
... 5) Name two organelles that plant cells have and animal cells do not. 6) Which organelle creates ATP energy for cells? 7) Which organelle converts sunlight into sugar? 8) Which organelle creates ribosomes? 9) Which organelle fuses with the cell membrane to release proteins? 10)Which molecule holds t ...
... 5) Name two organelles that plant cells have and animal cells do not. 6) Which organelle creates ATP energy for cells? 7) Which organelle converts sunlight into sugar? 8) Which organelle creates ribosomes? 9) Which organelle fuses with the cell membrane to release proteins? 10)Which molecule holds t ...
Protists
... The eyespot of a Euglena is sensitive to light and once light is detected it moves towards it for photosynthesis. The long whip-like structure is a flagellum that quickly moves back and forth the propel the Euglena through water. Amoeba: An amoeba is a unicellular protist. They are animal-l ...
... The eyespot of a Euglena is sensitive to light and once light is detected it moves towards it for photosynthesis. The long whip-like structure is a flagellum that quickly moves back and forth the propel the Euglena through water. Amoeba: An amoeba is a unicellular protist. They are animal-l ...
Cell Structures Quick Check
... b. cell wall tough outer structure of plant cells that provides shape, support & protection c. vesicles small packages that are used to help move materials into or out of the cell d. chloroplast contains green pigment in plant cells to make glucose e. ribosome builds proteins f. cytoskeleton microtu ...
... b. cell wall tough outer structure of plant cells that provides shape, support & protection c. vesicles small packages that are used to help move materials into or out of the cell d. chloroplast contains green pigment in plant cells to make glucose e. ribosome builds proteins f. cytoskeleton microtu ...
Chlamydomonas
... Chloroplast: cup-shaped, contains the green pigment chlorophyll which traps energy from sunlight. Contractile vacuoles: Chlamydomonas has one pair of contractile vacuoles, hollow balls that rhythmically fill with excess water and then contract as they pump the excess water from the cell. Eyespot (st ...
... Chloroplast: cup-shaped, contains the green pigment chlorophyll which traps energy from sunlight. Contractile vacuoles: Chlamydomonas has one pair of contractile vacuoles, hollow balls that rhythmically fill with excess water and then contract as they pump the excess water from the cell. Eyespot (st ...
doc Answers to Lab 2 Manual
... What is the bacterium’s shape? The spirillum type. You see spirally-curved rods. Can you find the cell wall or the nucleus? Yes, almost all bacteria have cell walls. It is the outermost layer, outside of the plasma membrane. No, there is no nucleus. A nucleus is an organelle and bacteria do not ...
... What is the bacterium’s shape? The spirillum type. You see spirally-curved rods. Can you find the cell wall or the nucleus? Yes, almost all bacteria have cell walls. It is the outermost layer, outside of the plasma membrane. No, there is no nucleus. A nucleus is an organelle and bacteria do not ...
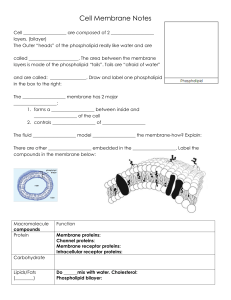
Cell Membrane Notes
... called ______________________. The area between the membrane layers is made of the phospholipid “tails”. Tails are “afraid of water” and are called: ________________. Draw and label one phospholipid in the box to the right: The ___________________ membrane has 2 major ___________________: 1. forms a ...
... called ______________________. The area between the membrane layers is made of the phospholipid “tails”. Tails are “afraid of water” and are called: ________________. Draw and label one phospholipid in the box to the right: The ___________________ membrane has 2 major ___________________: 1. forms a ...
Eukaryotes
... Organelles Organelles are independent, distinct , membrane-bounded structures or compartments within a eukaryotic cell which perform specific tasks for the overall success and well being of the cell. The specific funtions of organelles vary widely and typically depend on their proximity within the c ...
... Organelles Organelles are independent, distinct , membrane-bounded structures or compartments within a eukaryotic cell which perform specific tasks for the overall success and well being of the cell. The specific funtions of organelles vary widely and typically depend on their proximity within the c ...
7.3 Structures and Organelles
... acids together to make proteins · can be free or attached to ER · ROLE: manufactures proteins ...
... acids together to make proteins · can be free or attached to ER · ROLE: manufactures proteins ...
Jim`s Viruses and Bacteria Quizizzle
... ____ 22. Cell organelles that Escherichia coli and other bacteria have in common with eukaryotes are a. chloroplasts. c. nuclei. b. mitochondria. d. ribosomes. ____ 23. Escherichia coli is an example of a bacterium that has short, thin, hairlike projections called a. pili. c. cocci. b. cilia. d. ri ...
... ____ 22. Cell organelles that Escherichia coli and other bacteria have in common with eukaryotes are a. chloroplasts. c. nuclei. b. mitochondria. d. ribosomes. ____ 23. Escherichia coli is an example of a bacterium that has short, thin, hairlike projections called a. pili. c. cocci. b. cilia. d. ri ...
A View of the Cell
... Eukaryotic cells – these cells do have a nucleus, they do have organelles attached to the membrane. These cells can be much larger than prokaryotic cells. An organelle is a specialized structure in a cell that carries out a specific function. A “little organ.” ...
... Eukaryotic cells – these cells do have a nucleus, they do have organelles attached to the membrane. These cells can be much larger than prokaryotic cells. An organelle is a specialized structure in a cell that carries out a specific function. A “little organ.” ...
Cell membrane structure File
... • MOST COMMON MATERIAL IN THE CELL MEMBRANE • TWO LAYERS THICK • EACH LAYER HAS A ROUNDED HEAD END (HYDROPHILIC = LOVES WATER) THAT ALWAYS FACES THE WATER BASED SOLUTION (EITHER THE CELL’S ENVIRONMENT OR THE CELL’S CYTOPLASM. • EACH PHOSPHOLIPID HAS TWO TAILS ON ONE END (HYDROPHOBIC = FEARS WATER) T ...
... • MOST COMMON MATERIAL IN THE CELL MEMBRANE • TWO LAYERS THICK • EACH LAYER HAS A ROUNDED HEAD END (HYDROPHILIC = LOVES WATER) THAT ALWAYS FACES THE WATER BASED SOLUTION (EITHER THE CELL’S ENVIRONMENT OR THE CELL’S CYTOPLASM. • EACH PHOSPHOLIPID HAS TWO TAILS ON ONE END (HYDROPHOBIC = FEARS WATER) T ...
Cellular Structure
... Golgi Apparatus Package proteins for storage and secretion from the cell. Exocytosis, package particles (forms lysosomes) ...
... Golgi Apparatus Package proteins for storage and secretion from the cell. Exocytosis, package particles (forms lysosomes) ...
SHRIMATI INDIRA GANDHI COLLEGE
... Cell wall is a very rigid structure that gives shape to the cell. The main function is to prevent the cell from expanding and bursting of cell because of uptake of water the rigidity of the wall can be destroyed by very high pressure or other severe physical conditions. Most bacterial retain their ...
... Cell wall is a very rigid structure that gives shape to the cell. The main function is to prevent the cell from expanding and bursting of cell because of uptake of water the rigidity of the wall can be destroyed by very high pressure or other severe physical conditions. Most bacterial retain their ...
Page 1 of 1 DTU Systems Biology Mette Voldby Larsen, CBS
... 6. Prokaryotic cells each contain a nucleoid region, ribosomes and cytoplasm. Many also have cell walls, internal membranes, flagella, pili, and/or a cytoskeleton. 7. Eukaryotic cells (cells in the domain Eukarya) have many different membraneenclosed organelles. Eu = true/real, karyon = nut/kernel ~ ...
... 6. Prokaryotic cells each contain a nucleoid region, ribosomes and cytoplasm. Many also have cell walls, internal membranes, flagella, pili, and/or a cytoskeleton. 7. Eukaryotic cells (cells in the domain Eukarya) have many different membraneenclosed organelles. Eu = true/real, karyon = nut/kernel ~ ...
Cell Organelles
... Found only inside eukaryotic cells All the gel like fluid between the organelles is cytosol Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm ...
... Found only inside eukaryotic cells All the gel like fluid between the organelles is cytosol Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm ...
binomial-nomenclature-activity
... 2. To what kingdom do you belong? What is your phylum? To what class do you belong? What is your order? To what family do you belong? What is your genus? To what species do you belong? 3. What is your scientific name? 4. How does the number of characteristics shared by all members of a classificatio ...
... 2. To what kingdom do you belong? What is your phylum? To what class do you belong? What is your order? To what family do you belong? What is your genus? To what species do you belong? 3. What is your scientific name? 4. How does the number of characteristics shared by all members of a classificatio ...
Plant Cell
... Nucleus The nucleus directs all of the cell‘s activities, including reproduction. Endoplasmic Reticulum This network of passageways carries materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
... Nucleus The nucleus directs all of the cell‘s activities, including reproduction. Endoplasmic Reticulum This network of passageways carries materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
document
... • Nuclear pores in the membrane allow the passage of large molecules in & out (eg messengerRNA) • Material inside the nucleus is called nucleoplasm – this contains chromatin which makes up the DNA of the cell – in non-dividing cells it is spread out and during cell division it condenses to form the ...
... • Nuclear pores in the membrane allow the passage of large molecules in & out (eg messengerRNA) • Material inside the nucleus is called nucleoplasm – this contains chromatin which makes up the DNA of the cell – in non-dividing cells it is spread out and during cell division it condenses to form the ...
Biological Classification
... items according to similar characteristics • Taxonomy - the science of naming • Carl Linnaeus developed a system using a two-word Latin name for each species • Called binomial nomenclature - uses the genus and species names to identify organisms ...
... items according to similar characteristics • Taxonomy - the science of naming • Carl Linnaeus developed a system using a two-word Latin name for each species • Called binomial nomenclature - uses the genus and species names to identify organisms ...
Flagellum
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. Flagella are organelles defined by function rather than structure. There are large differences between different types of flagella; the prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ greatly in protein composition, structure, and mechanism of propulsion. However, both are used for swimming.An example of a flagellate bacterium is the ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. An example of a eukaryotic flagellate cell is the mammalian sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract. Eukaryotic flagella are structurally identical to eukaryotic cilia, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.